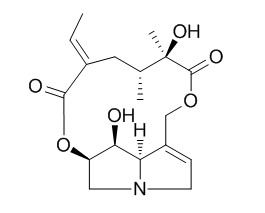
Madurensine
Madurensine and doronenine show moderate cytotoxicity on cancerous U-937 cells (IC(50) values: 47.97 and 29.57 M respectively). Madurensine induces autophagy, which in prolonged circumstances may lead to autophagic cell death.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(5),1713.
The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences.2020, 30(6):1366-1373
Microchemical Journal2018, 137:168-173
J Appl Microbiol.2022, 132(2):949-963.
J Formos Med Assoc.2020, S0929-6646(20)30425-3
Viruses2023, 15(6), 1377
Anat Rec2018, 24264
Front Pharmacol.2019, 10:1355
Medicina (Kaunas).2020, 56(12):685.
Molecules.2022, 27(22):7997.
Related and Featured Products
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2012 Sep;95:547-54.
A micro-Raman spectroscopic investigation of leukemic U-937 cells treated with Crotalaria agatiflora Schweinf and the isolated compound madurensine.[Pubmed:
22580136]
In South Africa traditional medicine plays an important role in primary health care and therefore it is very important that the medicinal use of plants is scientifically tested for toxicity and effectiveness.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
It was established that the ethanolic extract of the leaves of Crotalaria agatiflora, as well as the isolated compound Madurensine, is moderately toxic against leukemic U-937 cells. Light microscopic investigations indicated that symptoms of cell death are induced during treatments, but flow cytometry analysis of treated cells, using annexin-V and propidium iodide, showed that apoptosis and necrosis are insignificantly induced. The Raman results suggested that protein extraction and DNA melting occur in the cells during treatment with the ethanolic extracts (IC(50) value 73.9 μg/mL), drastically changing the molecular content of the cells. In contrast, treatment with Madurensine (IC(50) value 136.5 μg/mL), an isolated pyrrolizidine alkaloid from the ethanolic extract of the leaves, did not have the same effect. The results are also compared to that of cells treated with actinomycin D, a compound known to induce apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
The investigation showed that micro-Raman spectroscopy has great promise to be used for initial screening of samples to determine the effects of different treatments on cancerous cell lines together with conventional methods. The results highlight the fact that for many natural products used for medicinal purposes, the therapeutic effect of the crude plant extract tends to be significantly more effective than the particular action of its individual constituents.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Dec 8;138(3):748-55.
In vitro chemo-preventative activity of Crotalaria agatiflora subspecies agatiflora Schweinf.[Pubmed:
22041105]
Crotalaria species have been widely used in Chinese traditional medicine to treat several types of internal cancers. Crotalaria agatiflora is used as a medicinal plant in several African countries for the treatment of bacterial and viral infections as well as for cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Water and ethanol extracts of the leaves of Crotalaria agatiflora were evaluated for cytotoxicity on four cancerous and one noncancerous cell lines, using XTT (Sodium 3'-[1-(phenyl amino-carbonyl)-3,4-tetrazolium]-bis-[4-methoxy-6-nitro] benzene sulfonic acid hydrate) colorimetric assay. Antioxidant activity was determined using DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl hydrazyl). Light microscopy (eosin and haematoxylin staining) and flow cytometry (Annexin-V and propidium iodide) were used to evaluate the mechanism of action of the ethanol extract and one of the isolated compounds.
The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) of the ethanol extract was found to be 73.9 μg/mL against leukemic U-937 cells. Good antioxidant activity (IC(50)=18.89 μg/mL) of the ethanol extract indicated the potential of Crotalaria agatiflora as chemo-preventative supplement. A bioassay guided fractionation of the ethanol extract led to the isolation of two pure compounds, namely Madurensine and doronenine. Madurensine and doronenine showed moderate cytotoxicity on cancerous U-937 cells (IC(50) values: 47.97 and 29.57 M respectively). The crude extract treated U-937 cells showed definite signs of cell death during light microscopic investigation, while little apoptosis (10-20%) and necrosis (<2%) were detected in cells treated with the extract or Madurensine.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that Crotalaria agatiflora possesses potential chemopreventative and therapeutic properties. The exact mechanism of action should still be determined in future studies. It is hypothesized that the ethanolic extract as well as Madurensine induces autophagy, which in prolonged circumstances may lead to autophagic cell death.