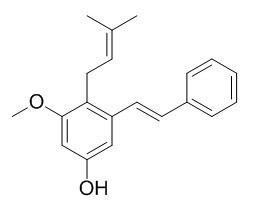
Longistylin C
Longistylin A and longistylin C show some cytotoxic effects, with IC(50) values of 0.7-14.7 microM against the range of cancer cell lines. Longistylin A and longistylin C, and betulinic acid show a moderately high in vitro activity against the chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum strain 3D7.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Separation Science & Technology2016, 51:1579-1588
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(8):2790.
Food and Fermentation Industries2018, 44(371)
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2021, 427:115668.
Primary and Industrial.2018, 52(11)
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):13610.
Biomolecules2021, 11(10),1513.
Molecules.2019, 24(1):E159
Korean J Pain.2021, 34(4):405-416.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(8),2804
Related and Featured Products
J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Mar 24;128(2):501-12.
Ethnobotanical survey and cytotoxicity testing of plants of South-western Nigeria used to treat cancer, with isolation of cytotoxic constituents from Cajanus cajan Millsp. leaves.[Pubmed:
20064598 ]
A total of 30 healers from S W Nigeria were involved in the study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
45 species were recorded with their local names with parts used in the traditional therapeutic preparations. Cytotoxicity (IC(50) values less than 50 microg/mL) was observed in 5 species (Acanthospermum hispidum, Cajanus cajan, Morinda lucida, Nymphaea lotus and Pycnanthus angolensis). Acanthospermum hispidum and Cajanus cajan were the most active. The dichloromethane fraction of Cajanus cajan had IC(50) value 5-10 microg/mL, with the two constituent stilbenes, longistylin A and Longistylin C, being primarily responsible, with IC(50) values of 0.7-14.7 microM against the range of cancer cell lines.Most of the species tested had some cytotoxic effect on the cancer cell lines, which to some extent supports their traditional inclusion in herbal preparations for treatment of cancer. However, little selectivity for cancer cells was observed, which raises concerns over their safety and efficacy in traditional treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
The longistylin A and Longistylin C appear to be responsible for much of the activity of Cajanus cajan extract.
Phytother Res. 2004 Feb;18(2):128-30.
Antiplasmodial constituents of Cajanus cajan.[Pubmed:
15022164 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioactivity-guided fractionation of extracts of roots and leaves of Cajanus cajan afforded 8 compounds: betulinic acid, biochanin A, cajanol, genistein and 2'-hydroxygenistein, longistylin A and Longistylin C, and pinostrobin.
CONCLUSIONS:
The two stilbenes, longistylin A and Longistylin C, and betulinic acid showed a moderately high in vitro activity against the chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum strain 3D7.
Chin J Nat Med. 2015 Apr;13(4):311-5.
Synthesis and cytotoxicity of longistylin C derivatives.[Pubmed:
25908631]
The present study was designed to identify potent anti-tumor compounds from a series of new Longistylin C derivatives.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ten Longistylin C derivatives were synthesized and their structures were confirmed by (1)H NMR, MS, and elemental analyses. Their cytotoxicity in vitro against three human cancer cell lines (A549, HepG2, and MCF-7) were evaluated by the MTT assay. Among these compounds, DT-6 and DT-9 displayed much better cytotoxicity against A549, HepG2, and MCF-7 cells, DT-1 exhibited selective cytotoxicity against HepG2, and the structure-activity relationships were investigated.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Compounds DT-6 and DT-9 may serve as potential lead compounds for the discovery of new anti-cancer drugs.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Oct;36(19):2680-3.
Determination of longistylin A and longistylin C in Cajanus cajan.[Pubmed:
22242429]
To establish quality control criteria for medicinal herb Cajanus cajan based on the determination of longistylin A and Longistylin C, two bioactive and specific stilbenes of the plant.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Longistylin A and Longistylin C were obtained from the leaves of C. cajan by silica gel column chromatography and identified as marker compounds of this plant by spectroscopic analysis. A RP-HPLC method was established to determine the two compounds.
Longistylin A and Longistylin C were well separated on a Thermo BDS Hypersil C18 column (4.6 mm x 250 mm, 5 microm) with a mobile phase methanol-water (8:2), and showed good linearity in the range of 0.00288 - 0.0576 microg and 0.0112 - 0.224 microg, respectively. The average recoveries were 98.9% and 97.2% with RSD of 2.4% and 2.2% for these two compounds, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The established analysis method is simple and accurate, whicn can be used for quality control of C. cajan.