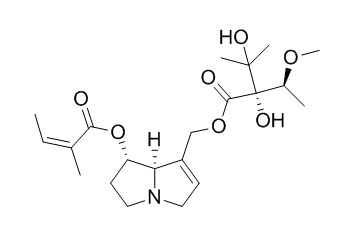
Lasiocarpine
Lasiocarpine has antimitotic action,it has hepatocarcinogenicity, the effect can be better explained by its strong selection (promotion) influence on initiated hepatocytes, rather than by its very weak initiating activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Chem.2024, 458:140201.
Nutrients.2023, 15(12):2644.
Front Pharmacol.2017, 8:205
Food Chem Toxicol.2024, 186:114589.
Plant Pathology2022, 10.1111:ppa.13651.
Nutr Res Pract2019, 13:e45
Phytomedicine.2023, 114:154813.
Research Square2021, March 3rd.
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(9):3239.
J of Essential Oil Research2019, 1677272
Related and Featured Products
Chem.Biol. Interact., 1975, 10(3):185-97.
Localization in the cell cycle of the antimitotic action of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid, lasiocarpine and of its metabolite, dehydroheliotridine[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antimitotic action of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid Lasiocarpine on rat liver parenchyma was investigated using as the experimental model the wave of mitosis produced in liver by a single dose of thioacetamide. A single low dose of Lasiocarpine administered two weeks before the thioacetamide, almost completely inhibited the mitotic wave without inhibiting to the same extent the preceding wave of DNA synthesis. By the use of selective inhibitors and radioisotope labelling, the location of the mitotic block was found to be either in the latter half of the DNA synthetic phase, S, or early in G2, the post-synthetic phase.
CONCLUSIONS:
The mitotic wave was similarly inhibited by pretreatment of the rats with a single injection of dehydroheliotridine, a pyrrolic metabolite of heliotridine-based pyrrolizidine alkaloids.
J.Pathol. Bacteriol., 1959, 78(2):483–502.
The chronic pathological effects on the liver of the rat of the pyrrolizidine alkaloids heliotrine, lasiocarpine, and their N -oxides[Pubmed:
13805866]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Pure crystalline alkaloids and N-oxides used were heliotrine, Lasiocarpine, heliotrine N-oxide, Lasiocarpine N-oxide, heliotridine and heliotric acid. Young male rats, bodyweight 120 to 220 g., were given intraperitoneal injections of the alkaloids; in preliminary experiments the dose was 0.1 LD50 twice or three times a week, which produced liver damage and caused death generally in about 6 mon...
Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3726-34.
Initiation and selection of resistant hepatocyte nodules in rats given the pyrrolizidine alkaloids lasiocarpine and senecionine.[Pubmed:
2861891]
The biological mechanisms by which pyrrolizidine alkaloids contribute to initiation and nodule selection (promotion) steps in hepatic carcinogenesis were studied in male Fischer 344 rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Lasiocarpine at single or double dosages (up to 80 mumol/kg) delayed hepatic regeneration for at least 8 weeks after partial hepatectomy (PH). This regimen of Lasiocarpine and PH had a strong selective influence on the growth of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (gamma-GT)-positive hepatocyte nodules in rats previously initiated with diethylnitrosamine. However, both Lasiocarpine (up to 80 mumol/kg) and senecionine (up to 160 mumol/kg) were inactive as initiators of gamma-GT-positive nodules in rats exposed to a similar selection regimen consisting of 2-acetylaminofluorene and PH. When Lasiocarpine or senecionine was given 12 h after PH, very few nodules were initiated. Lasiocarpine pretreatments reduced the initiating activity of diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomethylurea in rats subsequently selected with 2-acetylaminofluorene and PH. Resistant nodules selected with Lasiocarpine had the typical resistant nodule phenotype (positive for gamma-GT and epoxide hydrolase) and also lacked pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced megalocytosis. Lasiocarpine treatment also resulted in small regenerative nodular proliferations of hepatocytes that were distinct from resistant nodules because they were negative for gamma-GT and epoxide hydrolase and unrelated to diethylnitrosamine pretreatments.
CONCLUSIONS:
These studies suggest that the hepatocarcinogenicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids can be better explained by their strong selection (promotion) influence on initiated hepatocytes, rather than by their very weak initiating activity.