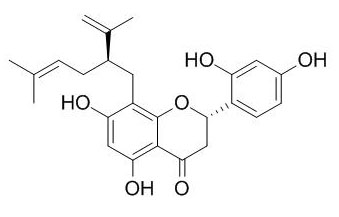
Kushenol F
Kushenol F is a tyrosinase inhibitor, it shows significant inhibitory effects on monoamine oxidase ( in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values of 69.9 microM). Kushenol F preferentially inhibits the MAO-B activity than MAO-A activity with the IC50 values of 63.1 and 103.7 microM, respectively.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(8):4211.
BMC Complement Med Ther.2023, 23(1):264.
Horticulturae2024, 10(5), 486.
BMC Plant Biol.2023, 23(1):239.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2022, 9767292,2.
Int Immunopharmacol.2019, 71:361-371
Food Analytical Methods2017, 10:3225-3234
Acta horticulturae2017, 1158:257-268
Mol Med Rep.2022, 25(1):8.
Molecules.2021, 26(23):7390.
Related and Featured Products
Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):154-8.
Inhibitory effects of kurarinol, kuraridinol, and trifolirhizin from Sophora flavescens on tyrosinase and melanin synthesis.[Pubmed:
18175961]
Previously, it was reported that some prenylated flavonoids contained in the dichloromethane fraction of the ethanolic extract of Sophora flavescens, such as kuraridin, sophoraflavanone G, kurarinone, and Kushenol F, are tyrosinase inhibitors; however, based on the level of these inhibitors in the extract, its inhibitory effect on tyrosinase activity was higher than expected. This has led us to further investigate other possible constituents that may contribute to the extract's strong inhibitory activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results of this study indicate that kurarinol (1), kuraridinol (2), and trifolirhizin (3), from the ethyl acetate fraction of Sophora extract, can inhibit tyrosinase activity. Compared with kojic acid (16.22+/-1.71 microM), compounds 1-3 possessed potent tyrosinase inhibitory activity with IC(50) values of 8.60+/-0.51, 0.88+/-0.06, and 506.77+/-4.94 microM, respectively. These three compounds were further tested for their inhibitory effects on melanogenesis.
CONCLUSIONS:
In cultured B16 melanoma cells, 1-3 markedly inhibited (>50%) melanin synthesis at 50 microM. This is the first study indicating that 1-3 exert varying degrees of inhibition on tyrosinase-dependent melanin biosynthesis, and therefore, are candidates as skin-whitening agents.
Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Feb;28(2):190-4.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitory components from the roots of Sophora flavescens.[Pubmed:
15789750]
In our search for monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors from natural resources, we found that the methanol extract of the roots of Sophora flavescens showed an inhibitory effect on mouse brain monoamine oxidase (MAO).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioactivity-guided isolation of the extract yielded two known flavonoids, formononetin (1) and Kushenol F (2), as active compounds along with three inactive compounds, oxymatrine (3), trifolirhizin (4), and beta-sitosterol (5). Formononetin (1) and Kushenol F (2) showed significant inhibitory effects on MAO in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values of 13.2 and 69.9 microM, respectively. Formononetin (1) showed a slightly more potent inhibitory effect against MAO-B (IC50: 11.0 microM) than MAO-A (IC50: 21.2 microM). Kushenol F (2) also preferentially inhibited the MAO-B activity than MAO-A activity with the IC50 values of 63.1 and 103.7 microM, respectively.