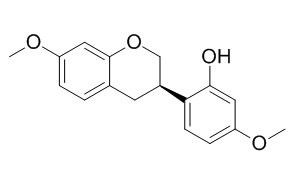
Isosativan
Isosativan, sativan and vestitol are isoflavan phytoalexins.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Oncol Rep.2021, 46(2):166.
Oxid Med Cell Longev.2021, 2021:4883398.
J.of Traditional&Complementary Med.2022, 10.1016:j.jtcme.
Environ Toxicol.2024, 39(3):1556-1566.
Arch Toxicol.2024, 98(5):1415-1436.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117395.
The Korea Journal of Herbology2020, 35(3):33-45.
Molecules2022, 27(3),1140.
EXCLI J.2023, 22:482-498.
Mol Divers.2022, s11030-022-10586-3.
Related and Featured Products
Biochemical Systematics and Ecology,1979,7( 1): 29-34.
Isoflavonoid phytoalexins of the genus Medicago[Reference:
WebLink]
Detached leaves of 25 annual and perennial Medicago species have been inoculated with the fungus, Helminthosporium carbonum, and examined for subsequent production of isoflavonoid phytoalexins.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Hydroxylated pterocarpan (medicarpin) and isoflavan (vestitol, sativan and Isosativan) phytoalexins were obtained from most of the species investigated. Although large quantities of two flavonoid derivatives, isoliquiritigenin and liquiritigenin, were isolated from leaves of M. lupulina, this species was apparently unable to produce isoflavonoid compounds. Traces of 7-hydroxy-2′,4′-dimethoxyisoflavanone (a substance not previously recorded in the tribe Trifolieae) were obtained (together with medicarpin, vestitol and sativan) from M. sativa cv Du Puits.
CONCLUSIONS:
Some taxonomic aspects of phytoalexin induction are discussed with reference to the generic location of certain controversial Medicago species including M. (Trigonella) radiata.