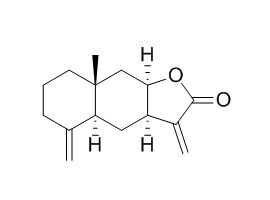
Isoalantolactone
Isoalantolactone, an apoptosis inducer, possesses multiple biological activities including antifungal, anthelmintic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antitrypanosomal activities and antiproliferative effects on several cancer cell lines, such as colon, melanoma, ovary, prostate, lung, and leukemia. Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis, may be mediated through caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, inhibition of phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Plants (Basel).2022, 11(21):2947.
Mol Biol Rep.2024, 51(1):117.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2016, 2016:1739760
Molecules.2019, 24(4):E744
Cytotechnology2022, s10616
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016, 408(15)
Int J Nanomedicine.2022, 17:6513-6525.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176800.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(1):538.
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(6):1119.
Related and Featured Products
Phytother Res. 2014 Nov;28(11):1679-86.
Growth inhibition effects of isoalantolactone on K562/A02 cells: caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl.[Pubmed:
24865355]
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, is the active component of Inula helenium (Compositae). It has been reported that Isoalantolactone has the capacity to inhibit tumor cell growth through induction of apoptosis. The purposes of this study were to evaluate the effects of Isoalantolactone on the human erythroleukemia drug-resistant cell line K562/A02 and to provide evidence of its function as a potent therapeutic agent in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia with the Bcr/Abl phenotype.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our results showed that Isoalantolactone significantly inhibited K562/A02 cell growth by downregulating Bcr/Abl expression. Isoalantolactone also induced apoptosis via increase generation of reactive oxygen species, modulation of the protein levels of Bcl-2 family members, caspase activation, poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage, and release of cytochrome c. We also observed that Isoalantolactone inhibited proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest in the S phase.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, all these findings support that growth inhibition effects of Isoalantolactone on K562/A02 cells may be mediated through caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways, S phase arrest, and downregulation of Bcr/Abl.
Crop Prot., 2006, 25(5):508-11.
Repellent, insecticidal and phytotoxic activities of isoalantolactone from Inula racemosa.[Reference:
WebLink]
Isoalantolactone, a natural product isolated from traditional Chinese medicinal herb roots of Inula racemosa Hook. f. (Fam. Compositae), has been shown to possess strong antifungal activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present investigation showed that Isoalantolactone also exhibited repellent and toxic activities against rice weevil [Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)] based on a food preference apparatus and a poisoned food technique. The toxicity of Isoalantolactone to rice weevil was dose dependent, whereas the repellency was not. Isoalantolactone showed strong phytotoxic effects on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat at a concentration of 500 μg ml−1 for 60 h; however, this side effect could be reduced markedly by shortening the treating time at this concentration.
CONCLUSIONS:
Results indicate that Isoalantolactone might be considered for wheat seeds preservation in control of storage weevils.
Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(4):533-47.
Isoalantolactone induces reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma PANC-1 cells.[Pubmed:
22532787 ]
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone compound possesses antifungal, antibacteria, antihelminthic and antiproliferative activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we found that Isoalantolactone inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Further mechanistic studies revealed that induction of apoptosis is associated with increased generation of reactive oxygen species, cardiolipin oxidation, reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c and cell cycle arrest at S phase. N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC), a specific ROS inhibitor restored cell viability and completely blocked Isoalantolactone-mediated apoptosis in PANC-1 cells indicating that ROS are involved in Isoalantolactone-mediated apoptosis. Western blot study showed that Isoalantolactone increased the expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 and decreased the expression of Bcl-2 in a dose-dependent manner. No change in expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK and Bax was found when cells were treated with Isoalantolactone in the presence of NAC, indicating that activation of these proteins is directly dependent on ROS generation.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study provides evidence for the first time that Isoalantolactone induces ROS-dependent apoptosis through intrinsic pathway. Furthermore, our in vivo toxicity study demonstrated that Isoalantolactone did not induce any acute or chronic toxicity in liver and kidneys of CD1 mice at dose of 100 mg/kg body weight. Therefore, Isoalantolactone may be a safe chemotherapeutic candidate for the treatment of human pancreatic carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 2014 Oct;32(4):1585-93.
Isoalantolactone inhibits constitutive NF-κB activation and induces reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in osteosarcoma U2OS cells through mitochondrial dysfunction.[Pubmed:
25109871]
Human osteosarcoma is an aggressive tumor which frequently resists chemotherapy; therefore, the search for new agents for its treatment is of great importance. Isoalantolactone, isolated from Inula spp., has been reported to inhibit the growth of several types of cancer cells. However, no prior research has been conducted to demonstrate the antiproliferative potential of Isoalantolactone on osteosarcoma. The present study is the first to investigate the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability in human osteosarcoma U2OS, MG-63 and Saos-2 cells, and its mechanism of action in Human osteosarcoma is an aggressive tumor which frequently resists chemotherapy; therefore, the search for new agents for its treatment is of great importance. Isoalantolactone, isolated from Inula spp., has been reported to inhibit the growth of several types of cancer cells. However, no prior research has been conducted to demonstrate the antiproliferative potential of Isoalantolactone on osteosarcoma.
The present study is the first to investigate the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability in human osteosarcoma U2OS, MG-63 and Saos-2 cells, and its mechanism of action in U2OS cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our results demonstrated that Isoalantolactone triggered S and mainly G2/M cell cycle phase arrest, accompanied by the downregulation of the expression of cyclin B1 at the protein and mRNA levels. Moreover, Isoalantolactone induced apoptosis that was associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). Furthermore, our results indicated that this compound upregulated DR5, FADD and cleaved caspase-8, increased the interation between DR5 and FADD, and inhibited the expression of nuclear NF-κBp65. We also found that Isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis was associated with the downregulation of Bcl-2 and upregulation of Bax, which finally led to the activation of caspase-3 and its downstream substrate, PARP, in osteosarcoma U2OS cells. Isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis was markedly abrogated when the cells were pretreated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a specific ROS inhibitor, suggesting that the apoptosis-inducing effect of Isoalantolactone in osteosarcoma cells was mediated by reactive oxygen species.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data demonstrated that Isoalantolactone induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in U2OS cells via a novel mechanism involving inhibition of NF-κBp65 and provide the rationale for further in vivo and preclinical investigation of Isoalantolactone against osteosarcoma.
Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Oct;36(10):1262-9.
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, induces apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells via mitochondrial and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways.[Pubmed:
23881702]
Isoalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone, possesses anti-fungal as well as cytotoxic properties. In this study, the effects of Isoalantolactone on cell viability, cell cycle, and apoptosis were investigated in human gastric adenocarcinoma SGC-7901 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results demonstrated that Isoalantolactone induced morphological changes and decreased cell viability. Subsequently, we found that Isoalantolactone induced G2/M and S phase arrest, which was associated with a decrease in the expression level of cyclin B1. Apoptosis triggered by Isoalantolactone was visualized using propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. Isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells was associated with the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨ m) that was due to the down-regulation of Bcl-2 and up-regulation of Bax that led to the cleavage of caspase-3. Additionally, it was found that Isoalantolactone was involved in the inhibition of phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt.
CONCLUSIONS:
Isoalantolactone-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis of SGC-7901 cells involve mitochondria-caspase and PI3K/Akt dependent pathways, which gives the rationale for in vivo studies on the utilization of Isoalantolactone as a potential cancer therapeutic compound.