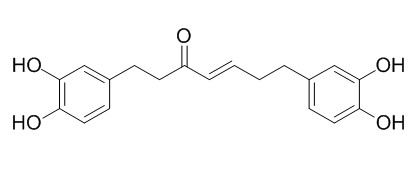
Hirsutenone
Hirsutenone has potent antioxidant activity, it shows significant free radical scavenging activity and exhibits inhibition effect on the mitochondrial lipid peroxidation.Hirsutenone exhibits anti-cancer, and anti-filarial effects, it may exert a preventive effect against microbial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory skin diseases through inhibition of ERK pathway-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Hirsutenone attenuates adipogenesis by directly targeting PI3K and ERK during MCE in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, underscoring the potential therapeutic application of Hirsutenone in preventing obesity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2020, 2020:1970349.
Phytomedicine.2022, 100:154036.
J Traditional Thai Medical Res.2022, 8(1):pp1-14.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).2020, 11:568436.
Int J Biol Sci.2023, 19(10):3077-3098.
Phytother Res.2019, 33(5):1490-1500
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016, 408(15)
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(9):3144.
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(21):E5488
Molecules.2023, 28(13):4971.
Related and Featured Products
J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 17;289(3):1723-31.
The diarylheptanoid hirsutenone sensitizes chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin via modulation of apoptosis-inducing factor and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis.[Pubmed:
24247248]
Cisplatin (CDDP) and its derivatives are considered first-line treatments for ovarian cancer (OVCA). However, despite initial results that often appear promising, in most cases patients will return with recurrent disease that fails to respond to further chemotherapy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We assayed a number of food phytochemicals with reported PI3K inhibitory ability to identify candidates that can influence CDDP treatment outcomes in chemoresistant OVCA cell lines.
A direct comparison revealed that the diarylheptanoid Hirsutenone from the tree bark of Alnus hirsuta var. sibirica was superior at inducing CDDP sensitivity in a number of chemoresistant cancer cell lines. Whereas Hirsutenone treatment activated p53, its modest efficacy in p53-mutant and -null cell lines suggested the existence of a p53-independent mode of action. Further investigation revealed that Hirsutenone causes CDDP-dependent apoptosis in chemoresistant cells by ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis degradation and by enhancing the translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor from the mitochondria to the nucleus. This was found to be, at least in part, under the influence of upstream Akt activity, linking Hirsutenone-dependent PI3K inhibition with downstream effects on apoptosis-inducing factor, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis, and apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings provide rationale for further investigation of the effects of Hirsutenone on chemoresistant OVCA in clinical studies.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Apr;10(4):520-5.
Hirsutenone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-kappaB-induced inflammatory mediator production by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4 and ERK activation.[Pubmed:
20138154]
Adipogenesis is a key driver of the expansion of adipose tissue mass that causes obesity. Hirsutenone (HST) is an active botanical diarylheptanoid present in Alnus species. In this study, we evaluated the effects of HST on adipogenesis, its mechanisms of action and the molecular targets involved.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using Oil Red O staining, we observed that HST dose-dependently suppresses lipid accumulation during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, concomitant with a decrease in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) and fatty acid synthase (FAS) protein expression. This inhibitory effect was largely limited to the early stage of adipogenesis, which includes mitotic clonal expansion (MCE), as evidenced by delayed cell cycle entry of preadipocytes from G1 to S phase. Furthermore, the regulation of MCE was accompanied by suppression of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) activity. HST was also shown to bind directly to PI3K and ERK1 in a non-ATP competitive manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that HST attenuates adipogenesis by directly targeting PI3K and ERK during MCE in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, underscoring the potential therapeutic application of HST in preventing obesity.
Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Oct;31(10):1287-9.
Cytotoxic activities of diarylheptanoids from Alnus japonica.[Pubmed:
18958419 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The diarylheptanoids (1-10) 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->3)-beta-D-xylopyranoside (1), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-O-beta-D-apiofuranosyl(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane (4), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-heptane-3-one-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (5), oregonin (6), hirsutanonol (7), Hirsutenone (8), 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside (9), and platyphylloside (10), isolated from the bark of Alnus japonica, were analyzed for their cytotoxic activities on various human and mouse cancer cell lines. The cytotoxic activities of these ten compounds were evaluated against murine B16 melanoma, human SNU-1 gastric cancer, human SNU-354 hepatoma cancer and human SNU-C4 colorectal cell lines.
CONCLUSIONS:
The diarylheptanoids showed potent cytotoxic activities against murine B16 melanoma cells and human SNU-C1 gastric cancer cell when the cell viability was analyzed by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide) assay.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Jul 15;90(2):115-25.
Hirsutenone reduces deterioration of tight junction proteins through EGFR/Akt and ERK1/2 pathway both converging to HO-1 induction.[Pubmed:
24853984]
The current study investigated the protective effect of Hirsutenone against disruption of the intestinal barrier in vitro and in a mouse model of colitis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Caco-2 cells were stimulated with tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BH). Hirsutenone prevented the t-BH-induced increase in permeability by inhibiting the reduction in zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) expression, and rapidly stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Hirsutenone-mediated protection against the loss of ZO-1 depends on the activation of both ERK1/2 and Akt signaling pathways. Interestingly, Hirsutenone-mediated activation of Akt, but not ERK1/2, signaling was EGFR-dependent. Hirsutenone increased heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression through both EGFR/Akt- and ERK1/2-dependent pathways, contributing to the protective effects against TJ dysfunction. Colitis was induced in mice by intrarectal administration of 2,4,6,-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS). Hirsutenone administration improved the clinical parameters and tissue histological appearance, increased HO-1 expression, attenuated reduction of ZO-1 and occludin mRNA, and promoted BrdU incorporation in the colonic epithelium of TNBS-treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our results demonstrate that Hirsutenone reverse disordered intestinal permeability by activating EGFR/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways, which are involved in the regulation of HO-1 expression. These findings highlight the potential of Hirsutenone for clinical applications in the treatment of IBD.
Mol Carcinog. 2014 Sep 11.
Hirsutenone in Alnus extract inhibits akt activity and suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation.[Pubmed:
25213146 ]
Hirsutenone from the tree bark of Alnus hirsuta var. sibirica was superior at inducing CDDP sensitivity in a number of chemoresistant cancer cell lines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Whereas Hirsutenone treatment activated p53, its modest efficacy in p53-mutant and -null cell lines suggested the existence of a p53-independent mode of action. Further investigation revealed that Hirsutenone causes CDDP-dependent apoptosis in chemoresistant cells by ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis degradation and by enhancing the translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor from the mitochondria to the nucleus. This was found to be, at least in part, under the influence of upstream Akt activity, linking Hirsutenone-dependent PI3K inhibition with downstream effects on apoptosis-inducing factor, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis, and apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings provide rationale for further investigation of the effects of Hirsutenone on chemoresistant OVCA in clinical studies.
Phytomedicine. 2013 Jan 15;20(2):124-32.
Antifilarial diarylheptanoids from Alnus nepalensis leaves growing in high altitude areas of Uttarakhand, India.[Pubmed:
23219341 ]
Diarylheptanoids such as oregonin and Hirsutenone have been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effect of Hirsutenone on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediator production in keratinocytes in relation to the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB pathways. Hirsutenone, dexamethasone, ERK inhibitor or Bay 11-7085 (an inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation) reduced the lipopolysaccharide-induced production of cytokines IL-1beta and IL-8, and the chemokine CCL17. Hirsutenone, ERK inhibitor or Bay 11-7085 also prevented the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of Toll-like receptor 4, the phosphorylation of inhibitory kappaB-alpha, the activation of NF-kappaB and the expression of ERK. The results show that Hirsutenone may reduce the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated production of inflammatory mediators in keratinocytes by suppressing the Toll-like receptor 4 expression-mediated NF-kappaB activation that is regulated by the ERK pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Hirsutenone may exert a preventive effect against microbial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory skin diseases through inhibition of ERK pathway-mediated NF-kappaB activation.
J Cell Biochem. 2015 Jul;116(7):1361-70.
Hirsutenone Directly Targets PI3K and ERK to Inhibit Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes.[Pubmed:
25756947]
Hirsutenone, a bioactive compound in Alnus japonica, exhibits anti-cancer effects against prostate cancer through a direct physical inhibition of Akt1/2.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Hirsutenone suppressed anchorage-dependent and independent cell growth of PC3 and LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Annexin V and Propidium iodide (PI) staining results demonstrated that Hirsutenone strongly induces apoptotic cell death in both PC3 and LNCaP cells. Furthermore, treatment of Hirsutenone attenuated phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a downstream substrate of Akt, without affecting Akt phosphorylation. Kinase and pull-down assay results clearly show that Hirsutenone inhibits Akt1 and 2 by direct binding in an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-noncompetitive manner in vitro and ex vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results show that Hirsutenone suppresses human prostate cancer by targeting Akt1 and 2 as a key component to explain for anti-cancer activity of Alnus species.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.,2005,13(2):85-90.
Constituents and their DPPH Scavenging Activities from the Leaves of Alnus hirsuta (Spach) Rupr.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Phytochemical study on the EtOAc fraction from a MeOH extract of the leaves of Alnus hirsuta Rupr. led to the isolation of nine compounds betulin (1), betulinic acid (2), Hirsutanonol (3), Hirsutenone (4), quercetin (5), avicularin (6), gallic acid (7), hyperin (8), and daucosterol (9). Among them, six compounds 1, 2, 57, and 9 are report from this plant for the first time. All isolated compounds were evaluated for their antioxidant activity using DPPH radical scavenging capacity and inhibition effect on mitochondrial lipid peroxidation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Six phenolic compounds 3-8 were found to have potent antioxidant activity. Of which, compounds 3, 4 and 5 showed significant free radical scavenging activity with the values of , respectively. In addition, the compounds 3-8 exhibited inhibition effect on the mitochondrial lipid peroxidation with the values of , respectively.