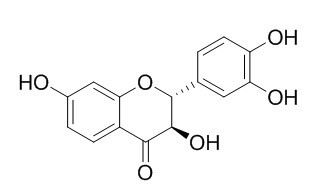
Fustin
Fustin shows protective effects on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal cell death.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Cell Mol Med.2022, 26(23):5807-5819.
Molecules.2021, 26(12):3652.
Org Biomol Chem.2017, 15(31):6483-6492
Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine2022, 345930.
Univerzita Karlova2022, 228192.
Prev Nutr Food Sci.2024, 29(4):504-511.
Toxins (Basel).2023, 15(3):231.
Arch Toxicol.2024, 98(5):1415-1436.
J Chromatogr Sci.2020, 58(6):485-493.
J Med Assoc Thai2024, P-04.
Related and Featured Products
J Neurosci Res. 2009 Dec;87(16):3658-70.
Fustin flavonoid attenuates beta-amyloid (1-42)-induced learning impairment.[Pubmed:
19533734]
Natural flavonoids ameliorate amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta)-induced neurotoxicity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We examined whether the Fustin flavonoid affects Abeta-induced learning impairment in mice. Repeated treatment with Fustin significantly attenuated Abeta (1-42)-induced conditioned fear and passive avoidance behaviors. This effect was comparable to that of EGb761, a standard extract of ginkgo. Fustin treatment significantly prevented decreases in acetylcholine (ACh) levels, choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) activity, and ChAT gene expression induced by Abeta (1-42). Fustin also consistently suppressed increases in acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) activity and AChE gene expression induced by Abeta (1-42). In addition, Fustin significantly attenuated Abeta (1-42)-induced selective decreases in muscarinic M1 receptor gene expression and muscarinic M1 receptor binding activity (as determined by [(3)H]pirenzepine binding) by modulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK 1/2) and cAMP response-element binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. These effects of Fustin were reversed by treatment with dicyclomine, a muscarinic M1 receptor antagonist, and SL327, a selective ERK inhibitor, but not by chelerythrine, a pan-protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our results suggest that Fustin attenuates Abeta (1-42)-impaired learning, and that the ERK/CREB/BDNF pathway is important for the M1 receptor-mediated cognition-enhancing effects of Fustin.