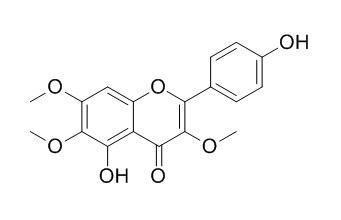
Penduletin
Penduletin has anti-inflammatory,anti-tumor cells, and anti-bacterical activities,it inhibits growth of the Gram-negative pathogen neisseria gonorrhoeae. Penduletin has strong activity in vitro against EV71 with low cytotoxicity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules2022, 27(12):3903.
Phytomedicine2022, 104:154337.
Hum Exp Toxicol.2023, 42:9603271221145386.
ScientificWorldJournal.2022, 2022:4806889.
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2024, 46(6):6018-6040.
Chem Biol Interact.2024, 395:110999.
Molecules2022, 27(14),4462
Applied Biological Chemistry2023, 66:85.
Plants (Basel).2020, 9(11):1535.
Molecules.2023, 28(2):727.
Related and Featured Products
5,7-Dihydroxy-3,4',8-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN99666
CAS No: 1570-09-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
5,7-Diacetoxy-3,4',8-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN98818
CAS No: 5128-43-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
4',5,7-Trihydroxy 3,6,8-trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN70413
CAS No: 57393-71-2
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Calycopterin
Catalog No: CFN70374
CAS No: 481-52-7
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Araneosol
Catalog No: CFN98797
CAS No: 50461-86-4
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
2',3,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN70373
CAS No: 480-15-9
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Kaempferol
Catalog No: CFN98838
CAS No: 520-18-3
Price: $30/20mg
Kaempferol 3,4,7-triacetate
Catalog No: CFN99479
CAS No: 143724-69-0
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Kaempferol tetraacetate
Catalog No: CFN99686
CAS No: 16274-11-6
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Isokaempferide
Catalog No: CFN93002
CAS No: 1592-70-7
Price: $368/5mg
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2011 Oct 9;44(3):392-8.
Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication by chrysosplenetin and penduletin.[Pubmed:
21914477]
In recent years, enterovirus 71 (EV71) infections have caused an increasing epidemic in young children, accompanying with more severe nervous system disease and more deaths. Unfortunately, there is no specific medication for it so far.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we investigated the anti-EV71 activity of chrysosplenetin and Penduletin, two o-methylated flavonols isolated from the leaves of Laggera pterodonta. These two compounds were found to have strong activity in vitro against EV71 with low cytotoxicity. In the cytopathic effect (CPE) inhibition assays, both plaque reduction assay and virus yield inhibition assay, the compounds showed a similar 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) value of about 0.20 μM. The selectivity indices (SI) of chrysosplenetin and Penduletin were 107.5 and 655.6 in African green monkey kidney (Vero) cells, and 69.5 and 200.5 in human rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells, accordingly. The preliminary mechanism analysis indicates that they function not through blocking virus entry or inactivating virus directly but inhibiting viral RNA replication. In the time-of-addition assay, both compounds inhibited progeny virus production and RNA replication by nearly 100% when introduced within 4h post infection. In addition to EV71, both compounds inhibited several other human enteroviruses with similar efficacy.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings provide a significant lead for the discovery of anti-EV71 drug.
Oncol Res. 2005;15(2):59-68.
Antineoplastic agents 540. The Indian Gynandropsis gynandra (Capparidaceae).[Pubmed:
16119003 ]
The CH3OH-CH2Cl2 extract of an Indian collection (entire plant) of Gynandropsis gynandra (L.) Briq. was separated based on bioassay results employing cancer cell lines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Six cancer cell growth inhibitors were isolated and found to be known flavone apegenin (4) and flavonols 1-3, 5, and 6. The structure of flavonol 2 was confirmed by X-ray crystal structure determination. All of the five flavonols (1-3, 5, 6) inhibited the murine P388 lymphocytic leukemia cell line with ED50 values of 3.0, 9.2, 4.0, 0.37, and 3.9 microg/ml, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
All six of the flavonoids (1-6) also exhibited activity against a panel of six human cancer cell lines. Penduletin (3) inhibited growth of the Gram-negative pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae and apegenin (4) inhibited growth of the Gram-positive opportunist Enterococcus faecalis.
Planta Med. 2006 Jan;72(1):72-4.
Flavonoids from Artemisia copa with anti-inflammatory activity.[Pubmed:
16450301 ]
Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the dichloromethane and ethanol extracts from the aerial parts of Artemisia copa led to the isolation of the flavonoids spinacetin, jaceosidin, axillarin, Penduletin, tricin and chrysoeriol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
These compounds were studied for possible inhibitory activity on the generation of inflammatory mediators in a cell line of mouse macrophages (RAW 264.7) stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Spinacetin and jaceosidin weakly inhibited nitric oxide production whereas all flavonoids reduced prostaglandin E2 levels to different extents. The most active flavonoid was jaceosidin that inhibited cyclooxygenase-2 activity in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 2.8 microM. In addition, the other flavonoids partially inhibited synovial phospholipase A2 activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These mechanisms may provide a basis for explaining the anti-inflammatory activity of this plant.
Phytother Res. 2011 Jun;25(6):916-21.
Flavonoids inhibit angiogenic cytokine production by human glioma cells.[Pubmed:
21170924]
VEGF and TGF-β1 are cytokines that stimulate tissue invasion and angiogenesis. These factors are considered as molecular targets for the therapy of glioblastoma. Bevacizumab, a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody developed against VEGF, inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and vessel formation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Flavonoids obtained from Dimorphandra mollis and Croton betulaster have been described as proliferation inhibitors of a human glioblastoma derived cell line. VEGF and TGF-β1 levels were dosed by ELISA in a GL-15 cell line treated with bevacizumab and also with the flavonoids rutin, 5-hydroxy-7,4'-dimethoxyflavone, casticin, apigenin and Penduletin. Rutin reduced the VEGF and TGF-β1 levels after 24 h but not after 72 h. The other flavonoids significantly reduced TGF-β1 production. Bevacizumab reduced only the VEGF levels in the supernatant from GL-15 cultures.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the flavonoids studied, and commonly used in popular medicine, present an interesting subject of study due to their potential effect as angiogenic factor inhibitors.
Phytother Res. 2009 Sep;23(9):1336-9.
Antiinflammatory and lipoxygenase inhibitory compounds from Vitex agnus-castus.[Pubmed:
19173281]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Several secondary metabolites, artemetin (1), casticin (2), 3,3'-dihydroxy-5,6,7,4'-tetramethoxy flavon (3), Penduletin (4), methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate (5), p-hydroxybenzoic acid (6), methyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate (7), 5-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzoic acid (8), vanillic acid (9) and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (10) were isolated from a folkloric medicinal plant, Vitex agnus-castus. The structures of compounds 1-10 were identified with the help of spectroscopic techniques. Compounds 3-10 were isolated for the first time from this plant. These compounds were screened for their antiinflammatory and lipoxygenase inhibitory activities.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 6, 7 and 10 were found to have significant antiinflammatory activity in a cell-based contemporary assay, whereas compounds 1 and 2 exhibited a potent lipoxygenase inhibition.
Arjunglucoside I
Catalog No: CFN95049
CAS No: 62319-70-4
Price: $268/10mg
7,2',4'-Trihydroxy-5-methoxy-3-arylcoumarin
Catalog No: CFN95070
CAS No: 1092952-62-9
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
New Compound 1
Catalog No: CFN95152
CAS No: N/A
Price: $318/5mg
Genistein 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside-4'-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucopyranoside]
Catalog No: CFN95159
CAS No: 70404-42-1
Price: $318/10mg
Aegineoside
Catalog No: CFN95270
CAS No: 752209-48-6
Price: $413/5mg
(2S)-5,7,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95406
CAS No: 74628-43-6
Price: $318/10mg
Barbaloin-related compound A
Catalog No: CFN95453
CAS No: 473225-21-7
Price: $318/5mg
Isosecotanapartholide
Catalog No: CFN95471
CAS No: 102926-01-2
Price: $318/10mg
12beta-Acetoxy-3,7,11,15,23-pentaoxo-lanost-8,20-dien-26-oic acid
Catalog No: CFN95505
CAS No: 1309931-91-6
Price: $318/5mg
New compound 22
Catalog No: CFN95570
CAS No: N/A
Price: $413/5mg