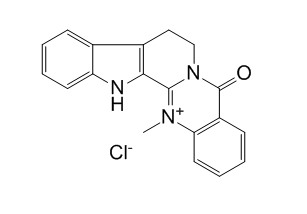
Dehydroevodiamine Chloride
Dehydroevodiamine Chloride produces long-lasting facilitation of synaptic transmission, and that this facilitation depends upon the activation of both the muscarinic and NMDA receptors. It might be an effective drug for not only the Alzheimer's disease type, but also the vascular type of dementia.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Anticancer Res.2020, 40(10):5529-5538.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2017, 2017:1401279
Chemistry of plant raw materials2021, 1:pp 139-150
Int J Biol Sci.2023, 19(10):3077-3098.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2024, 241:115990.
J.Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica2017, 571-575
Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo).2024, 41(3):267-276.
Foods.2021, 10(11):2627.
Research Square2021, 10.21203.
Life Sci.2018, 209:498-506
Related and Featured Products
Neuroreport. 2003 Mar 3;14(3):399-403.
Long-lasting facilitation by dehydroevodiamine. HClof synaptic responses evoked in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices.[Pubmed:
12634491]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We tested the effects of dehydroevodiamine.Cl (Dehydroevodiamine Chloride, DHED) on field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) evoked by the electrical stimulation of Schaffer collaterals-commissural fibres in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. Bath applications of 10 microM DHED for 20 or 40 min induced long-lasting facilitation of fEPSPs, which outlasted the presence of DHED. A 10 min treatment with a higher concentration (100 microM) also induced long-lasting facilitation. The long-lasting facilitation was blocked either by 10 microM atropine, the muscarinic receptor antagonist, or by 50 microM D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D-AP5), an NMDA receptor antagonist.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results show that DHED produces long-lasting facilitation of synaptic transmission, and that this facilitation depends upon the activation of both the muscarinic and NMDA receptors.
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology, 2014, 18(1):55.
Dehydroevodiamine·HCl Improves Stress-Induced Memory Impairments and Depression Like Behavior in Rats[Pubmed:
24634597 ]
Dehydroevodiamine·HCl (Dehydroevodiamine Chloride,DHED) has been reported to prevent memory impairment and neuronal cell loss in a rat model with cognitive disturbance. We investigated the effect of DHED on memory impairment and behavioral abnormality caused by stress.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We demonstrated that DHED can improve stress-induced memory impairments and depression-like behaviors by using open-field test, Y-maze test and forced swimming test. DHED treatment significantly recovered the decreases in the levels of neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) proteins caused by stress and the decreases in cell viability.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggested that DHED is a potential drug candidate for neuronal death, memory impairment and depression induced by stress.
J Neurochem. 2000 Jan;74(1):244-53.
Dehydroevodiamine.HCl prevents impairment of learning and memory and neuronal loss in rat models of cognitive disturbance.[Pubmed:
10617126 ]
We previously reported that dehydroevodiamine.HCl (Dehydroevodiamine Chloride, DHED) has anticholinesterase and antiamnesic activities. To verify the effects of DHED on cognitive deficits further, we tested it on the scopolamine-induced amnesia model of the rat using the passive avoidance and eight-arm radial maze tests.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A single (20 mg/kg p.o.) and repeated (10 mg/kg p.o.) administrations of DHED could significantly reverse the latency time shortened by scopolamine (1 mg/kg i.p.) to control level. The impaired spatial working memory induced by scopolamine (1 mg/kg i.p.) was also improved significantly by a single injection (6.25 mg/kg i.p.) and repeated administrations of DHED (10 mg/kg p.o.) in the eight-arm radial maze test. In addition, we examined the effects of DHED on the memory impairment and the histological changes of the brain after unilateral electrolytic lesion of the entorhinal cortex (EC) and middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. The cognitive deficits caused by EC lesion and middle cerebral artery occlusion were improved significantly by repeated administrations of DHED (6.25 mg/kg i.p.) after EC lesion or ischemic insult once a day for 7 days in the passive avoidance test. Histological analysis showed that the neuronal loss in the DHED-treated group was notably reduced in the hippocampal area (CA1) of ischemic rats and in the dentate gyrus and hippocampal area (CA1 and CA3) of EC-lesioned rats compared with the nontreated group. The infarction area was decreased significantly by a single administration of DHED (6.25 mg/kg i.p.) 30 min before ischemic insult for 6 h.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that DHED might be an effective drug for not only the Alzheimer's disease type, but also the vascular type of dementia.