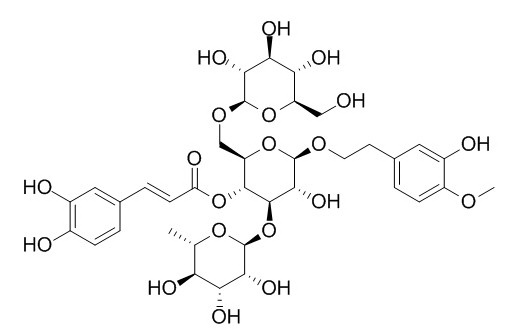
Cistanoside A
Cistanoside A possesses protective activities on CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in mice, which is involved with increasing free radicals clearing activities, alleviating lipid-overoxidation damage, and improving respiratory chain function in mitochondria.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Cells.2021, 10(11):2919.
Toxicol In Vitro.2022, 81:105346.
VNU Journal of Science2023, No. 20.
Toxicol In Vitro.2019, 59:161-178
J Agric Food Chem.2019, 67(27):7748-7754
Antioxidants (Basel).2023, 12(2):447.
J Nat Prod.2019, 82(4):1002-1008
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2017, 2017:6360836
J Biomol Struct Dyn.2024, 1-12.
Cardiovasc Toxicol.2019, 19(4):297-305
Related and Featured Products
Eur J Pharmacol . 2000 Jul 14;400(1):137-44.
Inhibition of nitric oxide by phenylethanoids in activated macrophages[Pubmed:
10913595]
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the pro-inflammatory molecules. Some phenylethanoids have been previously shown to possess anti-inflammatory effects. Seven phenylethanoids from the stems of Cistanche deserticola, viz. isoacteoside, tubuloside B, acteoside, 2'-O-acetylacteoside, echinacoside, Cistanoside A and tubuloside A, were tested for their effect on NO radical generation by activated murine macrophages. At the concentration of 100-200 microM, all the phenylethanoids reduced (6.3-62.3%) nitrite accumulation in lipopolysaccharide (0.1 microgram/ml)-stimulated J774.1 cells. At 200 microM, they inhibited by 32.2-72.4% nitrite accumulation induced by lipopolysaccharide (0.1 microgram/ml)/interferon-gamma (100 U/ml) in mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages. However, these compounds did not affect the expression of inducible nitric oxide (iNOS) mRNA, the iNOS protein level, or the iNOS activity in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated J774.1 cells. Instead, they showed a clear scavenging effect (6.9-43.9%) at the low concentrations of 2-10 microM of about 12 microM nitrite generated from an NO donor, 1-propanamine-3-hydroxy-2-nitroso-1-propylhydrazino (PAPA NONOate). These results indicate that the phenylethanoids have NO radical-scavenging activity, which possibly contributes to their anti-inflammatory effects.
Latin American Journal of Pharmacy; 2012 vol. 31, no. 3
Protective Activities of Cistanoside A on CCl4 Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To evaluate the protective efficacy of Cistanoside A (C.A), a phenylethanol glycoside isolated from Cistanche deserticola, on CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in mice, 50 animals were divided into five different protocols, and hepatic functional index were detected by diagnostic kits.To confirm the effect of Cistanoside A on free radical, tests on the free radical scavenging activities were also carried out in vitro. We found treatment with Cistanoside A (10, 20 mg/kg o.p. for 7 days) could significantly ameliorated the levels of hepatic function indices (AST, ALT, ALP and LDH) (P < 0.05). The biochemical results were also confirmed by histopathological examination. Cistanoside A treatment decreased the ballooning degeneration, moderated the hepatocytes apoptosis, and alleviated centrilobular and bridging necrosis which were observed in the CCl4 control group. Following experiments revealed that Cistanoside A could increase the activities of mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes (GST, SOD, and CAT) and respiratory marker enzymes (MDH, SDH, NADH dehydrogenase, and cytochrome c oxidases) (P < 0.05). In vitro, Cistanoside A exhibited strong scavenging activities for DPPH radical and superoxide anion radical.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results revealed that Cistanoside A possess protective activities on CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in mice, which was involved with increasing free radicals clearing activities, alleviating lipid-overoxidation damage, and improving respiratory chain function in mitochondria.