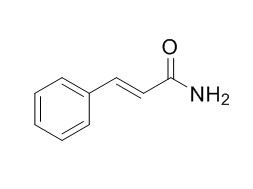
Cinnamamide
Cinnamamide, a non-lethal repellent, deters feeding by a wide range of avian species;cinnamamide has the potential for use against the commensal rodent Mus musculus in situations where use of lethal control methods could be hazardous (e.g. food stores). Cinnamamide is also an antitumor agent with low cytotoxicity acting on matrix metalloproteinase, and may serve as a lead compound in the development of antitumor drugs. Cinnamamide and betaine cinnamamide have growth-regulating activity on wheat.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Applied Biological Chemistry2020, 63:37.
J Integr Plant Biol.2023, 13564.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(5):2796.
Phytomedicine.2018, 38:12-23
Natural Product Sciences2023, 29(4):276-280.
Cell Physiol Biochem.2019, 52(6):1255-1266
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(16):8641.
ACS Omega.2023, 8(36):32424-32431.
Molecules.2023, 28(5):2376.
Archives of Biological sciences2022, 00:21-21
Related and Featured Products
ChemMedChem. 2015 Aug;10(8):1302-25.
Cinnamamide Derivatives for Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders-A Review of Structure-Activity Relationships.[Pubmed:
26083325]
The Cinnamamide scaffold has been incorporated in to the structure of numerous organic compounds with therapeutic potential.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The scaffold enables multiple interactions, such as hydrophobic, dipolar, and hydrogen bonding, with important molecular targets. Additionally, the scaffold has multiple substitution options providing the opportunity to optimize and modify the pharmacological activity of the derivatives. In particular, Cinnamamide derivatives have exhibited therapeutic potential in animal models of both central and peripheral nervous system disorders. Some have undergone clinical trials and were introduced on to the pharmaceutical market. The diverse activities observed in the nervous system included anticonvulsant, antidepressant, neuroprotective, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. Over the last decade, research has focused on the molecular mechanisms of action of these derivatives, and the data reported in the literature include targeting the γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA ) receptors, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, transient receptor potential (TRP) cation channels, voltage-gated potassium channels, histone deacetylases (HDACs), prostanoid receptors, opioid receptors, and histamine H3 receptors.
CONCLUSIONS:
Here, the literature data from reports evaluating cinnamic acid amide derivatives for activity in target-based or phenotypic assays, both in vivo and in vitro, relevant to disorders of the central and peripheral nervous systems are analyzed and structure-activity relationships discussed.
Advance Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2015, 7(8).
Growth-regulating Activity of Cinnamamide and Betaine Cinnamamide on Wheat.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Growth-regulating Activity of Cinnamamide and Betaine Cinnamamide on Wheat.
Anticancer Drugs. 2000 Jan;11(1):49-54.
Cinnamamide, an antitumor agent with low cytotoxicity acting on matrix metalloproteinase.[Pubmed:
10757563]
The antitumor activity of Cinnamamide (CNM), an agent acting on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), was investigated in the present study. CNM displayed low cytotoxicity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
By the MTT assay the IC50 (50% inhibitory concentration) values of CNM on cell proliferation ranged from 1.29 to 1.94 mM in human oral epidermoid carcinoma KB cells, human hepatoma BEL-7402 cells and human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells. Moreover, the IC50 for human fetal lung 2BS cells reached 4.33 mM. The administration of CNM in the range of 50-150 mg/kg (i.p. or p.o.) showed moderate antitumor effects in mice. When administered i.p. or p.o., CNM (150 mg/kg) inhibited the growth of transplanted hepatoma 22 by 48.8 or 40.5%, respectively. At the dose of 100 mg/kg, CNM inhibited the growth of colon 26 carcinoma by 39.0% and that of Lewis lung carcinoma by 53.9%. In the Lewis lung carcinoma model, CNM at the dose of 100 mg/kg (i.p.) also reduced the lung metastasis by 59.1%. Gelatine zymography revealed that CNM was able to decrease the level of MMP-2 in conditioned medium of HT-1080 tumor cells in a concentration-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that CNM is an antitumor agent with low cytotoxicity acting on MMP and may serve as a lead compound in the development of antitumor drugs.
Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 1996, 49(4):353-363.
Non-lethal mouse repellents: Evaluation of cinnamamide as a repellent against commensal and field rodents[Reference:
WebLink]
Cinnamamide, a non-lethal repellent, deters feeding by a wide range of avian species.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the potential of Cinnamamide as a repellent for house mice (Mus musculus) and wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus), using a 3 day, ‘short-term no-choice test’. Both species were presented with Cinnamamide-treated food at 0.8% w/w. After an initial sampling period, both the house mice and wood mice reduced their consumption of Cinnamamide-treated food to 32% and 17%, respectively, of control (pre-trial) consumption. Consumption of treated food by house mice remained depressed for the remainder of the trial, suggesting that at this concentration, the house mice had developed a strong and persistent learned aversion to the treated food. In contrast, the wood mice rapidly habituated to the presence of Cinnamamide and food consumption returned to control (pre-trial) levels on days 2 and 3. In a subsequent trial to determine the dose-response relationship between Cinnamamide concentration and consumption of treated food by the house mouse, Cinnamamide reduced food consumption at concentrations as low as 0.1% w/w and this reduction increased with increasing concentration.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results indicate that Cinnamamide has the potential for use against the commensal rodent Mus musculus in situations where use of lethal control methods could be hazardous (e.g. food stores).