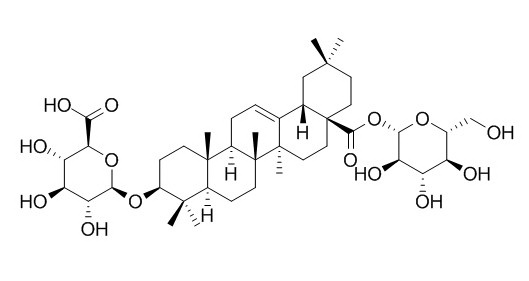
Chikusetsusaponin IVa
Chikusetsusaponin IVa is a novel AMPK activator, can induce insulin secretion from βTC3 cells via GPR40 mediated calcium and PKC pathways, may be developed into a new potential for therapeutic agent used in T2DM patients.Chikusetsusaponin IVa exerts antithrombotic effects, including minor hemorrhagic events.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Comp. & Mathematical Methods in Med.2022, 5475559.
Antioxidants (Basel).2023, 12(7):1324.
Life Sci.2021, 270:119074.
iScience.2024, 4790628.
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(9):E2244
Industrial Crops and Products2019, 140:111612
Heliyon.2022, e12337.
J Colloid Interface Sci.2024, 662:760-773.
Phytomedicine.2023, 114:154813.
The University of Manitoba2021, 35690.
Related and Featured Products
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Apr 17;459(4):591-6.
Chikusetsusaponin IVa methyl ester induces cell cycle arrest by the inhibition of nuclear translocation of β-catenin in HCT116 cells.[Pubmed:
25749342]
We demonstrate that Chikusetsusaponin IVa methyl ester (CME), a triterpenoid saponin from the root of Achyranthes japonica, has an anticancer activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigate its molecular mechanism in depth in HCT116 cells. CME reduces the amount of β-catenin in nucleus and inhibits the binding of β-catenin to specific DNA sequences (TCF binding elements, TBE) in target gene promoters. Thus, CME appears to decrease the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins such as Cyclin D1, as a representative target for β-catenin, as well as CDK2 and CDK4. As a result of the decrease of the cell cycle regulatory proteins, CME inhibits cell proliferation by arresting the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, we suggest that CME as a novel Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor can be a putative agent for the treatment of colorectal cancers.
J Med Food. 2012 Dec;15(12):1073-80.
Antithrombotic effect of chikusetsusaponin IVa isolated from Ilex paraguariensis (Maté).[Pubmed:
23134458]
The triterpene Chikusetsusaponin IVa was isolated from the fruit of Ilex paraguariensis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using biochemical and pharmacological methods, we demonstrated that Chikusetsusaponin IVa (1) prolongs the recalcification time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and thrombin time of normal human plasma in a dose-dependent manner, (2) inhibits the amidolytic activity of thrombin and factor Xa upon synthetic substrates S2238 and S2222, (3) inhibits thrombin-induced fibrinogen clotting (50% inhibition concentration, 199.4 ± 9.1 μM), and (4) inhibits thrombin- and collagen-induced platelet aggregation. The results also indicate that Chikusetsusaponin IVa preferentially inhibits thrombin in a competitive manner (K(i)=219.6 μM). Furthermore, when administered intravenously to rats, Chikusetsusaponin IVa inhibited thrombus formation in a stasis model of venous thrombosis, although it did not induce a significant bleeding effect. Chikusetsusaponin IVa also prolonged the ex vivo activated partial thromboplastin time.
CONCLUSIONS:
Altogether, these data suggest that Chikusetsusaponin IVa exerts antithrombotic effects, including minor hemorrhagic events. This appears to be important for the development of new therapeutic agents.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;67(7):997-1007.
Chikusetsu saponin IVa regulates glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation: implications in antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects.[Pubmed:
25677570]
The aim of this study is to investigate antidiabetic effects and molecular mechanisms of the chemical Chikusetsu saponin IVa (CHS) that isolated from root bark of Aralia taibaiensis, which has multiple pharmacological activity, such as relieving rheumatism, promoting blood circulation to arrest pain and antidiabetic action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats with streptozotocin/nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and insulin-resistant myocytes were used. Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase were quantified by immunoblotting. Assays of glucose uptake, fatty acid oxidation, glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation and carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT-1) activity were performed.
Chronic oral administration of CHS effectively decreases blood glucose, triglyceride, free fatty acid (FFA) and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels in T2DM rats. In both normal and insulin-resistant C2C12 myocytes, CHS activates AMPK, and increases glucose uptake or fatty acid oxidation through enhancing membrane translocation of GLUT4 or CPT-1 activity respectively. Knockdown of AMPK significantly diminishes the effects of CHS on glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation.
CONCLUSIONS:
CHS is a novel AMPK activator that is capable of bypassing defective insulin signalling and could be useful for the treatment of T2DM or other metabolic disorders.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 22;164:334-9.
Insulinotropic effect of Chikusetsu saponin IVa in diabetic rats and pancreatic β-cells.[Pubmed:
25701750]
As a well-known traditional Chinese medicine the root bark of Aralia taibaiensis has traditionally been used as the medicine considered alleviating several disorders including diabetes mellitus (DM). Chikusetsusaponin IVa (CHS) has been defined as a major active ingredient of triterpenoid saponins extracted from Aralia taibaiensis. The scientific evidence of anti-diabetic effect for Chikusetsusaponin IVa remains unknown and the purpose of our study was to study its hypoglycemic and insulin secretagogue activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vivo studies were performed on type 2 diabetic mellitus (T2DM) rats given Chikusetsusaponin IVa for 28 days to test the antihyperglycemic activity. The in vitro effects and possible mechanisms of Chikusetsusaponin IVa on the insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cell line βTC3 were determined. RESULTS: Oral administration of Chikusetsusaponin IVa dose-dependently increased the level of serum insulin and decreased the rise in blood glucose level in an in vivo treatment. In vitro, Chikusetsusaponin IVa potently stimulated the release of insulin from βTC3 cells at both basal and stimulatory glucose concentrations, the effect which was changed by the removal of extracellular Ca(2+). Two methods showed that Chikusetsusaponin IVa enhanced the intracellular calcium levels in βTC3 cells. Chikusetsusaponin IVa was capable of enhancing the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases C (PKC), which could be reversed by a PKC inhibitor (RO320432), and the insulin secretion induced by Chikusetsusaponin IVa was also inhibited by RO320432. Further study also showed that the insulinotropic effect, intracellular calcium levels and the phosphorylation of PKC were reduced by inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) by a GPR40 inhibitor (DC126026).
CONCLUSIONS:
These observations suggest that the signaling of Chikusetsusaponin IVa -induced insulin secretion from βTC3 cells via GPR40 mediated calcium and PKC pathways and thus Chikusetsusaponin IVa might be developed into a new potential for therapeutic agent used in T2DM patients.
Torosachrysone 8-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No: CFN95131
CAS No: 94356-13-5
Price: $318/5mg
Specioside B
Catalog No: CFN95165
CAS No: 126589-95-5
Price: $368/5mg
3,7,23,24-tetrahydroxycucurbita-5,25-dien-19-al
Catalog No: CFN95168
CAS No: 1446447-97-7
Price: $318/5mg
Pueroside A
Catalog No: CFN95177
CAS No: 100692-52-2
Price: $318/5mg
19-O-beta-D-carboxyglucopyranosyl-12-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-11,16-dihydroxyabieta-8,11,13-triene
Catalog No: CFN95217
CAS No: 1011714-20-7
Price: $318/5mg
New compound 5
Catalog No: CFN95258
CAS No: N/A
Price: $413/5mg
4,7-Didehydroneophysalin B
Catalog No: CFN95317
CAS No: 134461-76-0
Price: $338/5mg
Toddalolactone 3'-O-methyl ether (6-(2-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-3-methylbutyl)-5,7-dimethoxycoumarin)
Catalog No: CFN95372
CAS No: 143614-35-1
Price: $318/10mg
Isorhamnetin 3,5-O-diglucoside
Catalog No: CFN95488
CAS No: 2035413-03-5
Price: $318/10mg
Ganoderenic acid G
Catalog No: CFN95517
CAS No: 120481-73-4
Price: $318/5mg