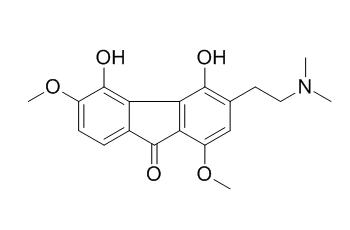
Caulophine
Caulophine has the ability to protect cardiomyocytes from oxidative and ischemic injury through an antioxidative mechanism.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
PLoS One.2017, 12(8):e0181191
Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2024, e0031424.
J Pharmaceut Biomed2020, 182:113110
J Appl Microbiol.2024, 135(7):lxae180.
Processes2020, 8(12),1540.
Int J Med Sci.2020, 17(5):626-631
Nutrients.2021, 13(3):978.
Drug Dev Res.2022, 83(7):1673-1682.
Vietnam Journal of Food Control.2022, 5(2): 115-128.
Int J Oncol.2016, 49(4):1497-504
Related and Featured Products
J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;113(4):368-77.
Caulophine protects cardiomyocytes from oxidative and ischemic injury.[Pubmed:
20724803]
Caulophine is a new fluorenone alkaloid isolated from the radix of Caulophyllum robustum MAXIM and identified as 3-(2-(dimethylamino) ethyl)-4,5-dihydroxy-1,6-dimethoxy-9H-fluoren-9-one. Due to its new chemical structure, the pharmacological activities of Caulophine are not well characterized. The present study evaluated the protective effect and the primary mechanisms of Caulophine on cardiomyocyte injury.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Viability of cardiomyocytes was assayed with the MTT method, and cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. Myocardial infarction was produced by ligating the coronary artery, and myocardial ischemia was induced by isoproterenol in rats. Myocardial infarction size was estimated with p-nitro-blue tetrazolium staining. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase (CK), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and free fatty acid (FFA) were spectrophotometrically determined. Histopathological and ultrastructural changes of ischemic myocardium were observed. The results showed that pretreatment with Caulophine increased the viability of H(2)O(2)- and adriamycin-injured cardiomyocytes; decreased CK, LDH, and MDA; increased SOD; and inhibited H(2)O(2)-induced cellular apoptosis. Caulophine reduced myocardial infarct size and serum CK, LDH, FFA, and MDA; raised serum SOD; and improved histopathological and ultrastructural changes of ischemic myocardium.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results demonstrate that Caulophine has the ability to protect cardiomyocytes from oxidative and ischemic injury through an antioxidative mechanism that provides a basis for further study and development of Caulophine as a promising agent for treating coronary heart disease.
Arch Pharm Res. 2009 Apr;32(4):521-6.
Fluorenone alkaloid from Caulophyllum robustum Maxim. with anti-myocardial ischemia activity.[Pubmed:
19407969]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new fluorenone alkaloid (Caulophine) was isolated from the radix of Caulophyllum robustum Maxim. (collected from the Qinling mountains) using cell membrane chromatography as the screening method. Caulophine was identified as 3-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-4,5-dihydroxy-1,6-dimethoxy-9H-fluoren-9-one based on physicochemic and spectroscopic analyses, particularly by NMR spectroscopic data (i.e., COSY, HMQC, HMBC, NOESY).
CONCLUSIONS:
Caulophine possessed anti-myocardial ischemia activity.