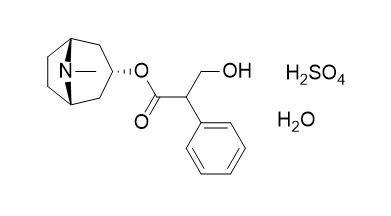
Atropine sulfate monohydrate
Atropine sulfate monohydrate has anticholinergic activity.Atropine sulfate monohydrate can inhibit dose-dependently spontaneous bladder contractions caused by raising the intravesical volume in conscious rats.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Applied Biological Chemistry2022, 65(12)
Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine2024, 4802935.
J Nat Med.2017, 71(4):745-756
Food Science&Tech. Res.2022, 28(2):123-132.
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2022, 44(10):5106-5116.
Viruses.2017, 9(10)
Korean Herb. Med. Inf.2020, 8(2):233-242.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci2021, 10:345-352.
Front Neurosci.2019, 13:1091
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(3):352.
Related and Featured Products
Arzneimittel-Forschung, 1994, 44(11):1242-9.
Urinary bladder-selective action of the new antimuscarinic compound vamicamide.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
1. The inhibitory action of vamicamide (FK176, (+/-)-(2R*,4R*)-4-dimethylamino-2-phenyl-2-(2-pyridyl)valeramide, CAS 132373-81-0) on the responses of various tissues to the cholinergic agonists, carbachol and McN-A-343 (4-[m-chlorophenylcarbamoyloxy]-2-butynyl-trimethylammonium chloride, CAS 55-45-8), was investigated in isolated tissue preparations. Vamicamide showed competitive antagonistic actions against all the preparations tested and its pA2 value for the urinary bladder was 6.82, which was higher than that for the atria (5.94) and almost the same as that for the vas deferens (6.90) and for the stomach (6.81). The pA2 values of oxybutynin hydrochloride (oxybutynin) and Atropine sulfate monohydrate (atropine) were nearly the same in all the tissues tested. 2. Oral administration of vamicamide 0.1-1.0 mg/kg inhibited dose-dependently spontaneous bladder contractions caused by raising the intravesical volume in conscious rats. Inhibitory actions were also obtained with 0.32-3.2 mg/kg of oxybutynin or 0.0032-0.032 mg/kg of atropine, but the duration of action of oxybutynin was shorter than that of vamicamide or atropine. Vamicamide further inhibited bladder contractions in rats following intravesical administration of 0.05-0.5 mg/ml solution. 3. Vamicamide had no effect or only slightly inhibited spontaneous motility of the stomach and distal colon in conscious rats, as well as heart rate and salivary secretion in conscious dogs, after oral dosing with 3.2 mg/kg of the compound.
CONCLUSIONS:
Similar results were obtained with oxybutynin, excepting the occurrence of tachycardia.
Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 2014, 38(3):477-487.
Spectroscopic investigation and oxidation of the anticholinergic drug atropine sulfate monohydrate by hexacyanoferrate(III) in aqueous alkaline media: a mechanistic approach.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The oxidation of the anticholinergic drug Atropine sulfate monohydrate by hexacyanoferrate(III) in aqueous alkaline media was investigated spectrophotometrically by monitoring the decrease in absorbance of hexacyanoferrate(III) (HCF(III)). Oxidation products were identified. The oxidation mechanism was proposed from kinetic studies. The reaction constants involved in the different steps of the mechanism were calculated. The effects of added products, ionic strength, and dielectric constant of the reaction were investigated.
CONCLUSIONS:
The polymerization test revealed that oxidation occurred with intervention of free radicals. The activation parameters were evaluated.