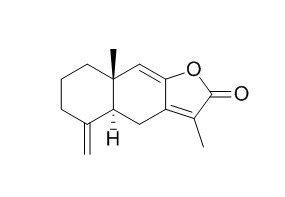
Atractylenolide I
Atractylenolide I, a TLR4-antagonizing agent, shows a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, digestion promoting,significant antitumor, and antioxidant effects. It ameliorates sepsis syndrome,liver and kidney functions by reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and LPS.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Biomed Pharmacother.2020, 128:110318.
Life (Basel).2023, 13(2):457.
Nature Ecology & Evolution2020, doi: 10.1038
PLoS One.2020, 15(2):e0220084.
J Nat Med.2021, doi: 10.1007.
Srinagarind Medical Journal2019, 34(1)
Industrial Crops and Products2022, 188:115596.
Molecules2022, 27(9):2613.
Sci Rep.2024, 14(1):28864.
Comput Biol Chem.2019, 83:107096
Related and Featured Products
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2014 Dec;36(6):420-5.
Atractylenolide I inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed:
25270720]
Atractylenolide I (ATL-I) is a bioactive component of Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae. Although increasing evidence shows that Atractylenolide I has an anti-inflammatory effect, the anti-inflammatory molecular mechanism of Atractylenolide I is still unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the effect of Atractylenolide I on cell viability by 3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and the level of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Further, we examined the effect of Atractylenolide I on the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38) by Western blot. We also investigated the effect of Atractylenolide I on the expression of myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD-2), CD14, complement receptor 3 (CR3), scavenger receptor class A (SR-A), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88). We found that Atractylenolide I showed no inhibitory effect on cell viability at concentrations ranging from 1 μM to 100 μM and markedly reduced the release of IL-6 and TNF-α at a concentrate-dependent manner. In addition, Atractylenolide I suppressed the activity of nuclear NF-κB and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 in LPS-treated RAW264.7 cells. Further analysis showed that ATL-I inhibited the expression of MD-2, CD14, SR-A, TLR4 and MyD88, but the expression of CR3 was unaffected.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
These data suggest that Atractylenolide I shows an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting TNF-α and IL-6 production. The anti-inflammatory effects of Atractylenolide I may be associated with the inhibition of the NF-κB, ERK1/2 and p38 signaling pathways.
Sci Rep. 2014 Jan 23;4:3840.
Atractylenolide-I sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by blocking activation of TLR4/MyD88-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:
24452475]
Paclitaxel, a known TLR4 ligand, leads to activation of TLR4/MyD88-dependent pathway that mediates chemoresistance and tumor progression in epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC). Atractylenolide I (AO-I), a novel TLR4-antagonizing agent, inhibits TLR4 signaling by interfering with the binding of LPS or paclitaxel to membrane TLR4 of human leukocytes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, AO-I was found to attenuate paclitaxel-induced protein expression of IL-6, VEGF and survivin, and to enhance early apoptosis and growth inhibition in MyD88(+) EOC cells; AO-I was shown to fit into the hydrophobic pocket of human MD-2 and to partially overlap with the binding site of paclitaxel by docking simulations, suggesting that AO-I may block the MD-2-mediated TLR4/MyD88-dependent paclitaxel signaling in MyD88(+) EOC cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, AO-I could significantly sensitize the response of MyD88(+) EOC cells to paclitaxel by blocking MD-2-mediated TLR4/MyD88 signaling, and that AO-I-paclitaxel combination could be a promising strategy for the treatment of EOC with a functional TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.
Exp Dermatol . 2018 Feb;27(2):201-204.
The JAK2/STAT3 pathway is involved in the anti-melanoma effects of atractylenolide I[Pubmed:
29078004]
Abstract
In this study, we aimed to investigate the anti-melanoma effects and the JAK2/STAT3 pathway-related mechanism of action of Atractylenolide I in human melanoma cells. Our results showed that Atractylenolide I effectively reduced viability, induced apoptosis and inhibited migration of melanoma cells. Meanwhile, Atractylenolide I decreased the protein expression levels of phospho-JAK2 and phospho-STAT3, and in turn downregulated the mRNA levels of STAT3-targeted genes, including Bcl-xL, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Furthermore, the cytotoxic effect of Atractylenolide I was attenuated in STAT3-overactivated A375 cells. These findings indicate that inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signalling contributes to the anti-melanoma effects of Atractylenolide I.
Exp Cell Res . 2017 Apr 1;353(1):26-34.
Atractylenolide I restores HO-1 expression and inhibits Ox-LDL-induced VSMCs proliferation, migration and inflammatory responses in vitro[Pubmed:
28274716]
Abstract
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis is characterized by the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and inflammatory lesions. The aim of this study is to elucidate the effect of Atractylenolide I (AO-I) on smooth muscle cell inflammation, proliferation and migration induced by oxidized modified low density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL). Here, We found that Atractylenolide I inhibited Ox-LDL-induced VSMCs proliferation and migration in a dose-dependent manner, and decreased the production of inflammatory cytokines and the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in VSMCs. The study also identified that AO-I prominently inhibited p38-MAPK and NF-κB activation. More importantly, the specific heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) inhibitor zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) IX partially abolished the beneficial effects of Atractylenolide I on Ox-LDL-induced VSMCs. Furthermore, Atractylenolide I blocked the foam cell formation in macrophages induced by Ox-LDL. In summary, inhibitory roles of AO-I in VSMCs proliferation and migration, lipid peroxidation and subsequent inflammatory responses might contribute to the anti-atherosclerotic property of AO-I.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Atractylenolide I; Inflammation; Migration; Proliferation; Vascular smooth muscle cells.
Pharm Biol. 2015 Apr 8:1-5.
The protective effect of atractylenolide I on systemic inflammation in the mouse model of sepsis created by cecal ligation and puncture.[Pubmed:
25853971]
Atractylenolide I (AT-I), an active compound isolated from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz (Compositae), shows several pharmacological activities. Our present study is designed to investigate the protective effect of Atractylenolide I on systemic inflammation in the mouse model of sepsis created by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), and explore the possible mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sepsis mouse model was established by CLP, and the tested dosages of Atractylenolide I were 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg (ip). Pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) were determined by the ELISA method; serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) level was measured by the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) test; white blood cells (WBC) were counted by Blood cell analyzer; contents of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transarninase (AST), creatinine (Cre), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum were determined by automatic biochemistry analyzer. For survival rate tests, CLP mice were observed within 7 days, and body temperature was measured at 0, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h after surgery. Our results indicated that Atractylenolide I significantly increased the survival rate of mice with sepsis (p < 0.05), whereas the WBCs and levels of LPS, pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6), ALT, AST, Cre, and BUN decreased significantly after treatment with Atractylenolide I (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, the Atractylenolide I ameliorates sepsis syndrome by reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and LPS, and provides an improvement in liver and kidney functions.
Exp Ther Med . 2018 Feb;15(2):1574-1579.
Anti-depressant-like effect of atractylenolide I in a mouse model of depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress[Pubmed:
29434743]
Abstract
Atractylenolide I (AT-I), a major component of the rhizoma of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., exerts a wide range of activities. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the anti-depressant-like effect of AT-I in a mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS), and to explore the possible molecular mechanism involved. It was revealed that AT-I significantly ameliorated CUMS-induced depressive-like behaviors, as evidenced by increased sucrose preference as well as shortened immobility time in the forced swimming and the tail suspension test. In addition, AT-I reduced CUMS-induced decreases in the concentrations of serotonin and norepinephrine in the hippocampus. Furthermore, AT-I inhibited the activation of the nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome as well as the concentration of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β in the hippocampi of mice subjected to CUMS. In conclusion, the results of the present study suggested that AT-I exerts anti-depressant-like effects in a CUMS-induced model of depression in mice, the molecular mechanism of which is associated with the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation to decrease IL-1β production.
Keywords: Atractylenolide I; depression; inflammation; interleukin-1β; nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome.
Molecules. 2013 Oct 29;18(11):13357-68.
Anti-tumor effects of atractylenolide I isolated from Atractylodes macrocephala in human lung carcinoma cell lines.[Pubmed:
24172243]
Atractylenolide I (ATL-1) is the major sesquiterpenoid of Atractylodes macrocephala. This study was designed to investigate whether Atractylenolide I induced apoptosis in A549 and HCC827 cells in vitro and in vivo.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In our results, Atractylenolide I significantly decreased the percentage of in vitro viability, in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, DAPI staining and flow cytometry tests demonstrated the induction of apoptosis by Atractylenolide I. Western blot analysis indicated that the protein levels of caspase-3, caspase-9 and Bax were increased in A549 and HCC827 cells after Atractylenolide I exposure; to the contrary, the expressions of Bcl-2, Bcl-XL were decreased after treatment with Atractylenolide I. In the in vivo study, Atractylenolide I effectively suppressed tumor growth (A549) in transplanted tumor nude mice with up-regulation of caspase-3, caspase-9, and Bax and down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, our results demonstrated that Atractylenolide I has significant antitumor activity in lung carcinoma cells, and the possible mechanism of action may be related to apoptosis induced by Atractylenolide I via a mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2006 Aug;44(8):1308-15.
Pro-oxidant and cytotoxic activities of atractylenolide I in human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells.[Pubmed:
16624472 ]
The dried rhizome of Bai Zhu (Atractylodes ovata) is widely used as a Chinese herbal medicine. Two sesquiterpenolides of similar structures (Atractylenolide I, AT-I; Atractylenolide III, AT-III) were isolated from dried rhizome of Atractylodes ovata.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Incubation of AT-I with recombinant human Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase (rhCu,Zn-SOD) resulted in rhCu,Zn-SOD fragmentations and Zn releases. However, these were not observed in the AT-III reaction. The AT-1 showed dose-dependent cytotoxic activities (7.5, 15, and 30 microg/ml) on the human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells while AT-III did not, and the IC50 of the former being 10.6 microg/ml (corresponding to 46 microM) on 12 h-treated cells. The results of DNA ladder and DNA contents in sub-G1 type revealed that AT-I induced apoptosis in human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells. The cytotoxic and pharmacological mechanisms of AT-I against human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells was investigated. The AT-I appeared to exhibit both pro-oxidant and antioxidant properties after an ESR spectrometer was used to detect hydroxyl radical productions in vitro and flow cytometry to detect intracellular ROS productions in AT-I treated cells. The AT-1 also showed dose-dependent Cu,Zn-SOD inhibitory activity in HL-60 cells treated for 12 h, confirmed by activity and immune stainings. However, catalase, Mn-SOD, and glutathione peroxidase did not apparently change activities under the same treatments. The addition of commercial rhCu,Zn-SOD (25-100 U/mL) to the AT-I-treated HL-60 cells (15 microg/ml) resulted in significant differences (p<0.01) and could reduce the AT-I cytotoxicity from 78% to 28% on HL-60 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
It was proposed that the AT-I might work via Cu,Zn-SOD inhibition in HL-60 cells to induce apoptosis and bring about cytotoxicity.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 10;612(1-3):143-52.
Inhibitory effect of atractylenolide I on angiogenesis in chronic inflammation in vivo and in vitro.[Pubmed:
19356732]
Angiogenesis is involved in the pathology of chronic inflammatory diseases. Application of anti-angiogenic strategies is beneficial in the treatment of inflammatory disorders. Atractylenolide I is an anti-inflammation agent.
CONCLUSIONS:
To further investigate the anti-angiogenesis mechanism of Atractylenolide I in cell and mice based on inflammation model, the vascular index and microvessel outgrowth were measured by using the Freunds complete adjuvant (FCA) induced mouse air pouch model as well as the mice aortic ring co-cultured with peritoneal macrophages model. The ID 50 values of Atractylenolide I were 15.15mg/kg and 3.89μg/ml for inhibiting the vascular index in vivo and microvessel outgrowth in vitro , respectively. Atractylenolide I could dose-dependently inhibit the production of nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and placenta growth factor (PlGF) activity in the flute of mouse air pouch and the peritoneal macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
CONCLUSIONS:
Atractylenolide I displayed a potent inhibitory effect on angiogenesis by a set of down-regulatory actions of NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, VEGF and PlGF in chronic inflammation..