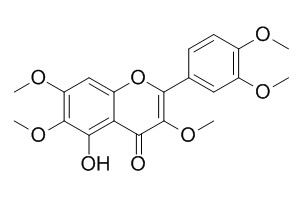
Artemetin
Artemetin has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antiapoptotic activities, it protects endothelial function through the activation of ERK1/2 and Akt. Intravenous injection of Artemetin (0.75 mg/kg) significantly reduces the hypertensive response to angiotensin I while increases the average length of bradykinin-induced hypotension.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Fitoterapia.2022, 157:105130.
Onco Targets Ther.2017, 10:3467-3474
Nutrients.2019, 11(11):E2694
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176800.
Biomolecules.2023, 13(2):227.
Int Immunopharmacol.2024, 143(Pt 2):113486.
Antiviral Res.2013, 98(3):386-93
Mol Biol Rep.2024, 51(1):117.
Molecules.2020, 25(3):734
Applied Physics B2021, 127(92).
Related and Featured Products
Phytother Res. 2015 May 29.
Effects of Artemetin on Nitric Oxide Release and Protection against Peroxidative Injuries in Porcine Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells.[Pubmed:
26032176]
Artemetin is one of the main components of Achillea millefolium L. and Artemisia absinthium, which have long been used for the treatment of various diseases. To date, however, available information about protective effects of their extracts on the cardiovascular system is scarce.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Therefore, we planned to analyze the effects of Artemetin on nitric oxide (NO) release and the protection exerted against oxidation in porcine aortic endothelial (PAE) cells. In PAE, we examined the modulation of NO release caused by Artemetin and the involvement of muscarinic receptors, β2-adrenoreceptors, estrogenic receptors (ER), protein-kinase A, phospholipase-C, endothelial-NO-synthase (eNOS), Akt, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK). Moreover, in cells treated with hydrogen peroxide, the effects of Artemetin were examined on cell survival, glutathione (GSH) levels, apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential and transition pore opening. Artemetin increased eNOS-dependent NO production by the involvement of muscarinic receptors, β2-adrenoreceptors, ER and all the aforementioned kinases. Furthermore, Artemetin improved cell viability in PAE that were subjected to peroxidation by counteracting GSH depletion and apoptosis and through the modulation of mitochondrial function.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Artemetin protected endothelial function by acting as antioxidant and antiapoptotic agent and through the activation of ERK1/2 and Akt.
Planta Med. 1990 Feb;56(1):36-40.
Anti-inflammatory activity and sub-acute toxicity of artemetin.[Pubmed:
2356241]
The 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,3',4'-pentamethoxyflavone (Artemetin) from Cordia verbenacea DC (Boraginaceae) showed marked anti-inflammatory activity using various experimental models in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Artemetin significantly inhibited carrageenin-induced paw edema following oral doses from 30.4 to 153.9 mg.kg-1. The doses of 102.6 and 153.9 mg.kg-1 showed an inhibitory effect similar to that of 50.0 mg.kg-1 of calcium phenylbutazone. The ED50 value of Artemetin in rats was estimated to be 67.07 mg.kg-1. Repeated administration of Artemetin at doses of 67.07 mg.kg-1 for a 6-day period reduced granuloma formation with a response comparable to that of 20.0 mg.kg-1 of calcium phenylbutazone. This same dose of Artemetin also reduced the vascular permeability to intracutaneous histamine. Sub-acute toxicological experiments indicated a very low toxicity.
Biomed Chromatogr . 2018 Dec;32(12):e4356.
Development of an LC-MS/MS-based assay to determine artemitin in rat plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study[Pubmed:
30073671]
Abstract
Artemitin, a significant flavonol compound existing in Laggera pterodonta (DC.) Benth., Artemisia rupestris L, etc., is the subject of attention by researchers owing to its pharmacological activities (such as antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and antiviral). In this work, a highly sensitive and specific high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS) assay combined with protein precipitation has been established and validated for determining artemitin concentration in rat plasma. Both artemitin and warfarin sodium (internal standard, IS) were separated on an Agela Venusil XBP Phenyl column through the isocratic elution mode of methanol-water containing 0.1% formic acid (80:20, v/v), at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. The MS/MS system was operated in a positive ion and ESI multiple reaction monitoring mode, and the multiple reaction monitoring transition was optimized as m/z 389.0 → 373.0 for artemitin and 309.2 → 163.0 for IS. The method showed good linearity in the range of 2.5-2000 ng/mL (R2 = 1.0000) and high sensitivity for artemitin with the lower limit of quantification of 2.5 ng/mL. The intra- and inter-day accuracies were 97.4-100.9 and 93.4-100.3%, respectively. The intra- and inter-day precisions were <4.8 and 6.5%, respectively. The extraction efficiency and absolute recovery were >66.5 and 71.3%, respectively. In addition, a good matrix effect of <9.5% was obtained. As a result, the method developed herein was successfully applied for the pharmacokinetic study of artemitin after an intravenous administration in rats.
Keywords: HPLC-ESI-MS/MS; artemitin; pharmacokinetics; rat plasma.
Phytomedicine. 2011 Jul 15;18(10):819-25.
Hypotensive mechanism of the extracts and artemetin isolated from Achillea millefolium L. (Asteraceae) in rats.[Pubmed:
21420289 ]
Traditional uses of Achillea millefolium L. (Asteraceae) include the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we used anesthetized rats to assess the hypotensive effect of a hydroethanolic extract (HEAM), and its dichloromethane (DCM), ethyl acetate (EA), butanolic (BT), and dichloromethane-2 (DCM-2) fractions, besides the flavonoid Artemetin, isolated from A. millefolium. The oral administration of HEAM (100-300 mg/kg), DCM (20mg/kg), DCM-2 (10-30 mg/kg), but not EA (10 mg/kg) and BT (50 mg/kg) fractions significantly reduced the mean arterial pressure (MAP) of normotensive rats. The phytochemical analysis by NMR (1)H of DCM and DCM-2 fractions revealed high amounts of Artemetin, that was isolated and administered by either oral (1.5 mg/kg) or intravenous (0.15-1.5 mg/kg) routes in rats. This flavonoid was able to dose-dependently reduce the MAP, up to 11.47 ± 1.5 mmHg (1.5 mg/kg, i.v.). To investigate if Artemetin-induced hypotension was related to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition, we evaluated the influence of this flavonoid on the vascular effects of both angiotensin I and bradykinin. Intravenous injection of Artemetin (0.75 mg/kg) significantly reduced the hypertensive response to angiotensin I while increased the average length of bradykinin-induced hypotension. Artemetin (1.5 mg/kg, p.o.) was also able to reduce plasma (about 37%) and vascular (up to 63%) ACE activity in vitro, compared to control group. On the other hand, Artemetin did not change angiotensin II-induced hypertension.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our study is the first showing the hypotensive effects induced by the extract and fractions obtained from A. millefollium. In addition, our results disclosed that this effect may be, at least in part, associated with high levels of Artemetin and its ability to decrease angiotensin II generation in vivo, by ACE inhibition.