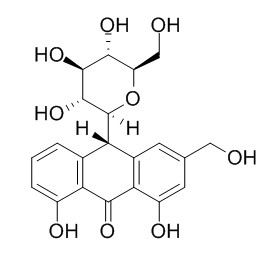
Aloin A
Plants containing aloin A, aloe emodin, and structurally related anthraquinones have long been used as traditional medicines and in the formulation of retail products such as laxatives, dietary supplements, and cosmetics; however, topically applied aloe emodin increases the sensitivity of skin to UV light, although aloin A is not directly photocytotoxic, but human skin fibroblasts can metabolize aloin A to aloe emodin. Aloin A and aloe emodin have antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Indian J Pharm Sci.2022, 84(4): 874-882.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(8):1300.
Nutrients.2024, 16(16):2612.
ACS Food Sci. Technol.2023, 3(2):273-282.
Hum. Ecol. Res.2025, 63(2):165-174
Phytother Res.2019, 33(3):676-689
JAOCS2021, 98(7):779-794.
Dental Journal2024, 57(4): 254-258
Sci Rep.2019, 9(1):18080
Plant Physiol Biochem.2023, 203:108073.
Related and Featured Products
Free Radic Biol Med. 2003 Jan 15;34(2):233-42.
In vitro studies on the photobiological properties of aloe emodin and aloin A.[Pubmed:
12521605]
Plants containing Aloin A, aloe emodin, and structurally related anthraquinones have long been used as traditional medicines and in the formulation of retail products such as laxatives, dietary supplements, and cosmetics.
Since a recent study indicated that topically applied aloe emodin increases the sensitivity of skin to UV light, we examined the events following photoexcitation of Aloin A and aloe emodin.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We determined that incubation of human skin fibroblasts with 20 microM aloe emodin for 18 h followed by irradiation with UV or visible light resulted in significant photocytotoxicity. This photocytotoxicity was accompanied by oxidative damage in both cellular DNA and RNA. In contrast, no photocytotoxicity was observed following incubation with up to 500 microM Aloin A and irradiation with UVA light. In an attempt to explain the different photobiological properties of Aloin A and aloe emodin, laser flash photolysis experiments were performed. We determined that the triplet state of aloe emodin was readily formed following photoexcitation. However, no transient intermediates were formed following photoexcitation of Aloin A. Therefore, generation of reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage after irradiation of Aloin A is unlikely.
CONCLUSIONS:
Although Aloin A was not directly photocytotoxic, we found that human skin fibroblasts can metabolize Aloin A to aloe emodin.
Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Jul;9(7):949-52.
A new antimicrobial anthrone from the leaf latex of Aloe trichosantha.[Pubmed:
25230501]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Phytochemical investigation of the leaf latex of Aloe trichosantha by preparative TLC gave two closely related anthrones, Aloin A/B (1) and aloin-6'-O-acetate A/B (2). The identity of the compounds was established from HRESI-MS, 1H, 13C, DEPT, HMQC and HMBC spectral and chemical data. Whilst Aloin A/B occurs in several Aloe species, aloin-6'-O-acetate A/B was isolated for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
The isolated compounds inhibited growth of several bacterial and fungal pathogens with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) from 10 to 400 microg/mL and 800 to 1000 microg/mL, respectively.
J AOAC Int. 2014 Sep-Oct;97(5):1323-8.
Determination of Aloin A and Aloin B in Aloe vera Raw Materials and Finished Products by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Single-Laboratory Validation.[Pubmed:
25902982]
A single-laboratory validation (SLV) was conducted on an HPLC method for the detection and quantification of Aloin A and aloin B in Aloe vera raw materials and finished products.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
An extraction procedure using sonication with an acidified solvent was used for solid test materials while liquid test materials only required dilution, if necessary, prior to filtration and analysis. Separation was achieved using a fused core C18 column in 18 min under isocratic elution conditions allowing for a single analyte (Aloin A) calibration curve to quantify both aloins. Adequate chromatographic resolution (Rs ≥ 1) was achieved for Aloin A and aloin B. The calibration curves for Aloin A exhibited coefficients of determination (r(2)) of ≥ 99.9% over the linear range of 0.3-50 μg/mL. The LOD values were 0.092 and 0.087 μg/mL, and LOQ 0.23 and 0.21 μg/mL for Aloin A and aloin B, respectively. Repeatability studies were performed on nine test materials on each of 3 separate days, with five of the test materials determined to be above the LOQ having repeatability RSD (RSDr) values ranging from 0.61 to 6.30%. Method accuracy was determined through a spike recovery study on both liquid and solid matrixes at three different levels: low, medium, and high.
For both aloins, the recovery in the liquid matrix ranged from 92.7 to 106.3% with an RSDr of 0.15 to 4.30%, while for the solid matrix, the recovery ranged from 84.4 to 108.9% with an RSDr of 0.23 to 3.84%.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on the results of the SLV study, it is recommended that this method be evaluated for reproducibility through a collaborative study.