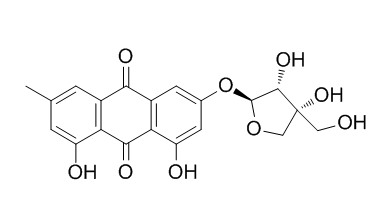
Frangulin B
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food and Fermentation Industries2018, 44(371)
Anticancer Res.2021, 41(3):1357-1364.
J Med Food.2022, 25(3):272-280.
Preprints2017, 2017120176
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(10):5468.
Plant Commun.2024, 5(10):101005.
ACS Synth Biol.2022, doi: 10.1021.
Cell Death Discov.2023, 9(1):350.
Molecules.2024, 29(5):1050.
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025, 417(17):3879-3892.
Related and Featured Products
Journal of Natural Products, 2014, 77(3):489-496.
Validated method for the analysis of frangulins A and B and glucofrangulins A and B using HPLC and UHPLC.[Reference:
WebLink]
In the present study, robust and validated HPLC and UHPLC methods for the quantitative determination of frangulin A and Frangulin B (3 and 4) and glucofrangulins A and B (1 and 2) in the bark of Frangula alnus have been developed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The HPLC method allowed the separation of the analytes in 25 min and the UHPLC method in just 13 min. The HPLC method used an MN Nucleodur C18 125 × 4 mm column with 3 μm particles, while the UHPLC method used a Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18, 100 × 2.1 mm column with 1.7 μm particles. Mobile phase A consisted of water and 1.25 mL/L phosphoric acid (85%), while mobile phase B consisted of CH3CN/MeOH (20:80). The flow rates were set to 1 mL/min for the HPLC method and 0.4 mL/min for the UHPLC method, with the column temperature held at 50 °C and the detection wavelength being 435 nm for either method. A fractional factorial design was used to check the robustness of the methods.
CONCLUSIONS:
The resolution of the analytes was never less than 1.5 when the factors were varied in the tested range. The conditions for ultrasonic extraction were optimized by response surface methodology and found to be 68% CH3CN in the extraction solvent, 35 °C extraction temperature, and a duration of 25 min. The extraction procedure was determined to be very robust against small deviations of these factors.