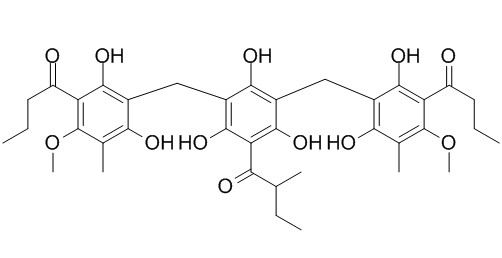
Agrimol B
Agrimol B has antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas syringae pv. lacrymans (bacterial leaf spot pathogen), Ralstonia solanacearum (tomato bacterial wilt pathogen) and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci (Tobacco wild fire pathogen). Agrimol B has a therapeutic potential on alleviating obesity, through modulation of SIRT1-PPARγ signal pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2018, 1080:27-36
ACS Pharmacol.Transl.Sci.2024, 4c00003.
Biol Pharm Bull.2021, 44(12):1891-1893.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2017, 2017:7383104
Cell Signal.2024, 124:111467.
Babol University of Medical Sciences2024, rs-4289336
Agriculture.2022, 12(3), 342.
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2360.
Phytomedicine2022, 104:154337.
Int Immunopharmacol.2024, 143(Pt 2):113486.
Related and Featured Products
The Korean Journal of Pesticide Science,2006, 10(3):230-6.
Antibacterial Activities against Plant Pathogens and Identification of Agrimol B from Agrimonia pilosa LEDEB.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eighty-five percent methanol extract of Agrimonia pilosa has antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas syringae pv. lacrymans (bacterial leaf spot pathogen), Ralstonia solanacearum (tomato bacterial wilt pathogen) and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci (Tobacco wild fire pathogen.). The active substance was purified by silica gel column chromatography and HPLC. The molecular weight of the active compound was determined by LC-Mass as 687.2.
CONCLUSIONS:
With NMR analysis, the active substance was identified as Agrimol B.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2016 Aug 26;477(3):454-60.
Agrimol B suppresses adipogenesis through modulation of SIRT1-PPAR gamma signal pathway[Pubmed:
27320865]
Abstract
Studies of human genetics have implicated the role of SIRT1 in regulating obesity, insulin resistance, and longevity. These researches motivated the identification of novel SIRT1 activators. The current study aimed to investigate the potential efficacy of Agrimol B, a polyphenol derived from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb., on mediating SIRT1 activity and fat metabolism. Results showed that Agrimol B significantly induced cytoplasm-to-nucleus shuttle of SIRT1. Furthermore, we confirmed that Agrimol B dramatically inhibited 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation by reducing PPARγ, C/EBPα, FAS, UCP-1, and apoE expression. Consequently, adipogenesis was blocked by treatment of Agrimol B at the early stage of differentiation in a dose-dependent manner, the IC50 value was determined as 3.35 ± 0.32 μM. Taken together, our data suggest a therapeutic potential of Agrimol B on alleviating obesity, through modulation of SIRT1-PPARγ signal pathway.
Keywords: Agrimol B; Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.; Lipid droplet; Obesity; PPARγ; SIRT1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Aug 26;477(3):454-60.
Agrimol B suppresses adipogenesis through modulation of SIRT1-PPAR gamma signal pathway.[Pubmed:
27320865]
Studies of human genetics have implicated the role of SIRT1 in regulating obesity, insulin resistance, and longevity. These researches motivated the identification of novel SIRT1 activators.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The current study aimed to investigate the potential efficacy of Agrimol B, a polyphenol derived from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb., on mediating SIRT1 activity and fat metabolism. Results showed that Agrimol B significantly induced cytoplasm-to-nucleus shuttle of SIRT1. Furthermore, we confirmed that Agrimol B dramatically inhibited 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation by reducing PPARγ, C/EBPα, FAS, UCP-1, and apoE expression. Consequently, adipogenesis was blocked by treatment of Agrimol B at the early stage of differentiation in a dose-dependent manner, the IC50 value was determined as 3.35 ± 0.32 μM.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data suggest a therapeutic potential of Agrimol B on alleviating obesity, through modulation of SIRT1-PPARγ signal pathway.
Biomed Chromatogr. 2015 Apr;29(4):481-4.
Development of a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for determination of agrimol B in rat plasma: application to preclinical pharmacokinetics.[Pubmed:
25065576]
A sensitive and accurate liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) method was developed for the determination of Agrimol B, a main active ingredient isolated from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb., in rat plasma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Chromatographic separation was achieved on a Zorbax CN column (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm), with isocratic elution consisting of acetonitrile and water (15:85, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. Agrimol B and dryocrassin ABBA, an internal standard (IS), were analyzed by selected ion monitoring at m/z transitions of 681.3 and 819.4, respectively. This assay exhibited a good linearity with a correlation coefficient >0.99 and showed no endogenous interference with the analyte and IS. The limit of quantification of Agrimol B was 8.025 ng/mL with acceptable precision and accuracy. The method was successfully applied in the pharmacokinetic study of Agrimol B in rats after intravenous (1 mg/kg) and oral (2, 5 and 10 mg/kg) doses of Agrimol B. The absolute bioavailability of Agrimol B was 16.4-18.0% in rat.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our study clarifies the pharmacokinetic behavior of Agrimol B in animals.