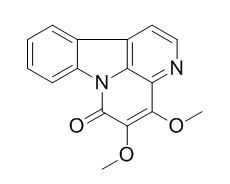
4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one has antibacterial actiyity, it exhibits inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and its drug-resistant strains. 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one has a strong inhibitory effect on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase. It also shows cytotoxicity against the tumor cell lines, U937 and HepG2.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Medicinal Chemistry Research 2021, 30:1117-1124.
Purinergic Signal.2024, doi: 10.1007.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 176:116765.
Molecules. 2013, 18(7):7376-88
Molecules.2023, 28(3):958.
JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography2023, 36:179-190
Sci Rep.2024, 14(1):23786.
Research SPJ.2024, 0377.
Foods.2023, 12(12):2412.
Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(1),14.
Related and Featured Products
J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem.,2009, 52(6):663-7.
Cytotoxic alkaloids from the wood of Picrasma quassioides.[Reference:
WebLink]
Six alkaloid compounds were isolated from the chloroform soluble fraction of the methanolic extract of the wood of Picrasma quassioides Benn (Simarobaceae) as the cytotoxic components against the tumor cell lines, U937 and HepG2.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were identified as 4,9-dimethoxy-1-vinyl-γ-carboline (1), 1-carbomethoxy-β-carboline (2), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (3), 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one (4), 3-methoxycanthin-5,6-dione (5) and 4,8-dimethoxy-1-vinyl-β-carboline (6) by spectroscopic analysis. Among them, compound 5 showed the most potent cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner against the two tumor cell lines.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of the cytotoxic effect of those isolated compounds 1-5 on U937 and HepG2 cell lines.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1984 May;32(5):1872-7.
Inhibitors of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Picrasma quassioides Bennet, and inhibitory activities of related .BETA.-carboline alkaloids.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) phosphodiesterase inhibitors present in Picrasma quassioides BENN. were identified as 1-methoxycarbonyl-β-carboline, 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one and 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one. The structure-inhibitory activity relationships were studied in 31 derivatives of β-carboline, 2 dimeric derivatives of β-carboline and 12 derivatives of canthin-6-one.
CONCLUSIONS:
β-Carboline derivatives with a methoxycarbonyl group and canthin-6-one derivatives with a methoxyl group generally had a strong inhibitory effect on cAMP phosphodiesterase.
Yao Xue Xue Bao,1979, 14(3):167-77.
Chemical investigation of the alkaloids of Ku-Mu [Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn.[Reference:
WebLink]
Some preparation of the total alkaloids of Ku-Mu (Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn.) was Shown to have antibacterial actiyity in clinical trial. For the exploration of the active principles, the present paper deals with the studies of the alkaloids of this medicinal plant.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From an alcohol extract of heartwood of Ku-Mu seven alkaloids were isolated through silica gel and alumina column chromatography as well as preparative thin layer chromatography. Beside the known alkaloids 1-carbomethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅱ), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (Ⅳ), canthin-6-one (Ⅴ), and 4-methoxy-5-hydroxycanthin-6-one (Ⅵ), three new alkaloids, named Kumujian A, Kumujian G, and Kumujian G, were ident fied as 1-carboethoxy-β-carbotine (Ⅰ), 1-formyl-β-carboline(Ⅲ) and 1-vinyl-4,8-dimethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅶ), respectively. In vitro screening of the above alkaloids demonstrated that 1-carbomethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅱ), 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one (Ⅳ), 4-methoxy-5-hydroxycanthin-6-one (Ⅵ) and 1-vinyl-4,8-dimethoxy-β-carboline (Ⅶ) exhibited inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus and its drug-resistant strains.
CONCLUSIONS:
Tests for the antibacterial activity of three other alkaloids were hampered by scarcity of material.
Journal of Chromatography B,2015, 986–987,(1):100–7.
Simultaneous quantification of two canthinone alkaloids of Picrasma quassioides in rat plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a rat pharmacokinetic study[Reference:
WebLink]
Picrasma quassioides (D. Don) Benn. is used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of inflammation. Characteristic components of the medicinal extract are canthinone alkaloids.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, a sensitive and rapid liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed for simultaneous quantification of two major canthinone alkaloids, 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one and 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one, in rat plasma after oral administration of P. quassioides extract (200 mg/kg). The chromatographic separation was performed on a C18 column using acetonitrile–aqueous 0.1% formic acid (90:10, v/v) as the mobile phase. Plasma samples were prepared for analysis using a simple liquid–liquid extraction with ethyl acetate. Analytes were detected using tandem mass spectrometry in positive multiple reaction monitoring mode. Method validation revealed excellent linearity over the range 1.25–900 ng/mL for 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one and 0.5–800 ng/mL for 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one with satisfactory intra- and inter-day precision, accuracy and recovery. Samples were stable under the conditions tested.
CONCLUSIONS:
The pharmacokinetic profiles of the analytes in rats showed that both canthinones were rapidly absorbed and that 4,5-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one was eliminated faster than 5-hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one.