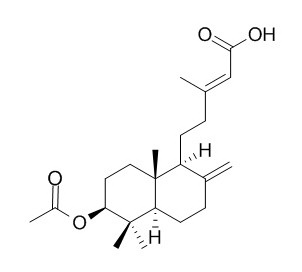
3-Acetoxy-8(17),13E-labdadien-15-oic acid
ent-3-Acetoxy-labda-8(17),13-dien-15-oic acid have vasorelaxant and hypotensive actions, the mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular actions of the labdane involve the activation of the endothelial NO-cGMP pathway, the opening of K+ channels and the alteration on Ca2+ mobilization.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.2021, 22(S1):97-106.
J Cell Biochem.2018, 119(2):2231-2239
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2017, 2017:7383104
Processes2021, 9(1), 153;
Molecules.2023, 28(13):4971.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2023, 210:115463.
Nat Prod Sci.2018, 24(2):109-114
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Biomol Ther (Seoul).2019, 10.4062
Foods.2022, 12(1):136.
Related and Featured Products
Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Mar 5;726:66-76.
Mechanisms underlying the vascular and hypotensive actions of the labdane ent-3-acetoxy-labda-8(17),13-dien-15-oic acid.[Pubmed:
24463178 ]
We investigated the mechanisms underlying the vasorelaxant and hypotensive actions of the labdane-type diterpene ent-3-acetoxy-labda-8(17),13-dien-15-oic acid (3-Acetoxy-8(17),13E-labdadien-15-oic acid,labda-15-oic acid).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Vascular reactivity experiments were performed in aortic rings isolated from male Wistar rats. cAMP and cGMP were measured by enzyme immunoassay (EIA) whereas nitrate measurement was performed by chemiluminescence. Nitric oxide (NO) concentration ([NO]c) was measured in endothelial cells by flow cytometry. The cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]c) in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) was measured by confocal microscopy. Blood pressure measurements were performed in conscious rats. Labda-15-oic acid inhibited the contraction induced by phenylephrine and serotonin in either endothelium-intact or endothelium-denuded rat aortic rings. The labdane significantly reduced CaCl2-induced contraction in a Ca2+-free solution containing KCl or phenylephrine. Labda-15-oic acid (0.1–300 μmol/l) concentration-dependently relaxed endothelium-intact and endothelium-denuded aortas pre-contracted with either phenylephrine or KCl. In endothelium-intact rings, the relaxation induced by labda-15-oic acid was affected by L-NAME, 7-nitroindazole, ODQ, hemoglobin, Rp-8-Br-Pet-cGMPS and thapsigargin. Blockade of K+ channels with 4-aminopyridine, apamin, charybdotoxin and glibenclamide affected the relaxation induced by labda-15-oic acid. The labdane increased cGMP and nitrate levels but did not affect cAMP levels in endothelium-intact aortas. Labda-15-oic acid increased [NO]c in endothelial cells and decreased [Ca2+]c in VSMC. The hypotension induced by intravenous administration of labda-15-oic acid (0.3–3 mg/kg) was partially reduced by L-NAME.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, the mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular actions of the labdane involve the activation of the endothelial NO-cGMP pathway, the opening of K+ channels and the alteration on Ca2+ mobilization.