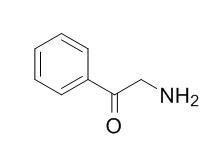
2'-Aminoacetophenone
A new route to oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drug, starting from commercially available 2'-aminoacetophenone and 1,2-dibromobenzene, is reported.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Phytomedicine.2024, 128:155527.
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed.2024, 40(1):e12950.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy.2020, 51(2):100-106
J Food Composition and Analysis2022, 104417.
Oncotarget.2017, 8(64):108006-108019
Food Chem.2020, 327:126992.
Industrial Crops and Products2024, 129:119014
Biomol Ther (Seoul).2019, 10.4062
Oncology Letters2018, 4690-4696
European Journal of Integrative Medicine2018, 20:165-172
Related and Featured Products
J Pharm Sci. 2009 Dec;98(12):4639-49.
Glycosylation of aromatic amines III: Mechanistic implications of the pH-dependent glycosylation of various aromatic amines (kynurenine, 2'-aminoacetophenone, daptomycin, and sulfamethoxzaole).[Pubmed:
19551894 ]
Glycosylation reaction kinetics of a series of aromatic amines (kynurenine, 2'-Aminoacetophenone, daptomycin, and sulfamethoxazole) was compared to propose a unifying reaction mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Kinetic studies were conducted in aqueous solutions containing glucose in the pH range 1-6.5 with 2'-Aminoacetophenone and daptomycin. The resultant pH-rate profiles were compared to previously reported profiles for the reactions of glucose and kynurenine or sulfamethoxazole. Glycosylation of weakly basic aromatic amines involved the addition of the unprotonated amine to the aldehydic sugar leading to carbinolamine formation followed by specific acid catalyzed dehydration. All of the pH-rate profiles displayed characteristic downward bend at pH 4-5 due to a change from rate-determining addition to dehydration. In the pH-rate profile for kynurenine, a second downward bend was observed in the pH region 2-4. This feature was absent for the other substrates and was attributed to differences in reactivity of the two ionization states of the alpha carboxylic acid in kynurenine. This stabilization was not possible for the other amines studied.
Org Lett. 2005 Oct 27;7(22):4787-9.
An advantageous route to oxcarbazepine (trileptal) based on palladium-catalyzed arylations free of transmetallating agents.[Pubmed:
16235889 ]
A new route to oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drug, starting from commercially available 2'-Aminoacetophenone and 1,2-dibromobenzene, is reported.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The sequentially accomplished key steps are palladium-catalyzed intermolecular alpha-arylation of ketone enolates and intramolecular N-arylation reactions. After several experiments to establish the best conditions for both arylation processes, the target oxcarbazepine is obtained in a satisfactory overall yield, minimizing the number of steps and employing scalable catalytic procedures developed in partially aqueous media.
Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2005 Apr;4(4):367-75.
Intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen-bonding effects on photophysical properties of 2'-aminoacetophenone and its derivatives in solution.[Pubmed:
15803207]
Effects of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen-bonds on the photophysical properties of 2'-Aminoacetophenone derivatives (X-C6H4-COCH3) having a substituted amino group (X) with different hydrogen-bonding ability to the carbonyl oxygen (X: NH2(AAP), NHCH3(MAAP), N(CH3)2(DMAAP), NHCOCH3(AAAP), NHCOCF3(TFAAP)) are investigated by means of steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy and time-resolved thermal lensing.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Based on the photophysical parameters obtained in aprotic solvents with different polarity and protic solvents with different hydrogen-bonding ability, the characteristic photophysical behavior of the 2'-Aminoacetophenone derivatives is discussed in terms of hydrogen-bonding and n,pi*-pi,pi* vibronic coupling. The dominant deactivation process of AAP and MAAP in nonpolar aprotic solvents is the extremely fast internal conversion (k(ic)= 1.0 x 10(11) s(-1) for AAP and 3.9 x 10(10) s(-1) for MAAP in n-hexane). The internal conversion rates of both compounds decrease markedly with increasing solvent polarity, suggesting that vibronic interactions between close-lying S1(pi,pi*) and S2(n,pi*) states lead to the large increase in the non-radiative decay rate of the lowest excited singlet state. It is also suggested that for MAAP, which has a stronger hydrogen-bond as compared to AAP, an intramolecular hydrogen-bonding induced deactivation is involved in the dissipation of the S1 state.
CONCLUSIONS:
For DMAAP, which cannot possess an intramolecular hydrogen-bond, the primary relaxation mechanism of the S1 state in nonpolar aprotic solvents is the intersystem crossing to the triplet state, whereas in protic solvents very efficient internal conversion due to intermolecular hydrogen-bonding is induced. In contrast, the fluorescence spectra of AAAP and TFAAP, which have an amino group with a much stronger hydrogen-bonding ability, give strongly Stokes-shifted fluorescence, indicating that these compounds undergo excited-state intramolecular proton transfer reaction upon electronic excitation.