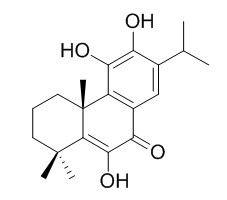
14-Deoxycoleon U
14-Deoxycoleon U has anti-termitic activity, it is highly active against both wood-decay fungi. 14-Deoxycoleon U shows antibacterial activity against the Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, and Micrococcus luteus.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Control2022, 132:108434.
Am J Chin Med.2022, 1-20.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).2019, 67(11):1242-1247
ACS Synth Biol.2022, 11(10):3296-3304.
Patanjali Research Foundation2024, ssrn.4807357
Molecules.2023, 28(13):4907.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(19):10405.
Cells.2021, 10(11):2919.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(15):8687.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2018, 18(1):303
Related and Featured Products
11-Hydroxy-sugiol
Catalog No: CFN90366
CAS No: 88664-08-8
Price: $490/5mg
Salvinolone
Catalog No: CFN92243
CAS No: 120278-22-0
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
14-Deoxycoleon U
Catalog No: CFN97924
CAS No: 88664-09-9
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
6,11,12,16-Tetrahydroxy-5,8,11,13-abitetetraen-7-one
Catalog No: CFN88024
CAS No: 1295650-67-7
Price: $318/5mg
20-Deoxocarnosol
Catalog No: CFN92175
CAS No: 94529-97-2
Price: $413/5mg
2,11,12-Trihydroxy-7,20-epoxy-8,11,13-abietatriene
Catalog No: CFN95428
CAS No: 1608462-12-9
Price: $318/10mg
6-Epidemethylesquirolin D
Catalog No: CFN99695
CAS No: 165074-00-0
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Carnosol
Catalog No: CFN99956
CAS No: 5957-80-2
Price: $80/20mg
Isorosmanol
Catalog No: CFN93009
CAS No: 93780-80-4
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Rosmanol
Catalog No: CFN93024
CAS No: 80225-53-2
Price: $298/10mg
J Chem Ecol. 2010 Dec;36(12):1381-6.
Antifungal abietane-type diterpenes from the cones of Taxodium distichum Rich.[Pubmed:
21072573]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The chemical composition of Taxodium distichum cones and the antifungal activities of twelve diterpenoids against two wood decay fungi, Trametes versicolor (white-rot) and Fomitopsis palustris (brown-rot) were examined. The chemical composition of the major extractive fraction, the n-C(6)H(14) extract, was evaluated and its antifungal properties were identified. Twelve diterpenoids including ten abietane-type components were isolated from the n-C(6)H(14) extract: 6,7-dehydroferruginol (1), ferruginol (2), 6,7-dehydroroyleanone (3), sandaracopimaric acid (4), taxodione (5), taxodal (6), taxodone (7), sugiol (8), xanthoperol (9), salvinolone (10), 5,6-dehydrosugiol (11), and 14-Deoxycoleon U (12). Compounds 5 and 14-Deoxycoleon U were highly active against both wood-decay fungi. In particular, the activities of these compounds against F. palustris were potent.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that the position and the number of hydroxyl groups on abietane-type structures may be related to antifungal activities against T. versicolor and F. palustris.
J Chem Ecol. 2009 Jun;35(6):635-42.
Antitermitic activities of abietane-type diterpenes from Taxodium distichum cones.[Pubmed:
19475449 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eight known abietane-type diterpenes were isolated from the weak acidic fraction of the n-hexane extract from cones of Taxodium distichum, one of the extant, living fossil conifers. They were identified as 6,7-dehydroroyleanone (1), taxodal (2), taxodione (3), salvinolone (4), 14-Deoxycoleon U (5), 5,6-dehydrosugiol (6), sandaracopimaric acid (7), and xanthoperol (8). The structures of these compounds were determined by comparison of NMR spectral data with published data. The antitermitic (termicidal and antifeedant) activities of the compounds 1-8 against the subterranean termite, Reticulitermes speratus Kolbe, were evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1 and 3 showed potent termicidal activity, and 5 and 8 showed potent antifeedant activity. Compound 1 was found to be one of the representative bioactive compounds in the n-hexane extract of T. distichum cones. Compounds 1-8, with the exception of 7, were oxides of ferruginol (9). Therefore, the presence of various oxidation forms of the abietane-type structure reflects their various bioactivities.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jun 15;25(12):2555-8.
An antibacterial ortho-quinone diterpenoid and its derivatives from Caryopteris mongolica.[Pubmed:
25958242]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To identify antibacterial components in traditional Mongolian medicinal plant Caryopteris mongolica, an ortho-quinone abietane caryopteron A (1) and three its derivatives caryopteron B-D (2-4) were isolated from the roots of the plant together with three known abietanes demethylcryptojaponol (5), 6α-hydroxydemethyl cryptojaponol (6), and 14-Deoxycoleon U (7). The chemical structures of these abietane derivatives were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data. Compounds 1-4 had C-13 methylcyclopropane substructures, and 2-4 had a hexanedioic anhydride ring C instead of ortho-quinone in 1. The stereochemistry of these compound was assumed from NOE spectra and ECD Cotton effects.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1 and 5-7 showed antibacterial activities against the Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, and Micrococcus luteus, being 1 the more potent.