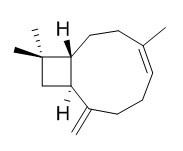
trans-Caryophyllene
trans-Caryophyllene, a PPAR-α agonist, which has neuroprotective effects in various neurological disorders, such as chemical induced seizure and brain damage. trans-Caryophyllene suppresses the hypoxia-induced neuroinflammatory response through inhibition of NF-κB activation in microglia.trans-Caryophyllene also reduces both acute and chronic pain in mice, which may be mediated through the opioid and endocannabinoid systems.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Journal of Functional Foods2022, 99: 105331.
Pharm Biol.2016, 54(7):1255-62
Life Sci.2023, 332:122107.
J Pharmacol Sci.2021, 147(2):184-191.
University of Guelph2021, 12.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 981:176883.
Biotechnol Bioeng.2020, 117(7):2198-2208.
PLoS One.2021, 16(9):e0257243.
Biomedicines.2020, 8(11):486.
Molecules.2020, 25(23):5636.
Related and Featured Products
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 21;444(4):451-4.
A role for trans-caryophyllene in the moderation of insulin secretion.[Pubmed:
24486541]
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) is essential for the control of metabolic fuel homeostasis and its impairment is a key element in the failure of β-cells in type 2 diabetes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
trans-Caryophyllene (TC), an important constituent of the essential oil of several species of plants, has been reported to activate the type 2 cannabinoid receptor (CB2R). The effects of TC on GSIS are still unknown. Our results demonstrate that administration of TC in MIN6 cells promotes GSIS in a dose dependent manner. However, inhibition of CB2R by a specific inhibitor or specific RNA interference abolished the effects of TC on GSIS, which suggests that the effects of TC on GSIS are dependent on activation of CB2R. Further study demonstrated that treatment with TC leads to the activation of small G protein Arf6 as well as Rac1 and Cdc42. Importantly, Arf6 silencing abolished the effects of TC on GSIS, which suggests that Arf6 participates in mediating the effects of TC on GSIS.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude from these data that TC has a novel role in regulating GSIS in pancreatic β-cells.
J Mol Neurosci. 2014 Sep;54(1):41-8.
Trans-caryophyllene suppresses hypoxia-induced neuroinflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-κB activation in microglia.[Pubmed:
24488604]
trans-Caryophyllene (TC), may have protective effects against hypoxia-induced neuroinflammatory responses.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, trans-Caryophyllene was found to significantly inhibit hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity as well as the release of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6, through activation of BV2 microglia following hypoxic exposure (1 % O2, 24 h). Furthermore, trans-Caryophyllene significantly inhibited hypoxia-induced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mitochondria as well as the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in microglia. Importantly, trans-Caryophyllene 's effects on inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and the secretion of inflammatory cytokines can be abolished by muting the CB2R using small RNA interference.
CONCLUSIONS:
These observations indicate that trans-Caryophyllene suppresses the hypoxia-induced neuroinflammatory response through inhibition of NF-κB activation in microglia. Therefore, trans-Caryophyllene may be beneficial in preventing hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation.
Neurochem Res. 2015 Jan;40(1):118-23.
Neuroprotective effects of trans-caryophyllene against kainic acid induced seizure activity and oxidative stress in mice.[Pubmed:
25417010]
trans-Caryophyllene (TC), a component of essential oil found in many flowering plants, has shown its neuroprotective effects in various neurological disorders. However, the effects of TC on epilepsy haven't been reported before.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the effect of TC on kainic acid-induced seizure activity caused by oxidative stress and pro-inflammation. We found that TC pretreatment significantly decreased seizure activity score compared to kainic acid treated group. Importantly, TC pretreatment leads to lowering the mortality in kainic acid treated mice. In addition, TC was found to significantly inhibit KA-induced generation of malondialdehyde. TC pretreatment also preserved the activity of GPx, SOD, and CAT. Notably, our data shows that an important property of TC is its capacity to exert cerebral anti-inflammatory effects by mitigating the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data suggest that TC has a potential protective effect on chemical induced seizure and brain damage.
Epilepsy Behav . 2016 Mar;56:26-31.
Anticonvulsant activity of β-caryophyllene against pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures[Pubmed:
26827298]
Abstract
Increasing evidence suggests that plant-derived extracts and their isolated components are useful for treatment of seizures and, hence, constitute a valuable source of new antiepileptic drugs with improved efficacy and better adverse effect profile. β-Caryophyllene is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that occurs in a wide range of plant species and displays a number of biological actions, including neuroprotective activity. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that β-caryophyllene displays anticonvulsant effects. In addition, we investigated the effect of β-caryophyllene on behavioral parameters and on seizure-induced oxidative stress. Adult C57BL/6 mice received increasing doses of β-caryophyllene (0, 10, 30, or 100mg/kg). After 60 min, we measured the latencies to myoclonic and generalized seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole (PTZ, 60 mg/kg). We found that β-caryophyllene increased the latency to myoclonic jerks induced by PTZ. This result was confirmed by electroencephalographic analysis. In a separate set of experiments, we found that mice treated with an anticonvulsant dose of β-caryophyllene (100mg/kg) displayed an improved recognition index in the object recognition test. This effect was not accompanied by behavioral changes in the open-field, rotarod, or forced swim tests. Administration of an anticonvulsant dose of β-caryophyllene (100mg/kg) did not prevent PTZ-induced oxidative stress (i.e., increase in the levels of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances or the decrease in nonprotein thiols content). Altogether, the present data suggest that β-caryophyllene displays anticonvulsant activity against seizures induced by PTZ in mice. Since no adverse effects were observed in the same dose range of the anticonvulsant effect, β-caryophyllene should be further evaluated in future development of new anticonvulsant drugs.
Keywords: Cannabinoids; Convulsion; EEG; Natural product; PTZ; Phytomedicine.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jul 15;24(14):3168-74.
trans-Caryophyllene is a natural agonistic ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α.[Pubmed:
24856059]
Intake of dietary aroma compounds may regulate cellular lipid metabolism. We demonstrated that trans-Caryophyllene, a flavor compound in plant foods and teas, activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-α through direct interaction with the ligand-binding domain of PPAR-α.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The agonistic activity of trans-Caryophyllene was investigated by the luciferase reporter assay, surface plasmon resonance, and time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. Following the stimulation of cells with trans-Caryophyllene, intracellular triglyceride concentrations were significantly reduced by 17%, and hepatic fatty acid uptake was significantly increased by 31%. The rate of fatty acid oxidation was also significantly increased. The expressions of PPAR-α and its target genes and proteins in fatty acid uptake and oxidation were significantly up-regulated as well. In HepG2 cells transfected with small interfering RNA of PPAR-α, the effects of trans-Caryophyllene on PPAR-α responsive gene expressions, intracellular triglyceride, fatty acid uptake and oxidation were disappeared.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the aroma compound, trans-Caryophyllene, is PPAR-α agonist thus regulates cellular lipid metabolism in PPAR-α dependent manners.
Phytomedicine. 2014 Feb 15;21(3):356-62.
The oral administration of trans-caryophyllene attenuates acute and chronic pain in mice.[Pubmed:
24055516]
trans-Caryophyllene is a sesquiterpene present in many medicinal plants' essential oils, such as Ocimum gratissimum and Cannabis sativa.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we evaluated the antinociceptive activity of trans-Caryophyllene in murine models of acute and chronic pain and the involvement of trans-Caryophyllene in the opioid and endocannabinoid systems. Acute pain was determined using the hot plate test (thermal nociception) and the formalin test (inflammatory pain). The chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve induced hypernociception was measured by the hot plate and von Frey tests. To elucidate the mechanism of action, mice were pre-treated with naloxone or AM630 30 min before the trans-Caryophyllene treatment. Afterwards, thermal nociception was evaluated. The levels of IL-1β were measured in CCI-mice by ELISA. trans-Caryophyllene administration significantly minimized the pain in both the acute and chronic pain models. The antinociceptive effect observed during the hot plate test was reversed by naloxone and AM630, indicating the participation of both the opioid and endocannabinoid system. trans-Caryophyllene treatment also decreased the IL-1β levels.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrate that trans-Caryophyllene reduced both acute and chronic pain in mice, which may be mediated through the opioid and endocannabinoid systems.