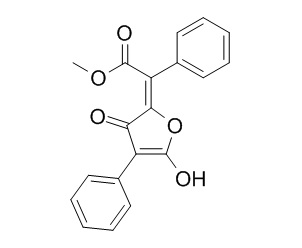
Vulpic acid
Vulpic acid has therapeutic and prophylactic potential to be antibacterial and antiplasmodial agents, it can inhibit one or more enzymes (PfFabI, PfFabG, and PfFabZ) from the plasmodial fatty acid biosynthesis (FAS-II) pathway, a potential drug target for liver stage activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Biol Macromol.2021, 199:189-200.
J Appl Biol Chem.2024, V67:46-53
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2020, 2020:2584783.
Foods.2022, 11(6):882.
Indian J Pharm Sci.2024, 86(2):736-741.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(20), 7323.
Research SPJ.2024, 0377.
Vietnam Journal of Food Control.2022, 5(3):pp.488-497.
Heliyon.2024, 10(16):e35645.
Nutrients.2020, 12(12):3607.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2013 Jun 28;76(6):1064-70.
Potential of lichen secondary metabolites against Plasmodium liver stage parasites with FAS-II as the potential target.[Pubmed:
23806111]
Chemicals targeting the liver stage (LS) of the malaria parasite are useful for causal prophylaxis of malaria.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, four lichen metabolites, evernic acid (1), Vulpic acid (2), psoromic acid (3), and (+)-usnic acid (4), were evaluated against LS parasites of Plasmodium berghei. Inhibition of P. falciparum blood stage (BS) parasites was also assessed to determine stage specificity. Compound 4 displayed the highest LS activity and stage specificity (LS IC50 value 2.3 μM, BS IC50 value 47.3 μM). The compounds 1-3 inhibited one or more enzymes (PfFabI, PfFabG, and PfFabZ) from the plasmodial fatty acid biosynthesis (FAS-II) pathway, a potential drug target for LS activity. To determine species specificity and to clarify the mechanism of reported antibacterial effects, 1-4 were also evaluated against FabI homologues and whole cells of various pathogens (S. aureus, E. coli, M. tuberculosis).
CONCLUSIONS:
Molecular modeling studies suggest that lichen acids act indirectly via binding to allosteric sites on the protein surface of the FAS-II enzymes. Potential toxicity of compounds was assessed in human hepatocyte and cancer cells (in vitro) as well as in a zebrafish model (in vivo). This study indicates the therapeutic and prophylactic potential of lichen metabolites as antibacterial and antiplasmodial agents.