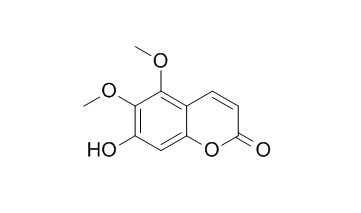
Umckalin
Umckalin shows antibacterial activity. Umckalin has antitubercular activity, it exhibited MIC values of 62.5 µg/mL against M. smegmatis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2019, 25(1):E103
Molecules.2024, 29(6):1392.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2018, 2018:8565132
Babol University of Medical Sciences2024, rs-4289336
Life Sci.2021, 286:120019.
Food Sci Nutr.2023, 11(9):5532-5542.
BMB Rep.2018, 51(5):249-254
Int Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83:106403.
Molecules. 2013, 18(11):14105-21
Current Analytical Chemistry2024, 20(8):599-610.
Related and Featured Products
Phytotherapy Research 22(6):841-845.
Antitubercular Activity of Compounds Isolated from Pelargonium sidoides.[Reference:
WebLink]
The recent increase in the incidence of tuberculosis with the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) cases has lead to the search for new drugs that are effective against MDR strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. and can augment the potential of existing drugs against tuberculosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Pelargonium sidoides. DC (Geraniaceae) is highly valued by traditional healers for its curative properties and is well-known to treat coughs, diarrhea, and tuberculosis. The butanol root extract was found have bioactive inhibitory activity against M. tuberculosis. at a concentration of 2.5 × 103 µg/mL. Phytochemical analysis of the active fraction from the root of P. sidoides. led to the isolation and identification of six compounds: coumarins (Umckalin, scopoletin, 6,8-dihydroxy-5.7-dimethoxy-2H.-benzopyran-2-one, and 6,8-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-2H.-benzopyran-2-one) and flavonoids (catechin and epigallocatechin, which is reported for the first time from P. sidoides.). The isolated compounds were evaluated for antitubercular activity with M. smegmatis. and M. tuberculosis.. Intracellular activity of these compounds was also investigated using THP-1 human macrophages infected with M. tuberculosis..
CONCLUSIONS:
The isolated compounds did not show activity inhibitory against M. tuberculosis., intracellularly and extracellularly, at the highest concentration tested in the current study. Epigallocatechin and scopoletin showed good inhibitory activity against M. smegmatis., exhibiting a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 7.8 µg/mL. Catechin and Umckalin exhibited MIC values of 31.25 and 62.5 µg/mL, respectively.
Planta Medica, 1998, 63(6):508-510.
Antibacterial activity of extracts and constituents of Pelargonium sidoides and Pelargonium reniforme.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antibacterial activity of extracts and isolated constituents (scopoletin, Umckalin, 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin, 6,8-dihydroxy-5,7-dimethoxycoumarin, (+)-catechin, gallic acid and its methyl ester) of Pelargonium sidoides and Pelargonium reniforme (Geraniaceae), plant species used in folk medicine by the Southern African native population, was evaluated against 8 microorganisms, including 3 Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and beta-hemolytic Streptococcus 1451) and 5 Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae).
CONCLUSIONS:
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) varied with the preparation of the extracts and microorganisms tested, from about 0.6 mg/ml for aqueous phases to over 10 mg/ml for crude Pelargonium extracts. With the exception of the ineffective (+)-catechin, all the potentially active compounds exhibited antibacterial activities with MICs of 200-1000 micrograms/ml. The results provide for a rational basis of the traditional use of the titled Pelargonium species.
Talanta, 2010, 81(4-5):1368-1372.
Determination of umckalin in commercial tincture and phytopreparations containing Pelargonium sidoides by HPLC: Comparison of sample preparation procedures.[Reference:
WebLink]
Roots of Pelargonium sidoides D.C. are used for the production of phytomedicines. Current quality control of phytopreparations containing P. sidoides extracts has been made in terms of total phenolics content.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this work we describe the development and validation of an HPLC method for the analysis of P. sidoides tincture and commercial syrup phytopreparations using Umckalin (7-hydroxy-5,6-dimethoxycoumarin) as chemical marker. Two sample preparation procedures, liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) and solid-phase extraction (SPE) were also developed and compared. The samples were analyzed by RP-HPLC and the two methods were then validated and compared. The repeatability of the two procedures showed coefficients of variation (CV) of 1.2% for SPE procedure, and 1.3% for LLE. Recovery for both methods was higher than 95.2%.
CONCLUSIONS:
The linearity showed correlation coefficients better than 0.999 for both methods. The detection and quantification limit were 0.0098 and 0.0298 μg mL−1, respectively. The validated procedure was then used for the analysis of tincture and five batches of two commercial phytopreparations containing P. sidoides tincture.