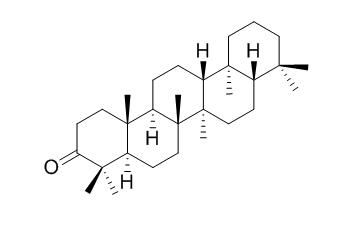
Tetrahymanone
Tetrahymanone is a natural product from Bradyrhizobium japonicum.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo).2024, 41(3):267-276.
Metabolites.2020, 11(1):E11.
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(21):E5488
Br J Pharmacol.2020, 10.1111
J Ethnopharmacol.2023, 309:116302.
Molecules.2020, 25(18):4283.
Environ Toxicol.2024, 39(3):1556-1566.
J Nat Prod.2019, 82(4):1002-1008
Separations2021, 8(1), 1.
Journal of Life Science2017, 233-240
Related and Featured Products
Sci Total Environ. 2014 Feb 1;470-471:180-92
Occurrence and sources of polar lipid tracers in sediments from the Shatt al-Arab River of Iraq and the northwestern Arabian Gulf.[Pubmed:
24140688 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Shallow surface sediment samples from the southern part of the Shatt al-Arab River estuary of Iraq and the northwestern Arabian Gulf were analyzed for polar lipid compounds including n-alkanoic acids, n-alkanols, steroids and triterpenoids. The results showed that the n-alkanoic acids, methyl n-alkanoates and n-alkanols typically ranged from C12 to C32 with total concentrations of 3.2 to 108.2 μg g(-1)dwt sample, from C12 to C30 with totals of 1.1 to 18.9 μg g(-1)dwt sample, and from C14 to C32 at 1.8 to 112.6 μg g(-1)dwt sample, respectively. Steroids and triterpenoids were detected and included stenols, stanols, stenones, stanones, tetrahymanol, Tetrahymanone and extended ββ-hopanes. The total steroid concentrations ranged from 2.8 to 78.4 μg g(-1)dwt sample, whereas the triterpenoids varied from 0.05 to 7.6 μg g(-1)dwt sample. The simple regression analysis of the results and the spatial distribution patterns of the identified organic tracers indicated that the inter-compound relationships were related mainly to their major sources.
CONCLUSIONS:
Cluster analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) of data set showed that the sampling sites are similar. These sources were allochthonous (terrestrial vegetation), autochthonous (plankton residues and bacteria in the sediments) and anthropogenic (sewage and petroleum).