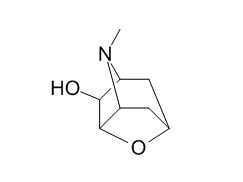
Scopoline
Scopoline, tropinol, ecgonine, and granatoline derivatives are therapeutic agents of the pyrrole and pyridine group. Scopoline has fungitoxic effects, it is inhibitory to Sclerotinia at similar doses to scopoletin; as scopolin is known to be less phytotoxic than ayapin and scopoletin, its accumulation may well confer head rot resistance with minimal plant damage and might be one of the bases for resistance to Sclerotinia.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Life Sci.2021, 270:119074.
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(7):1376.
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology2022, 10.1007:s13273-022-00277-3
Sci Rep.2019, 9(1):4646
Sci Rep.2021, 11(1):14180.
Process Biochemistry2019, 87:213-220
Nutrients.2020, 12(11):3448.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(20):12516.
JLiquid Chromatography & Related Tech.2021, 10826076.
Molecules. 2013, 18(7):7376-88
Related and Featured Products
Euphytica, 2006, 147(3):451-60.
Fungitoxic effect of scopolin and related coumarins on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. A way to overcome sunflower head rot[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The content of coumarins, as probable phytoalexins, was analysed in four sunflower genotypes that ranged in responses to head rot from highly susceptible to highly resistant. Low levels of all coumarins (scopolin, scopoletin and ayapin) were detected in the three most susceptible genotypes irrespective of time after inoculation.
However, in the resistant genotype there was a clear time-dependent disease-induced increase of all coumarins that reached a maximum after 10-14 days. Detailed comparison of the most susceptible and the resistant genotype showed that in the resistant but not the susceptible, scopoletin peroxidase activity increased during the course of the experiment.
CONCLUSIONS:
Results confirmed a clear negative correlation between coumarin content and disease symptoms and in particular for scopolin(Scopoline). Furthermore we show for the first time that scopolin(Scopoline) is inhibitory to Sclerotinia at similar doses to scopoletin. As scopolin(Scopoline) is known to be less phytotoxic than ayapin and scopoletin, its accumulation may well confer head rot resistance with minimal plant damage and might be one of the bases for resistance to Sclerotinia.
Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club, 1970, 97(1):22-33.
Effects of Scopoletin on Growth, CO2 Exchange Rates, and Concentration of Scopoletin, Scopolin, and Chlorogenic Acids in Tobacco, Sunflower, and Pigweed.[Reference:
WebLink]
In an attempt to establish the effects of scopoletin on growth of tobacco, sunflower, and pigweed, seedlings were treated with scopoletin through a nutrient culture.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A threshold level of inhibition was found in all cases between 10-4M and 10-3M concentrations of scopoletin with the former showing no major growth effects, whereas the 10-3M solutions were greatly inhibitory to all three species. All 5 x 10-4M treatments had an intermediate effect on growth. Analyses of scopoletin, scopolin(Scopoline), and chlorogenic acid concentrations of tobacco and sunflower treated with 10-4M and 5 x 10-4M scopoletin concentrations showed that at both of these levels, scopoletin and scopolin(Scopoline) increased significantly in the tissue when compared with the control. The plants treated with the 5 x 10-4M solution had the largest increase in these compounds. The great increase in scopolin(Scopoline) suggested a direct conversion of scopoletin to its glycoside, scopolin(Scopoline), within the plant. Chlorogenic acid levels were not different from controls and the variations in isomers (band 510 and neochlorogenic acid) were indefinite. A reduced shoot:root ratio coincided with a greater build up of scopoletin and scopolin(Scopoline) in the shoots than in the roots of inhibited tobacco seedlings. Respiration rates in treated plants remained unchanged, but CO2 exchange analyses indicated that a reduced net photosynthetic rate was a contributing factor to reduced growth. Net photosynthesis in 10-3M scopoletin treated tobacco plants was depressed to as low as 34% of that of the controls by the fourth day after treatment. In sunflowers, which normally have very small amounts of scopoletin and scopolin(Scopoline) in the tissue, growth retardation was not as pronounced and the lowest photosynthetic rate resulting from treatment was 74% of controls. Reduced growth in leaf area over a 12 day experiment correlated well with the significant reduction in the rate of net photosynthesis in tobacco and a fairly good correlation was found also in sunflower. Amounts of CO2 fixed/illumination hour in treated plants compared with controls reinforced the conclusion that a reduction in net photosynthesis contributed to plant inhibition in tobacco and sunflower plants.
CONCLUSIONS:
Limited experiments with pigweed also indicated significantly reduced photosynthesis in the 10-3M scopoletin treated seedlings. Scopoletin could contribute to a cooperative effect causing plant inhibition in the natural environment and therefore be a factor of ecological significance.
Chemphyschem. 2013 Jun 24;14(9):1830-5.
The distorted tropane of scopoline.[Pubmed:
23640872]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structural isomerization of scopine into Scopoline (oscine) has been observed in a supersonic jet expansion using microwave spectroscopy. The rotational spectrum evidences a single structure in the gas phase, providing a first description of the (three-ring) structurally distorted tropane in Scopoline. The absence of rotational signatures of any scopine conformation suggests a practically quantitative isomerization at the vaporization temperatures of the experiment (ca. 90 °C).
CONCLUSIONS:
The determined rotational parameters of Scopoline reveal the structural consequences of the intramolecular cyclation of scopine, which breaks the original epoxy group and creates a new ether bridge and a 7β-hydroxytropane configuration. The hydroxy group further stabilizes the molecule by an O-H⋅⋅⋅N intramolecular hydrogen bond, which, in turn, forces the N-methyl group to the less stable axial form. Supporting ab initio (MP2) and DFT (B3LYP, M06-2X) calculations are included.