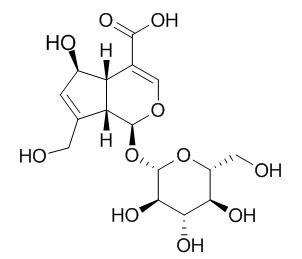
Scandoside
Scandoside exerts anti-inflammatory effect via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.It also inhibits LDL-oxidation.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Plant Direct.2021, 5(12):e372.
Biomimetics (Basel).2022, 7(4):154.
J Cell Mol Med.2023, jcmm.17968.
Int J Mol Sci.2015, 16(1):1232-51
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(18):9909.
JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography 2017, 30(2)
Biomed Pharmacother.2023, 162:114617.
Hindawi J of Food Biochemistry2023, P17:8883860
Food Chem.2023, 427:136647.
International J of Green Pharmacy2019, 13(3)
Related and Featured Products
Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2005, 28(10):1156-1160.
Iridoid glycosides isolated from Oldenlandia diffusa inhibit LDL-oxidation.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
An iridoid glycoside, oldenlandoside III ( 5 ) was isolated from the n -butanol fraction of methanol extracts of the aerial parts of Oldenlandia diffusa Roxb, along with six others previously characterized iridoid glycosides; geniposidic acid ( 1 ), Scandoside ( 2 ), feretoside ( 3 ), 10- O -benzoylScandoside methyl ester ( 4 ), asperulosidic acid ( 6 ) and deacetylasperulosidic acid ( 7 ).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1, 2 , and 7 inhibited LDL-oxidation, and showed 63.3±2.0, 62.2±1.6, and 63.8±1.5% inhibition, respectively, at a concentration of 20 μg/mL.
Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C, 2007, 62(7-8):597---602.
Iridoid glucosides with insecticidal activity from Galium melanantherum.[Reference:
WebLink]
The insecticidal activity of the endemic species Galium melanantherum was evaluated against Crematogaster scutellaris ants and Kalotermes flavicollis termites.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Iridoid glucosides 1-7 were isolated for the first time as metabolites of the investigated plant, along with the coumarin scopolin. The main components of the extract were found to be the non-acetylated iridoids: geniposidic acid (1), 10-hydroxyloganin (2), deacetyldaphylloside (3), monotropein (4), deacetylasperulosidic acid (5) and Scandoside (6), while asperulosidic acid (7) was present only in minute quantities. All isolated metabolites were identified on the basis of their spectral data.
CONCLUSIONS:
Laboratory bioassays revealed significant levels of toxicity for 1-4 against Kalotermes flavicollis termites and Crematogaster scutellaris ants.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(2):457.
Scandoside Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect Via Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages.[Reference:
WebLink]
The iridoids of Hedyotis diffusa Willd play an important role in the anti-inflammatory process, but the specific iridoid with anti-inflammatory effect and its mechanism has not be thoroughly studied.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
An iridoid compound named Scandoside (SCA) was isolated from H. diffusa and its anti-inflammatory effect was investigated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Its anti-inflammatory mechanism was confirmed by in intro experiments and molecular docking analyses. As results, SCA significantly decreased the productions of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E₂ (PGE₂), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) and inhibited the levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), TNF-α and IL-6 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. SCA treatment suppressed the phosphorylation of inhibitor of nuclear transcription factor kappa-B alpaha (IκB-α), p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The docking data suggested that SCA had great binding abilities to COX-2, iNOS and IκB.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results indicated that the anti-inflammatory effect of SCA is due to inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators via suppressing the nuclear transcription factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, which provided useful information for its application and development.