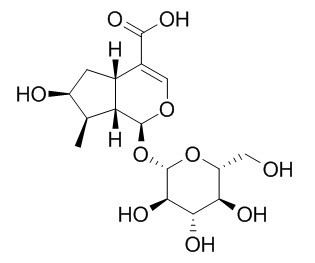
Loganic acid
Loganic acid( 0.7% solution) has a strong intraocular pressure (IOP)-hypotensive effect, it exhibits both sides effect on superoxide generation. Loganic acid also has protective effects on atherosclerosis risk factors in hypercholesterolemic rabbits, it shows significant anti-inflammatory effects decreasing TNF-α and IL-6 activity in serum.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Bioorg Chem.2024, 145:107184.
Food and Agriculture Org. Of the UN2019, 151-160
J Chromatogr Sci.2015, 53(5):824-9
Exp Parasitol.2018, 194:67-78
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2020, 527(4):889-895.
Dermatologica Sinica2024, 42(1):p19-30.
Plant Direct.2021, 5(4):e00318.
Food Science and Human Wellness2022, 11(4):965-974
Research Square2024, rs-4398438
Hortic Res.2023, 10(4):uhad039.
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(10):911-5.
Anti-inflammatory effect of three iridoids in human neutrophils.[Pubmed:
22417122]
To verify the anti-inflammatory potency of iridoids, three iridoids (two natural, Loganic acid: LA; geniposide: GE; and an artefact, 7(S)-n-butyl morroniside: BM) were investigated in vitro on the inhibition of superoxide generation in human neutrophils.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
All compounds showed inhibitory effect on fMLP-induced superoxide generation in a concentration-dependent manner with the following order: BM>LA>GE. BM exhibits potent inhibitory activity on superoxide anion induced by PMA, while LA and GE showed weak effect. When AA was used as stimulus, the generation of superoxide anion was suppressed by BM in a concentration-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
LA and GE exhibit both sides effect on superoxide generation.
Phytomedicine. 2014 Nov 15;21(13):1774-84.
The protective effect of the Cornus mas fruits (cornelian cherry) on hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis through PPARα activation in hypercholesterolemic rabbits.[Pubmed:
25444446 ]
Cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) fruits have been used in traditional cuisine and in folk medicine in various countries. This study was conducted to evaluate the constituents and impact of cornelian cherry (C. mas L.) fruits lyophilisate on lipid levels, PPARα protein expression, atheromatous changes in the aorta, oxido-redox state, and proinflammatory cytokines in hypercholesterolemic rabbits.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The HPLC-MS method was used for determining active constituents in cornelian cherry. In a subsequent in vivo study the protective effect of the cornelian cherry on diet-induced hyperlipidemia was studied using a rabbit model fed 1% cholesterol. Cornelian cherry (100mg/kg b.w.) or simvastatin (5mg/kg b.w.) were administered orally for 60 days. Two iridoids - Loganic acid and cornuside - and five anthocyanins were identified as the main constituents of the cornelian cherry. The administering of the cornelian cherry led to a 44% significant decrease in serum triglyceride levels, as well as prevented development of atheromatous changes in the thoracic aorta. Cornelian cherry significantly increased PPARα protein expression in the liver, indicating that its hypolipidemic effect may stem from enhanced fatty acid catabolism. Simvastatin treatment did not affect PPAR-α expression. Moreover, the cornelian cherry had a significant protective effect on diet-induced oxidative stress in the liver, as well as restored upregulated proinflammatory cytokines serum levels.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, we have shown Loganic acid to be the main iridoid constituent in the European cultivar of the cornelian cherry, and proven that the cornelian cherry could have protective effects on diet-induced hypertriglicerydemia and atherosclerosis through enhanced PPARα protein expression and via regulating oxidative stress and inflammation.
Adv Clin Exp Med . 2018 Nov;27(11):1505-1513.
Loganic acid and anthocyanins from cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) fruits modulate diet-induced atherosclerosis and redox status in rabbits[Pubmed:
29790688]
Abstract
Background: Cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) is a plant growing in southeast Europe, in the past used in folk medicine. There are many previous publications showing the preventive effects of (poly)phenolic compounds, especially anthocyanins, on cardiovascular diseases, but there is a lack of studies comparing the effects of (poly)phenolics and other constituents of fruits.
Objectives: We have attempted to determine if iridoids and anthocyanins from cornelian cherry fruits may affect the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta as well as lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in the livers of cholesterol-fed rabbits.
Material and methods: Fractions of iridoids and anthocyanins were analyzed using the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) methods. Loganic acid (20 mg/kg b.w.) and a mixture of anthocyanins (10 mg/kg b.w.) were administered orally for 60 days to rabbits fed with 1% cholesterol. Histopathological samples of the aortas and the livers were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde - MDA) and redox status (glutathione - GSH, glutathione peroxidase - Gpx and superoxide dismutase - SOD) were analyzed using spectrophotometrical methods.
Results: Both Loganic acid (an iridoid) and a mixture of anthocyanins diminished the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta. Both substances also diminished lipid peroxidation, measured as a decrease of MDA, and attenuated oxidative stress, measured as an increase of GSH in the livers depleted by cholesterol feeding. Unexpectedly, cholesterol feeding decreased the Gpx activity in the liver, which was reversed by both investigated substances.
Conclusions: We have shown that both iridoids and anthocyanins help prevent fed-induced atherosclerosis, and the consumption of fruits rich in these substances may elicit beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system.
Keywords: anthocyanins; atherosclerosis; cornelian cherry; glutathione; Loganic acid.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:939402.
Application of Cornelian Cherry Iridoid-Polyphenolic Fraction and Loganic Acid to Reduce Intraocular Pressure.[Pubmed:
26124854 ]
One of the most common diseases of old age in modern societies is glaucoma. It is strongly connected with increased intraocular pressure (IOP) and could permanently damage vision in the affected eye. As there are only a limited number of chemical compounds that can decrease IOP as well as blood flow in eye vessels, the up-to-date investigation of new molecules is important.
The chemical composition of the dried Cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) polar, iridoid-polyphenol-rich fraction was investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Loganic acid (50%) and pelargonidin-3-galactoside (7%) were found as the main components. Among the other constituents, iridoid compound cornuside and the anthocyans cyanidin 3-O-galactoside, cyanidin 3-O-robinobioside, and pelargonidin 3-O-robinobioside were quantified in the fraction. In an animal model (New Zealand rabbits), the influence of Loganic acid and the polyphenolic fraction isolated from Cornelian cherry fruit was investigated. We found a strong IOP-hypotensive effect for a 0.7% solution of Loganic acid, which could be compared with the widely ophthalmologically used timolol. About a 25% decrease in IOP was observed within the first 3 hours of use.
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 May;42(5):566-70.
Content of gentiopicroside and loganic acid in Radix gentianae and their fingerprints[Pubmed:
17703785]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To develop a HPLC-DAD-ESI-TOF/MS analysis method for the determination of gentiopicroside and Loganic acid in Radix gentianae samples and for the research of their fingerprints. The samples were extracted using ASE for 10 min under 100 degrees C and 9.65 MPa, and divided into water phase and chloroform phase and analyzed them with HPLC-DAD-ESI-TOF/MS method respectively. Based on this method, the HPLC fingerprints of Radix gentianae were established. Comparing the spectrogram and mass spectrum of the chromatogram peak with the reference value, three compounds in water phase were identified as gentiopicroside, asafetida acid and Loganic acid. There is no report of the compounds in chloroform phase. The content of gentiopicroside and Loganic acid in samples of different groups were determined, separately. The fingerprints were compared by the software of the similarity evaluation system for chromatographic fingerprint. The water phase fingerprint congruence coefficients of samples from six different areas were above 0.90, however, the chloroform phase fingerprint congruence coefficients were within 0.62 -0.99.
CONCLUSIONS:
This method can be used for determination of potent component in Radix gentianae and its quality control. Radix gentianae from different producing areas have the largest diversities, and the diversities embodied in the content of chloroform phase compounds.