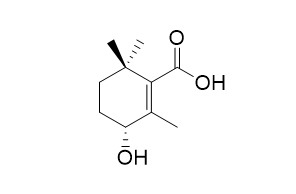
Rehmapicrogenin
Rehmapicrogenin, isolated from the root of Rehmannia glutinosa, exhibits potent anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting iNOS, COX-2 and IL-6. Rehmapicrogenin attenuates kidney damage by reducing inflammatory factor release through the oestrogen signalling pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Journal of Functional Foods2019, 52:430-441
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2019, 1113:1-13
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(11):2317.
Front Microbiol.2023, 14:921653.
Processes2024, 12(8), 1563
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2093.
J AOAC Int.2023, 106(1):56-64.
Anal Chim Acta.2021, 1180:338874.
Nutrients.2018, 10(10)
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:883475.
Related and Featured Products
J Ethnopharmacol . 2012 Oct 11;143(3):867-875.
Bioassay-guided isolation of anti-inflammatory components from the root of Rehmannia glutinosa and its underlying mechanism via inhibition of iNOS pathway[Pubmed:
23034094]
Ethnopharmacological relevance: The root of Rehmannia glutinosa (RR) is commonly used to reduce inflammation in various traditional Chinese herbal formulae; however, little is known regarding its active component(s).
Aim of study: The objective of the present study was to examine the active component(s) responsible for the anti-inflammatory activity of RR via anti-nitric oxide production assay-guided fractionation; and the underlying anti-inflammatory mechanism of action of such component(s) was further investigated.
Materials and methods: Anti-nitric oxide (NO) activities with lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 murine macrophages was used as screening platform. Gene, protein and inflammatory mediators' expression were also studied using real-time PCR, western blotting and ELISA, respectively.
Results: Using anti-NO assay-guided fractionation, sub-fraction C3 (from 31.25 to 62.5 μg/ml, p=0.001 to 0.01) possessed 100-fold more potent anti-inflammatory effect than that of the aqueous extract of RR. Characterization of C3 showed that the anti-inflammatory effect could be partly due to the presence of Rehmapicrogenin, which could significantly inhibit NO production (p<0.001). C3 was further demonstrated in blocking inflammation by inhibiting gene (p<0.001) and protein expression of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) dose-dependently. Besides, C3 also significantly inhibited the production of prostaglandin E(2) (p<0.001 to 0.01), IL-6 (p<0.001 to 0.05) and COX-2 (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Rehmapicrogenin was, for the first time, shown to possess nitric oxide inhibitory activities. Bioassay-guided fractionation demonstrated that Rehmapicrogenin-containing subfraction C3 exhibited potent anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting iNOS, COX-2 and IL-6, while Rehmapicrogenin was only partially responsible for the anti-inflammatory effect of RR.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi . 2021 May;46(9):2287-2297.
[Analysis of blood components of Yougui Yin in normal rats and rats with kidney deficiency caused by adenine based on UPLC-MS technology][Pubmed:
34047132]
Based on the serum medicinal method, this study aims to investigate the migrating components of Yougui Yin in the blood after intragastric administration, and to provide reference for the basic research of its pharmacodynamics. The kidney deficiency rat model was replicated by adenine method. Normal rats and model rats were administered orally for a single gavage of Yougui Yin. The components in blood were rapidly analyzed and identified by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry(UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) and multiple reaction monitoring(MRM), and the migrating components in blood of Yougui Yin were explored by multivariate statistical analysis. The results showed that there were 42 characteristic peaks in the plasma of normal rats by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS technology and 13 chemical components were identified, including 6 alkaloids, 2 flavonoids, 2 triterpenoid saponins, 1 iridoid, 1 phenylpropanoid and 1 monoterpenoid. There were 22 characteristic peaks in the plasma of kidney-deficiency rats, and 12 chemical components were identified, including 2 iridoids, 6 alkaloids, 2 flavonoids, 1 monoterpenoid and 1 triterpenoid saponin. Verbascoside, isoacteoside, acteoside, pinoresinoldiglucoside, loganin and morroniside were identified by MRM both in the plasma of normal rats and kidney-deficiency rats. Compared with 85 monomer components in Yougui Yin, 17 common prototype components were found by UPLC-MS in the plasma of normal rats and kidney deficiency rats, including verbascoside, isoacteoside, acteoside, Rehmapicrogenin derived from Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata, pinoresinol diglucoside and geniposidic acid from Eucommiea Cortex, loganin and morroniside derived from Corni Fructus, mesaconine, benzoylmesaconine, benzoylaconitine, benzoylhypacoitine, mesaconitine, aconitine derived from Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata, liquiritin, isoliquiritin and glycyrrhizic acid derived from Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma. Thirty-one metabolites of medicinal ingredients not found in the plasma of adenine-induced kidney deficiency rats were also detected in the plasma of normal rats. Twelve metabolites of medicinal materials not found in the plasma of normal rats were detected in the plasma of kidney deficiency rats. The results of the study provide reference for explaining the material basis and mechanism of Yougui Yin in the treatment of kidney deficiency.
Biomed Pharmacother . 2021 Jun;138:111305.
The nephroprotective effects and mechanisms of rehmapicrogenin include ROS inhibition via an oestrogen-like pathway both in vivo and in vitro[Pubmed:
33820633]
Background: The root of Rehmannia glutinosa (R. glutinosa) is commonly used in various traditional Chinese herbal formulae to ameliorate nephropathy; however, little is known about its active component(s) and mechanisms.
Aim: In the present study, we examined the protective effect and potential mechanism of Rehmapicrogenin, a monomeric compound extracted from R. glutinosa, against Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy (AN) in vivo and in vitro.
Methods: In this study, an ADR-induced kidney injury model was employed to investigate the nephroprotective effects of Rehmapicrogenin in mice. In vivo, ELISA kits, flow cytometry, haematoxylin-eosin staining, immunofluorescence techniques, and western blotting were used to evaluate the effect of Rehmapicrogenin on kidney injury in mice. In vitro, the effects of Rehmapicrogenin on NRK-52E cellular damage induced by ADR were determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) method. The mechanism was investigated using ELISA kits, flow cytometry and In-Cell Western™ blotting.
Results: In vivo, Rehmapicrogenin treatment significantly attenuated the pathological changes in the kidney induced by ADR; rescued weight, serum creatinine (Scr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and urine albumin (U-ALB) levels; reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation; and decreased oxidative stress, the apoptosis rate, and cell survival in ADR-treated mice. Importantly, both in vivo and in vitro experimental results demonstrated that Rehmapicrogenin regulates the Nrf2/ARE signalling pathway, the most important pathway for oxidative stress. Rehmapicrogenin attenuated ADR-induced kidney damage by reducing oxidative stress through the oestrogen receptor pathway. Moreover, after treatment with ICI 182780 (the oestrogen receptor-nonspecific antagonist Faslodex), the improvement induced by Rehmapicrogenin was significantly reversed.
Conclusions: In conclusion, Rehmapicrogenin attenuates kidney damage by reducing inflammatory factor release through the oestrogen signalling pathway.