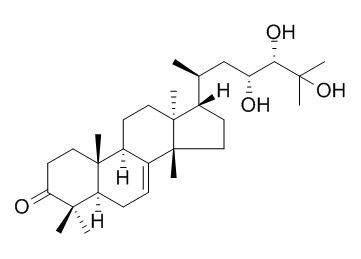
Piscidinol A
Piscidinol A is toxic against the 4T1 and HEp2 cancer cell lines, the IC50 of 8.0 ± 0.03 and 8.4 ± 0.01 uM, respectively. It can inhibit NO production in mouse peritoneal macrophages with inhibitory ratios ranging from 39.8±7.7 to 68.2±4.5%.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Br J Pharmacol.2018, 175(6):902-923
National Academy Science Letters2023, s40009.
Materials Today Communications2023, 37:107216
Food Chem.2018, 252:207-214
J Ethnopharmacol.2023, 321:117501.
J of Archaeological Science:Reports2024, 53:104298
Food Chem.2021, 360:130063.
Agriculture2022, 12(2),227.
SCOPUS.2020, 836-847.
bioRxiv2021, 462065.
Related and Featured Products
Chem Biodivers. 2013 Apr;10(4):695-702.
Tirucallane triterpenoids from the stems of Brucea mollis.[Pubmed:
23576355]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new tirucallane triterpenoids, brumollisols A-C (1-3, resp.), together with five known analogues, (23R,24S)-23,24,25-trihydroxytirucall-7-ene-3,6-dione (4), Piscidinol A (5), 24-epiPiscidinol A (6), 21α-methylmelianodiol (7), and 21β-methylmelianodiol (8), were isolated from an EtOH extract of the stems of Brucea mollis. Their structures were elucidated by means of spectroscopic methods including 1D- and 2D-NMR techniques and mass spectrometry.
CONCLUSIONS:
In the in vitro assays, compound 6 exhibited significant cytotoxic activity against A549 and BGC-823 cancer cells with IC50 values of 1.16 and 3.01 μM, respectively. At a concentration of 10 μM, compounds 1-5, 7, and 8 were found to inhibit NO production in mouse peritoneal macrophages with inhibitory ratios ranging from 39.8±7.7 to 68.2±4.5%.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;174:419-25.
Antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activities of the constituents of Turraea robusta and Turraea nilotica.[Pubmed:
26320684 ]
Turraea robusta and Turraea nilotica are African medicinal plants used for the treatment of a wide variety of diseases, including malaria. The genus Turraea is rich in limonoids and other triterpenoids known to possess various biological activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the stem bark of T. robusta six compounds, and from various parts of T. nilotica eleven compounds were isolated by the use of a combination of chromatographic techniques. The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated using NMR and MS, whilst the relative configuration of one of the isolated compounds, toonapubesin F, was established by X-ray crystallography. The antiplasmodial activities of the crude extracts and the isolated constituents against the D6 and W2 strains of Plasmodium falciparum were determined using the semiautomated micro dilution technique that measures the ability of the extracts to inhibit the incorporation of (G-(3)H, where G is guanine) hypoxanthine into the malaria parasite. The cytotoxicity of the crude extracts and their isolated constituents was evaluated against the mammalian cell lines African monkey kidney (vero), mouse breast cancer (4T1) and human larynx carcinoma (HEp2).
The extracts showed good to moderate antiplasmodial activities, where the extract of the stem bark of T. robusta was also cytotoxic against the 4T1 and the HEp2 cells (IC50<10 μg/ml). The compounds isolated from these extracts were characterized as limonoids, protolimonoids and phytosterol glucosides. These compounds showed good to moderate activities with the most active one being azadironolide, IC50 2.4 ± 0.03 μM and 1.1 ± 0.01 μM against the D6 and W2 strains of Plasmodium falciparum, respectively; all other compounds possessed IC50 14.4-40.5 μM. None of the compounds showed significant cytotoxicity against vero cells, yet four of them were toxic against the 4T1 and HEp2 cancer cell lines with Piscidinol A having IC50 8.0 ± 0.03 and 8.4 ± 0.01 μM against the 4T1 and HEp2 cells, respectively. Diacetylation of Piscidinol A resulted in reduced cytotoxicity.
CONCLUSIONS:
From the medicinal plants T. robusta and T. nilotica, twelve compounds were isolated and characterized; two of the isolated compounds, namely 11-epi-toonacilin and azadironolide showed good antiplasmodial activity with the highest selectivity indices.