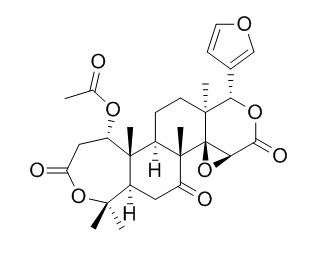
Nomilin
Nomilin has immunomodulatory, antioxidant, anti-human immunodeficiency virus(HIV), cancer chemopreventive, antiangiogenic, anti-obesity and anti-hyperglycemic effects. Nomilin inhibits tumor-specific angiogenesis by downregulating VEGF, NO and proinflammatory cytokine profile and also by inhibiting the activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. It inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro by suppression of NFATc1 and MAPK signaling pathways, indicates that nomilin-containing herbal preparations have potential utility for the prevention of bone metabolic diseases.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Processes2024, 12(8), 1563
Analytical Letters.2020, doi 10.1008
Nat Prod Commun.2017, 12(5):771-778
J Biosci.2020, 45:46.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 181:117647.
Biomolecules.2024, 14(4):451.
Plant Direct.2021, 5(4):e00318.
Appl. Sci. 2024, 14(13), 5815
J Control Release.2021, 336:159-168.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2020, 530(1):4-9.
Related and Featured Products
Food Chemistry, 2005, 93(4):599-605.
Contents and antioxidant capacity of limonin and nomilin in different tissues of citrus fruit of four cultivars during fruit growth and maturation.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The contents of limonin and Nomilin in different fruit tissues of Foxiangyou (Citrus grandis), Citrus unshiu, Penggan (Citrus reticulata) and Huyou (Citrus changshanensis KS Chen et CX Fu) were measured during fruit growth and maturation by HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography). Results showed that limonin and Nomilin were the predominant limonoids in the extracted samples. During fruit growth and maturation, the contents of limonin and Nomilin increased from April, peaked in early September and decreased afterwards until late October when they reached a steady low level. The antioxidant capacities of limonin and Nomilin in the four tissues of mature fruit were determined by beta-carotene bleaching assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results showed that the antioxidant capacities of limonin and Nomilin varied in different tissues and cultivars. In the three tissues other than albedo, the antioxidant capacities of limonin and Nomilin were high (2.9-8.3 times than that of vitamine C).
Planta Med. 2003 Oct;69(10):910-3.
Effect of limonin and nomilin on HIV-1 replication on infected human mononuclear cells.[Pubmed:
14648393 ]
In the last years several plant-derived natural compounds have been screened for their anti-HIV activity in order to find lead compounds with novel structures or mechanisms of action. Among these, several triterpenoids have been found to exhibit an antiretroviral activity with different mechanisms of action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study the effect of two limonoids, limonin and Nomilin, on the growth of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) in culture of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and on monocytes/macrophages (M/M) is described. Limonin and Nomilin were found to inhibit the HIV-1 replication in all cellular systems used. A dose-dependent inhibition of viral replication was observed in PBMC isolated from healthy donors and infected with HIV-1 strain after incubation with limonin and Nomilin (EC (50) values: 60.0 microM and 52.2 microM, respectively). The two terpenoids inhibited at all concentrations studied the production of HIV-p24 antigen even when the PBMC employed were chronically infected (EC (50) values of 61.0 microM for limonin and 76.2 microM for Nomilin). Moreover, these compounds inhibited the HIV-1 replication even in infected M/M. In this cellular system the inhibitory effect was significant at the concentrations of 20 microM, 40 microM and 80 microM starting from day 14 and reached the maximum effect after 18 days of incubation. As regards the mechanism of action, limonin and Nomilin inhibit in vitro HIV-1 protease activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
In general, the results obtained point out a similar anti-HIV activity of limonin and Nomilin indicating that this activity is not drastically influenced by the structural difference between the two compounds.
Food Funct . 2019 Sep 1;10(9):5323-5332.
Nomilin protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion induced neurological deficits and blood-brain barrier disruption via the Nrf2 pathway[Pubmed:
31389456]
Abstract
Oxidative stress is considered to play an important role in the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. The nuclear transcription factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 (NQO1) pathway has been considered as a potential target for neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nomilin (NOM) is a limonoid compound obtained from the extracts of citrus fruits. The purpose of our study was to determine whether NOM could exert beneficial effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats. Firstly, NOM treatment significantly mitigated cell death and decreased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and ROS production in SH-SY5Y cells induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD), which was almost abolished by Nrf2 knockdown. Secondly, NOM improved infarct area, brain edema and neurological deficits in an experimental stroke rat model via middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Furthermore, NOM attenuated blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption in MCAO rats, which might be associated with alleviating the loss of tight junction proteins, including ZO-1 and occludin-5. Further results revealed that NOM treatment effectively mitigated oxidative stress and facilitated the expressions of Nrf2 and NQO1, which might confirm that the loss of tight junction proteins in the microvasculature was likely mediated by oxidative stress. In conclusion, our study provided evidence that the protective effects of NOM in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats were related to the Nrf2/NQO1 pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jul 8;410(3):677-81.
Anti-obesity and anti-hyperglycemic effects of the dietary citrus limonoid nomilin in mice fed a high-fat diet.[Pubmed:
21693102]
TGR5 is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family and is activated by bile acids (BAs). TGR5 is thought to be a promising drug target for metabolic diseases because the activation of TGR5 prevents obesity and hyperglycemia in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we identified a naturally occurring limonoid, Nomilin, as an activator of TGR5. Unlike BAs, Nomilin did not exhibit the farnesoid X receptor ligand activity. Although the Nomilin derivative obacunone was capable of activating TGR5, limonin (the most abundant limonoid in citrus seeds) was not a TGR5 activator. When male C57BL/6J mice fed a HFD for 9 weeks were further fed a HFD either alone or supplemented with 0.2%w/w Nomilin for 77 days, Nomilin-treated mice had lower body weight, serum glucose, serum insulin, and enhanced glucose tolerance.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest a novel biological function of Nomilin as an agent having anti-obesity and anti-hyperglycemic effects that are likely to be mediated through the activation of TGR5.
Acs Symposium, 2000, 758:185-200.
Limonin and Nomilin Inhibitory Effects on Chemical-Induced Tumorigenesis.[Reference:
WebLink]
The increased enzyme activity was correlated with the ability of these compounds to inhibit carcinogenesis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Nomilin was found to reduce the incidence and number of tumors per mouse of forestomach tumors induced by benzo[a]pyrene (BP). Topical application of the limonoids was found to inhibit both the initiation and the promotion phases of carcinogenesis in the skin of SENCAR mice. Nomilin appeared to be more effective at the initiation stage while limonin was more potent as an inhibitor at the promotion phase of carcinogenesis. Administration of Nomilin and limonin to the diet or by gavage inhibited BP-induced and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-l-(3-pyridyl)-l-butanone-induced lung tumor formations, respectively, in A/J mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest citrus limonoids are potential cancer chemopreventive agents.
Vitam Horm. 2013;91:425-39.
Nomilin as an anti-obesity and anti-hyperglycemic agent.[Pubmed:
23374727]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Recent scientific findings support the notion that bile acids, which are cholesterol catabolites, are bioactive signaling molecules that function as ligands for the farnesoid X receptor or a G-protein-coupled receptor, TGR5. Through these receptors, bile acids can maintain not only bile acid homeostasis but also lipid and carbohydrate homeostasis. An intriguing finding regarding the role of TGR5 in energy metabolism and glucose homeostasis suggests a potential approach to combat obesity and insulin resistance by targeting this receptor to increase thermogenesis and incretin secretion.
CONCLUSIONS:
In this review, I have summarized the latest findings related to TGR5 agonists, in particular, a citrus limonoid, Nomilin, and the roles of these agonists in energy metabolism and glucose homeostasis.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 15;668(3):450-8.
Nomilin inhibits tumor-specific angiogenesis by downregulating VEGF, NO and proinflammatory cytokine profile and also by inhibiting the activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9.[Pubmed:
21839074]
Angiogenesis is a crucial step in the growth and metastasis of cancers. Antiangiogenic activity of Nomilin was studied using in vivo as well as in vitro models.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Nomilin significantly inhibited tumor directed capillary formation. Serum proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and GM-CSF and also serum NO levels were significantly reduced by the treatment of Nomilin. Administration of Nomilin significantly reduced the serum level of VEGF, a proangiogenic factor and increased the antiangiogenic factors IL-2 and TIMP-1. In vitro studies using rat aortic ring assay showed that administration of Nomilin at non-toxic concentrations significantly inhibited microvessel sprouting. Studies using human umbilical vein endothelial cells clearly demonstrated that administration of Nomilin significantly retarded endothelial cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tube formation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data clearly demonstrate the antiangiogenic potential of Nomilin by downregulating the activation of MMPs, production of VEGF, NO and proinflammatory cytokines as well as upregulating IL-2 and TIMP.
Integr Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(1):48-60.
Nomilin inhibits metastasis via induction of apoptosis and regulates the activation of transcription factors and the cytokine profile in B16F-10 cells.[Pubmed:
21665879]
Nomilin is a triterpenoid present in common edible citrus fruits with putative anticancer properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the authors investigated the antimetastatic potential of Nomilin and its possible mechanism of action. Metastasis was induced in C57BL/6 mice through the lateral tail vein using highly metastatic B16F-10 melanoma cells. Administration of Nomilin inhibited tumor nodule formation in the lungs (68%) and markedly increased the survival rate of the metastatic tumor-bearing animals. These results correlated with the biochemical parameters and histopathological analysis. Nomilin showed an inhibition of tumor cell invasion and activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Treatment with Nomilin induced apoptotic response, characterized by an increase in the sub-G1 fraction of cells with chromatin condensation and membrane blebbing, a typical ladder of DNA fragmentation, and detection of apoptotic cells by TUNEL assay. Nomilin treatment also exhibited a downregulated Bcl-2 and cyclin-D1 expression and upregulated p53, Bax, caspase-9, caspase-3, p21, and p27 gene expression in B16F-10 cells. Proinflammatory cytokine production and gene expression were found to be downregulated in Nomilin-treated cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The study also reveals that Nomilin could inhibit the activation and nuclear translocation of antiapoptotic transcription factors such as nuclear factor (NF)-κB, CREB, and ATF-2 in B16F-10 cells.
Phytomedicine. 2003;10(6-7):483-9.
Effect of naturally occurring triterpenoids glycyrrhizic acid, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and nomilin on the immune system.[Pubmed:
13678231 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effect of naturally occurring triterpenoid compounds such as glycyrrhizic acid, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, and Nomilin on the immune system was studied using Balb/c mice. Intraperitoneal treatments with 5 doses of these terpenoid compounds were found to enhance the total white blood cells (WBC) count. In ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and Nomilin treated animals the maximum total WBC count was observed on the 6th day, while in glycyrrhizic acid treated animals it was observed only on the 9th day after the drug treatment. In ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and Nomilin treated animals the percentage of increase in the total WBC count was to 91.48 +/- 4.6%, 135.75 +/- 6.4% and 117.33 +/- 17.9% respectively. In the glycyrrhizic acid treated animals the total WBC count was increased to 114.9 +/- 18%. Bone marrow cellularity and alpha-esterase positive cells were also enhanced by the treatment with these terpenoids. Treatment with various triterpenoids along with antigen produced an enhancement in the specific antibody titre and the number of plaque forming cells (PFC) in the spleen. Triterpenoids remarkably inhibited delayed type hypersensitivity reaction (DTH).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate the immunomodulatory activity of naturally occurring triterpenoids such as glycyrrhizic acid, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and Nomilin.