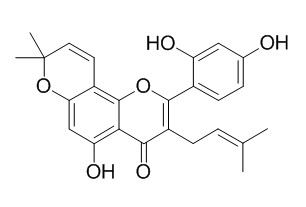
Morusin
Morusin exhibits antinociceptive, analgesic, anticonvulsant, antibacterial, and antitumor activities. Morusin can inhibit NF-κB and STAT3 activity, activate caspases activity, and restorate GABA level.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Eur J Pharmacol.2023, 950:175772.
J Pharmaceutical Research Int.2021, 33(41A):275-284.
Integr Med Res.2017, 6(4):395-403
Chin Med.2022, 17(1):66.
Pharmacol Res.2020, 161:105205.
J Nat Sc Biol Med2019, 10(2):149-156
Korean J of Food Science&Technology 2017, 49(2):146-150
Trop J Nat Prod Res.2019, 3(1):6-9
Cell Physiol Biochem.2019, 52(6):1255-1266
Molecules2020, 25(4):892
Related and Featured Products
Toxicol Lett. 2015 Jan 22;232(2):490-8.
Antitumor progression potential of morusin suppressing STAT3 and NFκB in human hepatoma SK-Hep1 cells.[Pubmed:
25476160]
Morusin is a prenylated flavonoid that has been isolated from the root bark of the mulberry tree (Morus species, Moraceae), a Chinese traditional medicine.
It has been synthesized by our laboratory from commercially available phloroglucinol, and has demonstrated to possess antitumor effects of cell lines including A549, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, at non-cytotoxic concentrations, Morusin altered invasive morphology and suppressed cell-matrix adhesion, cell motility and cell invasion in SK-Hep1 cells. Morusin also increased the expression of E-cadherin, an epithelial cell junction protein, decreased the expression of vimentin, a mesecnchymal marker, and α2-, α6-, β1- integrin, which regulated cancer attachment and migration. In addition, Morusin reduced the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9), which were involved in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and promoting cancer cell invasion. Furthermore, Morusin suppressed the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) signaling pathways, which modulate the protein expression involved in the invasion process. Finally, Morusin decreased the lung colonization of the SK-Hep1 cells in the nude mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate Morusin possesses antitumor progression potential through suppressing STAT3 and NFκB.
Mol Carcinog. 2014 Dec 31.
Morusin inhibits glioblastoma stem cell growth in vitro and in vivo through stemness attenuation, adipocyte transdifferentiation, and apoptosis induction.[Pubmed:
25557841]
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cancer stem cells (GSCs) are responsible for the progression and recurrence of GBM after conventional therapy. Morusin possesses anti-cancer activity in vitro. The purpose of this study is to confirm the growth inhibition effect of Morusin on human GSCs growth in vitro and in vivo and to explore the possible mechanism of its activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Human GSCs were enriched under nonadhesive culture system, and characterized through neurosphere formation, toluidine blue staining, immunofluorescence staining, Western blotting analysis of stemness markers of CD133, nestin, Sox2 and Oct4, and tumorigenecity in vivo; the growth inhibition effect of Morusin on human GSCs in vitro and in vivo were tested by cell cytotoxicity, neurosphere formation inhibition, adipogenic differentiation, apoptosis induction, and tumor growth inhibition in vivo assays. The potential molecular mechanisms underlying the growth inhibition effect of Morusin on GSCs in vitro and in vivo were investigated with Western blotting evaluation of stemness, adipogenic, and apoptotic proteins in Morusin treated GSCs and tumor tissues. GSCs enriched under nonadhesive culture system possess stemness characterstics; Morusin inhibited GSCs growth in vitro and in vivo, it reduced stemness of GSCs, induced them adipocyte-like transdifferention and apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Morusin has the potential to inhibit human GSCs growth in vitro and in vivo through stemness attenuation, adipocyte transdifferentiation, and apoptosis induction.
Science of Sericulture, 2013, 39(6):1150-4.
An Investigation on Antibacterial Activity and Stability of Morusin.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study,inhibitory effects of Morusin from mulberry( Morus L.) against 5 common food-borne pathogenic bacteria,namely Staphyloccocus aureus,Bacillus subtilis,Escherichia coli,Salmonella spp. and Proteus vulgaris,were tested by agar diffusion method and microscale double dilution method.
Meanwhile,the effects of thermal treatment,ultraviolet illumination,medium pH value,oxidant and reducer on the antibacterial activity of Morusin were also investigated.
The results indicated that inhibitory effects of Morusin against the 5 tested bacterial strains were different. The two Gram-positive bacteria( G+),Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus,were remarkably inhibited. Morusin had the highest antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis,with the minimum inhibitory concentration( MIC) below 1. 56μg /mL. Its inhibition to the three Gram-negative bacteria( G-),Salmonella spp.,P. vulgaris and E. coli,was relatively weak. Ultraviolet illumination and thermal treatment below 100 ℃ had no obvious influence on the antibacterial activity of Morusin. After thermal treatment of above100 ℃,the antibacterial activity of Morusin decreased obviously. Within pH 6 ~ 9 range,the antibacterial activity of Morusin decreased with increase of medium pH value.When the concentration of reducer Na2SO3was increased,the antibacterial activity of Morusin to Staphylococcus aureus declined gradually. The concentration of oxidant H2O2 had little influence on the antibacterial activity of Morusin.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Morusin is one of the important substances of mulberry with antibacterial activity. High temperature( above 100 ℃),strong alkaline and high concentration reducer had influence on the antibacterial activity of Morusin.
Z Naturforsch C. 2000 Mar-Apr;55(3-4):256-60.
Antinociceptive properties of morusin, a prenylflavonoid isolated from Morus nigra root bark.[Pubmed:
10817216]
The antinociceptive effects of Morusin (1), the main prenylflavonoid present in the Morus nigra root barks have been investigated in classical models of pain in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results showed that 1 exhibits a promising antinociceptive or analgesic profile by the intraperitoneal route, being more potent than some standard drugs used as reference.
CONCLUSIONS:
The mechanism by which the Morusin exerts antinociceptive activity still remains undetermined, but our results strongly suggest that it involves the participation of the opioid system.
Am J Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;5(1):289-99.
Morusin induces cell death through inactivating STAT3 signaling in prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed:
25628938]
STAT3 has been recognized as an efficacious drug target for prostate cancer because of its constitutive activation in this fatal disease. We recently identified the root bark of Morus alba Linn. as a potential STAT3 inhibitor among 33 phytomedicines traditionally used in Korea. Morusin, an active compound isolated from the root bark of Morus alba, has shown anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
In the present study, we examined whether Morusin has a potential as an anti-cancer agent in prostate cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Morusin suppressed viability of prostate cancer cells, but little effect in normal human prostate epithelial cells. Morusin also reduced STAT3 activity by inhibiting its phosphorylation, nuclear accumulation, and DNA binding activity. In addition, Morusin down-regulated expression of STAT3 target genes encoding Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, Survivin, c-Myc and Cyclin D1, which are involved in regulation of apoptosis and cell cycle. Furthermore, Morusin induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells by reducing STAT3 activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggest that Morusin could be a potentially therapeutic agent for prostate cancer by reducing STAT3 activity and inducing apoptosis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Jul 18;372(1):236-42.
Morusin induces apoptosis and suppresses NF-kappaB activity in human colorectal cancer HT-29 cells.[Pubmed:
18485277 ]
Morusin is a pure compound isolated from root bark of Morusaustralis (Moraceae). In this study, we Morusin is a pure compound isolated from root bark of Morusaustralis (Moraceae). In this study, we demonstrated that Morusin significantly inhibited the growth and clonogenicity of human colorectal cancer HT-29 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Apoptosis induced by Morusin was characterized by accumulation of cells at the sub-G(1) phase, fragmentation of DNA, and condensation of chromatin. Morusin also inhibited the phosphorylation of IKK-alpha, IKK-beta and IkappaB-alpha, increased expression of IkappaB-alpha, and suppressed nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB and its DNA binding activity. Dephosphorylation of NF-kappaB upstream regulators PI3K, Akt and PDK1 was also displayed. In addition, activation of caspase-8, change of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO, and activation of caspase-9 and -3 were observed at the early time point. Downregulation in the expression of Ku70 and XIAP was exhibited afterward. Caspase-8 or wide-ranging caspase inhibitor suppressed Morusin-induced apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, the antitumor mechanism of Morusin in HT-29 cells may be via activation of caspases and inhibition of NF-kappaB.
Biomed. Aging Pathol., 2013, 4(1):29–32.
Anticonvulsant activity of Morusin isolated from : Modulation of GABA receptor.[Reference:
WebLink]
Epilepsy is a complex neurological disorder affecting 50 million of world's total population. Number of medicinal plants has been used to treat the convulsion. In ancient time Morus alba was used to treat epilepsy and mental illness. In Chinese medicine also M. alba is used as neuroprotective herbs. The present study was designed to explore the effect of Morusin, a flavonoid glycoside isolated from M. alba as anticonvulsant activity along with biochemical mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Morusin was isolated from M. alba and acute toxicity study was determined. Anticonvulsant activity of Morusin (5 and 10mg/kg, i.p.) was studied by using isoniazid (INH) and maximal electroshock (MES)-induced convulsion models; diazepam (5mg/kg) and phenytoin (20mg/kg) were used as standards, respectively. Biochemical mechanism was investigated by estimating the GABA level in brain.
The median lethal dose (LD50 ) of Morusin was found up to 20mg/kg. Treatment with Morusin (5 and 10mg/kg) delayed onset of convulsion and tonic hind limb extension along with duration of tonic-clonic convulsions as well as it significantly reduced mortality in INH and MES-induced convulsion. Rats treated with Morusin (5 and 10mg/kg) significantly increased level of brain GABA at both doses.
CONCLUSIONS:
The findings of current study provide pharmacological credibility to anticonvulsant activity of Morusin. The protection against the convulsions and restoration of GABA level give a suggestion to its probable mechanism of action.