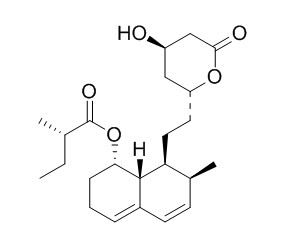
Mevastatin
Mevastatin inhibits HMGCR (HMG-CoA reductase) which in turn inhibits isoprenoid biosynthesis and therefore blocks protein isoprenylation and reduces plasma cholesterol levels in humans. Mevastatin inhibits the differentiation of TAO derived orbital preadipocytes by blocking PPAR-gamma mRNA expression. Mevastatin induces cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in SACC cells, it triggers the phosphorylation of the EGFR and inhibits the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Med Food.2021, 24(3):209-217.
Front Pharmacol.2020, 11:683.
Mol Cancer Ther.2024, 1535-7163.
Journal of Life Science2017, 233-240
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117365.
Cell.2022, 185(23):4298-4316.e21.
JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography2023, 36:179-190
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis2021, 100:103905.
ACS Omega.2023, 9(1):1278-1286.
Appl. Sci.2023, 13(17):9984.
Related and Featured Products
Anticancer Drugs. 2010 Aug;21(7):678-86.
Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for mevastatin-induced apoptosis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:
20629200]
Statins are inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, originally developed for lowering cholesterol. Statins also have pleiotropic effects, independent of cholesterol-lowering effects, including induction of apoptosis in various cell lines. However, the mechanism underlying statin-induced apoptosis is still not fully understood. This study aims to explore the proapoptotic effects and underlying mechanisms of statins on human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Exposure of SACC cells to Mevastatin resulted in cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner, accompanied by the release of cytochrome c and cleavage of caspase-3. A remarkable decrease in phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and increase in phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated kinase were observed. Furthermore, the JNK-specific inhibitor SP600125, but not the p38-specific inhibitor SB203580, abolished Mevastatin-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in SACC cells. This was supported by results in which the JNK inhibitor efficiently blocked Mevastatin-induced JNK phosphorylation, but not p38 phosphorylation, and further decreased Mevastatin-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results suggest that the JNK pathway was required for Mevastatin-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in SACC cells. Statins could be potential anticancer agents for SACC chemotherapy.
Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 May;35(5):511-7.
Mevastatin inhibits the differentiation of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy derived orbital preadipocytes.[Pubmed:
20543477]
To investigate the effect of Mevastatin (Mev) on the expression of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) mRNA and differentiation of Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO) derived orbital preadipocytes in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Orbital adipose tissues were obtained from TAO patients undergoing orbital decompression surgery. The orbital preadipocytes cultured from the orbital adipose tissues were divided into Group A (a control group) and Group B (an intervention group). Group B was subdivided into Group B1-B5, all groups were stimulated to differentiate into mature adipocytes with cocktail differentiation medium.The entire course of differentiation was 10 d. The differentiation of orbital preadipocytes in Group A was induced with routine inducer,while at in Group B1,B2, and B3 was interfered with 5 micromol/L (B1), 10 micromol/L(B2),20 micromol/L (B3) Mevastatin respectively during the whole process of differentiation. The differentiation of orbital preadipocytes in Group B4 and B5 was interfered with 10 micromol/L Mevastatin day 4 (B4) or day 8 (B5) of the differentiation process until the entire course was over. Intracellular fat accumulation in differentiated adipocytes was determined by oil red O staining. The value of optical absorption was measured at 492 nm with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The expression of PPAR-gamma mRNA was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
The light absorption value (A) and PPAR-gamma mRNA expression of differentiated cells in Group A,B1,B2,and B3 decreased successively,and there was significant difference in any of the 2 groups among Group A, B1 and B2, and B3 (P<0.05). The value A and PPAR-gamma mRNA expression of differentiated cells in Group A, B4, and B2 decreased successively, and the difference in any of the 2 groups among these 3 groups was significant. However, there were no significant difference between Group A and B5.
CONCLUSIONS:
Mevastatin inhibits the differentiation of TAO derived orbital preadipocytes by blocking PPAR-gamma mRNA expression. The degree of inhibition is not only concentration-dependent but also associated with the stage of differentiation. The earlier the differentiation, the stronger the inhibition.
J Neurosci Res. 2009 Jul;87(9):2138-44.
Mevastatin-induced neurite outgrowth of neuroblastoma cells via activation of EGFR.[Pubmed:
19224573]
Neuroblastoma cell lines are commonly used as models to study neuronal differentiation, as they retain the capacity to differentiate into a neuronal-like phenotype. Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling is essential for neuronal differentiation during development, and cholesterol-containing lipid-rafts are important for RTK signaling. Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors of the statin family impair cholesterol biosynthesis and are in widespread clinical use for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It is of great clinical interest that statin treatment also correlates with a lower incidence of malignancies. We found that Mevastatin triggered neurite outgrowth of neuroblastoma cells and examined the responsible signaling pathways.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Treatment of Neuro2a cells with Mevastatin for 24 hr induced neurite outgrowth associated with up-regulation of the neuronal marker protein NeuN. Interestingly, we found that Mevastatin triggered phosphorylation of the key kinases epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), ERK1/2, and Akt/protein kinase B. Inhibition of EGFR, PI3K, and the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade blocked Mevastatin-induced neurite outgrowth. Moreover, add-back experiments of cell-permeable cholesterol precursors indicated that farnesylated and geranylgeranylated proteins play a major role in statin-induced neurite outgrowth.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our results provide the first mechanistic insight into statin-triggered signaling pathways that lead to neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells. Surprisingly, we revealed that Mevastatin triggered the phosphorylation of the EGFR and that this was because of the inhibition of farnesylated and geranylgeranylated proteins. We propose that members of the large family of farnesylated or geranylgeranylated small GTPases (such as Rabs or Rap1) regulating the trafficking and signaling of EGFR might be responsible for the statin-induced effects on EGFR signaling.
Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014 Apr;33(4):414-23.
The DNA methyl transferase inhibitor, 5'-aza-2-deoxycitidine, enhances the apoptotic effect of Mevastatin in human leukemia HL-60 cells.[Pubmed:
23918904]
Statins induce antiproliferative effects and apoptotic response in various cancer cell types. Moreover, they also sensitize tumor cell lines from different origins to many agents.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We aimed to investigate possible effects of Mevastatin (Mev) alone and sequential treatment of 5'-aza-2-deoxycitidine (DAC) and Mev on HL-60 cell line using XTT (2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide) assay, lactate dehydrogenase release assay, flourescence microscopy, DNA fragmentation analysis, determination of DNA synthesis rate, and active caspase-3 assay. Messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of apoptotic and antiapoptotic genes were also evaluated by semiquantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for BAX, BCL2, and XIAP genes and quantitative Real-time PCR for CASP3, CASP8, and CASP9 genes. We showed that treatment with Mev alone and DAC followed by Mev resulted in apoptotic response in a time- and dose-dependent manner. We also found that pretreatment with DAC sensitized HL-60 cells to Mev and caused more apoptotic cell death than Mev-alone treatment via caspase-3 activation and DNA fragmentation. Moreover, sequential addition of Mev after DAC diminished DNA synthesis rate more effectively than Mev-alone treatment. Furthermore, DAC pretreatment significantly increased CASP3 and CASP9 mRNA expression even with lower doses of Mev. BAX, BCL2, and XIAP gene mRNA levels were also found to be changed in the presence of DAC and Mev.
CONCLUSIONS:
Determination of the exact molecular effects of statins and DAC would allow us to identify new molecular targets to develop more effective treatment regimens for cancer.