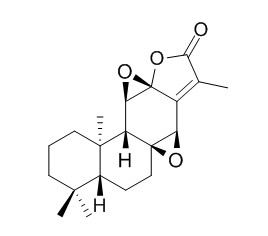
Jolkinolide B
Jolkinolide B has potent anti-inflammatory, and antitumor activities, it is able to enhance apoptosis of human leukemic HL-60 and THP-1 cells, at least in part, through downregulation of JAK2/STAT3 and bcl-2, and upregulation of Bax and cytosolic cytochrome c. Jolkinolide B can induce neuroendocrine differentiation of human prostate LNCaP cancer cell line, it also can induce apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Heliyon.2023, 9(11):e21944.
Herbal Formula Science2024, 32(2):155-179.
Oncotarget.2016, 8(51):88386-88400
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Cytotechnology2022, s10616
Molecules.2019, 24(11):E2044
Journal of Analytical Chemistry2017, 854-861
Nutrients.2021, 13(3):978.
J.Pharm. & Biome. Anal.2023, 2: 100018.
J Pharmaceutical Research Int.2021, 33(41A):275-284.
Related and Featured Products
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Mar 7;445(2):282-8.
Jolkinolide B inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing the activation NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.[Pubmed:
24491533]
Osteoclasts together with osteoblasts play pivotal roles in bone remodeling. The unique function and ability of osteoclasts to resorb bone makes them critical in both normal bone homeostasis and pathologic bone diseases such as osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Thus, new compounds that may inhibit osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast function may be of great value in the treatment of osteoclast-related diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we examined the effect of Jolkinolide B (JB), isolated from the root of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud on receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast formation. We found that Jolkinolide B inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation from bone marrow macrophages (BMMs) without cytotoxicity. Furthermore, the expression of osteoclastic marker genes, such as tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), cathepsin K (CtsK), and calcitonin receptor (CTR), was significantly inhibited. Jolkinolide Binhibited RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB by suppressing RANKL-mediated IκBα degradation. Moreover, Jolkinolide B inhibited RANKL-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38, JNK, and ERK).
CONCLUSIONS:
This study thus identifies Jolkinolide B as an inhibitor of osteoclast formation and provides evidence that Jolkinolide B might be an alternative medicine for preventing and treating osteolysis.
Mol Cells. 2011 Nov;32(5):451-7.
Jolkinolide B from Euphorbia fischeriana Steud induces apoptosis in human leukemic U937 cells through PI3K/Akt and XIAP pathways.[Pubmed:
22083305]
Jolkinolide B, a bioactive diterpene isolated from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud, is known to induce apoptosis in cancer cells. However, the molecular mechanism of its anti-cancer activity has not been fully elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we found that Jolkinolide B reduced cell viability and induced apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner in human leukemic U937. The induction of apoptosis was also accompanied by the downregulation of PI3K/Akt and the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family proteins. Moreover, we observed that Jolkinolide B treatment resulted in activation of caspase-3 and -9, which may partly explain the anti-cancer activity of Jolkinolide B.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our study for the first time suggest that Jolkinolide B is able to enhance apoptosis of U937 cells, at least in part, through downregulation of PI3K/Akt and IAP family proteins. Moreover, triggering of caspase-3 and -9 activation mediated apoptotic induction.
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Mar;51(3):170-8.
Jolkinolide B from Euphorbia fischeriana Steud induces in human leukemic cells apoptosis via JAK2/STAT3 pathways.[Pubmed:
23253949]
Jolkinolide B from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud exhibits significant antitumor activities against several tumor lines. Previous study has shown that Jolkinolide B could induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells. However, the exact mechanism and signaling pathway involved in Jolkinolide B-induced apoptosis have not been fully elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we found that Jolkinolide B reduced cell viability and induced apoptosis in dose- and time-dependent manner in human leukemic HL-60 and THP-1 cells. The induction of apoptosis was accompanied by the downregulation of JAK2/STAT3. Our results also suggest that expression of Bcl-2 and mitochondrial cytochrome c was dosedependently reduced following Jolkinolide B-treated THP-1 and HL-60 cells, whereas Jolkinolide B up-regulated the expression of Bax and cytosolic cytochrome c. Moreover, we observed that Jolkinolide B treatment resulted in activation of caspase-3, -8, and -9. JSI-124, a STAT-3 inhibitor, was able to block the negative effect of Jolkinolide B on cell apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our study for the first time suggests that Jolkinolide B is able to enhance apoptosis of human leukemic HL-60 and THP-1 cells, at least in part, through downregulation of JAK2/STAT3 and bcl-2, and upregulation of Bax and cytosolic cytochrome c. Moreover, the triggering of caspase-3, -8, and -9 activation mediated apoptotic induction.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 May;26(1):119-24.
Protective effect of Jolkinolide B on LPS-induced mouse acute lung injury.[Pubmed:
25819665 ]
Jolkinolide B (JB), an ent-abietane diterpenoid, isolated from the dried root of Euphorbia fischeriana, has been reported to have potent anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the effects of Jolkinolide B on acute lung injury (ALI) and underlying molecular mechanisms have not been investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study aimed to investigate the effect of Jolkinolide B on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI. Male C57BL/6 mice were pretreated with dexamethasone or Jolkinolide B 1h before intranasal instillation of LPS. The results showed that Jolkinolide B markedly attenuated LPS-induced histological alterations, lung edema, inflammatory cell infiltration, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity as well as the production of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β. Furthermore, Jolkinolide B also significantly inhibited LPS-induced the degradation of IκBα and phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and MAPK.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, our study provides the first line of evidence that pretreatment of Jolkinolide B has a protective effect on LPS-induced ALI in mice. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of Jolkinolide B may be attributed to its suppression of NF-κB and MAPK activation.
Oncol Rep. 2013 Jan;29(1):212-8.
Jolkinolide B induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.[Pubmed:
23129237]
The aim of this study was to explore the molecular mechanisms of Jolkinolide B (JB), which is extracted from the root of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we found that Jolkinolide B, a diterpenoid from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb, strongly inhibited the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Furthermore, we evaluated the effects of Jolkinolide B on the proliferation and apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Our results showed significant induction of apoptosis in MCF-7 cells incubated with Jolkinolide B. The viability of the MCF-7 cells was assessed by MTT assay. Flow cytometry was used to detect apoptosis and cell cycle analysis. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis was used to observe cell morphology. MCF-7 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into nude mice to study the in vivo antitumor effects of Jolkinolide B. The growth of MCF-7 cells was inhibited and arrested in the S phase by Jolkinolide B. The data showed significantly decreased tumor volume and weight in nude mice inoculated with MCF-7 cells. In addition, treatment with Jolkinolide B was able to induce downregulation of cyclinD1, cyclinE, mTOR, p-PI3K and p-Akt, and upregulation of PTEN and p-eIF4E.
CONCLUSIONS:
Collectively,Jolkinolide B-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 cells occurs through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Furthermore, the PI3K/Akt signaling cascade plays a role in the induction of apoptosis in Jolkinolide B-treated cells. These observations suggest that Jolkinolide B may have therapeutic applications in the treatment of cancer.