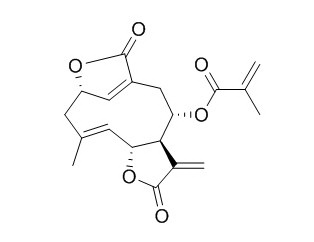
Isodeoxyelephantopin
Isodeoxyelephantopin exerts antitumor effects on several cancer cells by inducing apoptosis , cell cycle arrest , and inhibiting proliferation. It enhances apoptosis and inhibit invasion and osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Agronomy2023, 13(9), 2410.
Journal of Functional Foods2017, 30:30-38
Histol Histopathol.2022, 18518.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(8):1300.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 318(Pt B):116961.
J Ethnopharmacol.2019, 228:132-141
Molecules.2021, 26(4):817.
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia2024, 34:1276-1286.
Chem Res Toxicol.2023, 36(2):213-229.
Cell.2018, 172(1-2):249-261
Related and Featured Products
Chin Med. 2014 Apr 17;9:14.
Isodeoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber (Didancao) induces cell cycle arrest and caspase-3-mediated apoptosis in breast carcinoma T47D cells and lung carcinoma A549 cells.[Pubmed:
24742378]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Isodeoxyelephantopin (IDOE) isolated from Elephantopus scaber L. (Didancao) is used in Chinese medicine for the treatment of some types of cancer. The anti-cancer mechanism of Isodeoxyelephantopin remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the antiproliferative activity of Isodeoxyelephantopin on breast carcinoma T47D cells and lung carcinoma A549 cells. Isodeoxyelephantopininhibited the growth of A549 and T47D cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner with IC50 values of 10.46 and 1.3 μg/mL, respectively. Isodeoxyelephantopin was not significantly toxic to normal lymphocytes. The cells became detached from the monolayer and rounded up, had fragmented nuclei and condensed chromatin, and the numbers of apoptotic cells increased (P = 0.0003). Isodeoxyelephantopin-induced cell death was associated with activated caspase-3 expression followed by cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase.
CONCLUSIONS:
Isodeoxyelephantopin inhibited the proliferation of breast cancer cells and lung carcinoma cells and induced caspase-3-mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in the treated cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;12(19):5910-8.
Isodeoxyelephantopin, a novel sesquiterpene lactone, potentiates apoptosis, inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis through suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB (nf-kappaB) activation and nf-kappaB-regulated gene expression.[Pubmed:
17021000]
Deoxyelephantopin (ESD) and Isodeoxyelephantopin (ESI) are two sesquiterpene lactones derived from the medicinal plant Elephantopus scaber Linn. We postulated that ESD and Isodeoxyelephantopin mediate their activities through modulation of the NF-kappaB activation pathway.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effect of Isodeoxyelephantopin and ESD on NF-kappaB activation by electrophoretic mobility shift assay and NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression by Western blot analysis. We found that Isodeoxyelephantopin suppressed NF-kappaB activation induced by a wide variety of inflammatory agents, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-1beta, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, and lipopolysaccharide. Isodeoxyelephantopin did not interfere with the binding of NF-kappaB to DNA but rather inhibited IkappaBalpha kinase, IkappaBalpha phosphorylation, IkappaBalpha degradation, p65 phosphorylation, and subsequent p65 nuclear translocation. Isodeoxyelephantopin also suppressed the expression of TNF-induced NF-kappaB-regulated, proliferative, antiapoptotic, and metastatic gene products.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results indicate that Isodeoxyelephantopin inhibits NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression, which may explain the ability of Isodeoxyelephantopin to enhance apoptosis and inhibit invasion and osteoclastogenesis.
Proteomics. 2013 Nov;13(21):3222-32.
Quantitative proteomics characterization on the antitumor effects of isodeoxyelephantopin against nasopharyngeal carcinoma.[Pubmed:
23970500]
Isolated from Elephantopus scaber L., a Chinese medicinal herb that is widely used to prevent and treat cancers in China, Isodeoxyelephantopin (ESI) exerted antitumor effects on several cancer cells. However, its antitumor mechanism is still not clear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we found that Isodeoxyelephantopin could induce G2/M arrest and subsequently stimulate cell apoptosis in dose- and time-dependent manners. We used SILAC quantitative proteomics to identify Isodeoxyelephantopin-regulated proteins in cancer cells, and found that 124 proteins were significantly altered in expression. Functional studies demonstrated that Isodeoxyelephantopin induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis by inducing ROS generation, and that antioxidant N-acetyl-l-cysteine could block the Isodeoxyelephantopin-induced antitumor effects. Isodeoxyelephantopin upregulated the expression of anticancer inflammation factors IL-12a, IFN-α, and IFN-β through ROS-dependent and independent pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
The current work reveals that Isodeoxyelephantopin exerts its antitumor effects through ROS-dependent DNA damage, mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis mechanism and antitumor inflammation factor pathway.