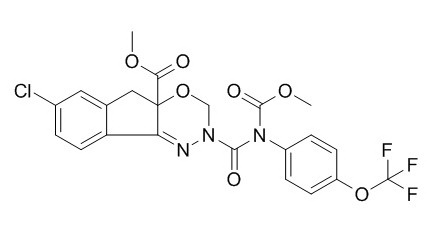
Indoxacarb
Given Indoxacarb's effect on adult fleas, egg production and egg viability, this formulation can interrupt flea reproduction on treated cats for at least 6 weeks after treatment.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Neuropharmacology.2018, 131:68-82
The Journal of Supercritical Fluids2021, 176:105305.
Foods.2022, 11(12):1773.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2023, 210:115463.
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 18(12)
J Breast Cancer.2015, 18(2):112-118
J Asian Nat Prod Res.2019, 5:1-17
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(9):5012.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(10):1638.
Food Chem.2024, 452:139555.
Related and Featured Products
Chirality. 2015 Mar;27(3):262-7.
Enantioselective degradation of indoxacarb from different commercial formulations applied to tea.[Pubmed:
25644775]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The stereoselective degradation of Indoxacarb enriched with (+)-S-Indoxacarb (S/R:70/30) was investigated in three typical green teas. A convenient and precise chiral method was developed and validated for measuring Indoxacarb enantiomers in green tea. The developed method was based on high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry using a Chiralpak IC column. The stereoselective degradation of Indoxacarb enantiomers showed that the (+)-S-enantiomer dissipated faster than the (-)-R-enantiomer in all three typical tea farms. However, no enantiomerization was observed after applying pure (+)-S-Indoxacarb.
CONCLUSIONS:
Residues on tea plant of the active ingredient (+)-S-Indoxacarb from suspension concentrate (SC) was more persistent than that from emulsifiable concentrate (EC).
Parasit Vectors. 2013 May 3;6:126.
Efficacy of indoxacarb applied to cats against the adult cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis, flea eggs and adult flea emergence.[Pubmed:
23642104]
A study was conducted to evaluate the effect of Indoxacarb applied to cats on adult cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis, flea egg production and adult flea emergence.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sixteen cats were selected for the study and allocated to two treatment groups. Eight cats were treated with a 19.5% w/v topical spot-on solution of Indoxacarb on day 0 and eight cats served as untreated controls. Each cat was infested with 50 fleas on Days -2, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42. On Days 1, 2, and 3, and at 2 and 3 days after each post treatment reinfestation flea eggs were collected from the pan under each cat cage. Eggs were counted and viability assessed by evaluating adult flea emergence 28 days after egg collection. Three days after treatment or infestation, each cat was combed to remove and count live fleas. Treatment with Indoxacarb provided 100% efficacy following infestations on day -2, 7, 14, 21 and 28 and efficacy was 99.6% following infestations on days 35 and 42. Egg production from Indoxacarb treated cats was reduced by 99.9% within 72 hours of treatment. For subsequent infestations no eggs were produced from treated cats from day 8 through day 30. Egg production was still reduced by ≥95.8% through day 45. Indoxacarb treatment also reduced adult flea emergence from eggs for 5 weeks after treatment. The combination of reduction in egg numbers and egg viability from Indoxacarb treated cats reduced predicted flea emergence by 100% from days 2 - 31 and 99.9%, 100%, 96.4% and 99.0% on days 37, 38, 44 and 45, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
A topical spot-on formulation of Indoxacarb provided ≥99.6% efficacy against flea infestations on cats for 6 weeks following a single treatment. Indoxacarb also eliminated or markedly reduced egg production for the entire evaluation period and reduced the viability of the few eggs that were produced from Day 1 through Day 38. Given Indoxacarb's effect on adult fleas, egg production and egg viability; this formulation can interrupt flea reproduction on treated cats for at least 6 weeks after treatment.
Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 Oct;28(10):1371-7.
Enantiomeric separation of indoxacarb on an amylose-based chiral stationary phase and its application in study of indoxacarb degradation in water.[Pubmed:
24687873]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Direct semipreparative enantioseparation of Indoxacarb was performed on a semipreparative Chiralpak IA column using normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with n-hexane-isopropanol-ethyl acetate (70:20:10) mixture as mobile phase. Degradation of Indoxacarb (2.33S + 1R) and its two enantiopure isoforms in three aqueous buffer solutions and four water samples collected from natural water sources was then elucidated by HPLC analysis on Chiralpak IA column.
CONCLUSIONS:
Degradation of all three Indoxacarbs complied with first-order kinetics and demonstrated linearity with regression coefficients R(2) > n0.88. Indoxacarb (2.33S + 1R) underwent enantioselective degradation in river water, rain water, and buffer solution of pH 7.0.
Enantiopure S-(+)-Indoxacarb and R-(-)-Indoxacarb were both found to be configurationally stable in water.
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Sep 17;62(37):9066-72.
Comparative study of the selective degradations of two enantiomers in the racemate and an enriched concentration of indoxacarb in soils.[Pubmed:
25134952]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, selective degradations of the two enantiomers of Indoxacarb in the concentrate (2.33S/1R) and racemate (1S/1R) are examined. The absolute configurations of Indoxacarb enantiomers were determined using X-ray diffraction. The results showed that in two alkaline soils, the S-(+)-Indoxacarb was preferentially degraded in both the concentrate and racemate. In one acid soil, the two enantiomers degraded no-selectivity. In another acid soil and one neutral soil, the R-(-)-Indoxacarb was preferentially degraded in both the concentrate and racemate. Indoxacarb enantiomers were configurationally stable in the five soils, and no interconversion was observed during the incubation. Because no significant difference in degradation was observed after samples were sterilized, the observed enantioselectivity may be attributed primarily to microbial activity in soils.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicate that the selective degradation behavior was the same for both formulations that were tested.