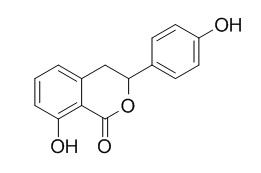
Hydrangenol
Hydrangenol is a strong contact sensitizer found in hydrangea (Hydrangea sp.; Hydrangeaceae), it can significantly inhibit the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) reaction, it has antiallergic activity. Hydrangenol has anti-inflammatory, and antifungal activities,it can attenuate NO production and inducible NO synthase expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV2 microglial cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation and by stimulating the Nrf2-mediated HO-1 signaling pathway. Hydrangenol has antifungal activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Phytomedicine.2018, 40:37-47
The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan2018, 138(4):571-579
Korea Food Research Institute2024, 4798082
J Inflamm Res.2022, 15:5347-5359.
Mol Med Rep.2024, 29(2):26.
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2023, 45(2):1587-1600.
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(15):8784-8797.
J Biol Chem.2021, 297(6):101362.
Dent Mater J. 2024, dmj.2023-294.
Appl. Sci.2022, 12(17), 8646.
Related and Featured Products
Biol Pharm Bull. 1999 Aug;22(8):870-2.
Effects of phyllodulcin, hydrangenol, and their 8-O-glucosides, and thunberginols A and F from Hydrangea macrophylla SERINGE var. thunbergii MAKINO on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in rats.[Pubmed:
10480329]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We examined the antiallergic effects of phyllodulcin, Hydrangenol, and their 8-O-glucosides, and thunberginols A and F isolated from the processed leaves (Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium) and dried leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla SERINGE var. thunbergii MAKINO using the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) reaction. With the exception of phyllodulcin, these constituents were found to significantly inhibit the PCA reaction.
CONCLUSIONS:
Although thunberginol A showed the most potent inhibitory effect, Hydrangenol was considered to be the principal antiallergic component in the processed leaves, after taking into account their contents.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1981 Sep;29(9):2689-91.
Antifungal activity of oosponol, oospolactone, phyllodulcin, hydrangenol, and some other related compounds.[Pubmed:
7349286]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antifungal activity of oosponol, oospolactone, phyllodulcin, Hydrangenol, and some other related compounds.
Contact Dermatitis. 1991 Mar;24(3):233-5.
Hydrangenol, a strong contact sensitizer found in hydrangea (Hydrangea sp.; Hydrangeaceae).[Pubmed:
1868712]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Hydrangenol, a strong contact sensitizer found in hydrangea (Hydrangea sp.; Hydrangeaceae).
Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jun;35:61-69.
Hydrangenol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing the NF-κB pathway and activating the Nrf2-mediated HO-1 pathway.[Pubmed:
27032067 ]
We previously demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effect of water extract of Hydrangea macrophylla in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophage cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated whether Hydrangenol, a bioactive component of H. macrophylla, attenuates the expression of nitric oxide (NO) and its associated gene, inducible NO synthase (iNOS), in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Our data showed that low dosages of Hydrangenol inhibited LPS-stimulated NO release and iNOS expression without any accompanying cytotoxicity. Hydrangenol also suppressed LPS-induced nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) subunits, consequently inhibiting DNA-binding activity of NF-κB. Additionally, the NF-κB inhibitors, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) and PS-1145, significantly attenuated LPS-induced iNOS expression, indicating that Hydrangenol-induced NF-κB inhibition might be a key regulator of iNOS expression. Furthermore, our data showed that Hydrangenol suppresses NO production by inducing heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). The presence of cobalt protoporphyrin, a specific HO-1 inducer, potently suppressed LPS-induced NO production. Hydrangenol also promoted nuclear translocation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and subsequently increased its binding activity at the specific antioxidant response element sites. Additionally, transient knockdown of Nrf2 significantly downregulated Hydrangenol-induced HO-1 expression, indicating that Hydrangenol-induced Nrf2 is an upstream regulator of HO-1.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these data suggest that Hydrangenol attenuates NO production and iNOS expression in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation and by stimulating the Nrf2-mediated HO-1 signaling pathway. Therefore, Hydrangenol is a promising therapeutic agent for treatment of LPS-mediated inflammatory diseases.