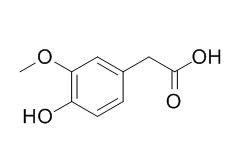
Homovanillic acid
Homovanillic acid is used as a reagent to detect oxidative enzymes, and is associated with dopamine levels in the brain. Abnormalities in white matter were associated with low CSF Homovanillic acid.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology 2024, 00444-8.
Pharmaceutics.2021, 13(2):187.
Toxicol Rep.2021, 8:1131-1142.
Pharmaceutics2022, 14(2),376.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy2022, 153:113404.
J Biol Chem.2014, 289(3):1723-31
Int J Cosmet Sci.2019, 41(1):12-20
NanoBioScience2024, v13:3:115.
Pak J Pharm Sci.2018, 31:311-315
Nutrients.2020, 12(5):1242.
Related and Featured Products
Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:253-7.
Analysis of vanillylmandelic acid and homovanillic acid by UPLC-MS/MS in serum for diagnostic testing for neuroblastoma.[Pubmed:
23830883]
Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA) are typically measured in urine for the diagnosis and monitoring of neuroblastoma, a tumor in children <5 y. A protocol for evaluation of serum VMA and Homovanillic acid has been utilized at our institution for approximately 25 y, originally validated using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with an electrochemical detector.
We recently validated a serum VMA/HVA method by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After solvent extraction and clean up with Ultrafree centrifugal filters, samples were analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS in multiple reaction monitoring mode. The assay was linear between 2 and 1000 ng/ml for VMA and Homovanillic acid . Within run and run to run CVs were <5% for VMA at all levels, <10% for HVA at high levels, and <20% at low levels. Correlation with the HPLC method was acceptable with a constant bias. The reference interval for VMA by UPLC-MS/MS was determined to be ≤20 ng/ml, and HVA≤30 ng/ml. Original patient data comparing urine to serum showed diagnostic agreement >80% for both VMA and Homovanillic acid .
CONCLUSIONS:
Correlation of VMA and Homovanillic acid was acceptable after adjustment of reference intervals. Collection of a single serum sample instead of 24-h urine collection saves time and improves accuracy of measurement due to difficulty of collecting a 24-h urine sample in infants and young children. UPLC-MS/MS also offers improved analyte specificity, improved signal to noise, and rapid analysis time.
Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013 Jun;55(6):559-66.
Homovanillic acid in cerebrospinal fluid of 1388 children with neurological disorders.[Pubmed:
23480488]
To determine the prevalence of dopaminergic abnormalities in 1388 children with neurological disorders, and to analyse their clinical, neuroradiological, and electrophysiological characteristics.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We studied biogenic amines in 1388 cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from children with neurological disorders (mean age 3y 10mo, SD 4y 5mo; 712 males, 676 females. Correlations among CSF Homovanillic acid (HVA) values and other biochemical, clinical, neuroradiological, and electrophysiological parameters were analysed. Twenty-one patients with primary dopaminergic deficiencies were identified. Of the whole sample, 20% showed altered Homovanillic acid. We report neurological diseases with abnormal CSF Homovanillic acid values such as pontocerebellar hypoplasia, perinatal asphyxia, central nervous system infections, mitochondrial disorders, and other genetic diseases. Overlapping Homovanillic acid levels between primary and secondary dopamine deficiencies were observed. Prevalence of low CSF Homovanillic acid levels was significantly higher in neonatal patients (χ(2) =84.8, p<0.001). Abnormalities in white matter were associated with low CSF Homovanillic acid (odds ratio 2.3, 95% confidence interval 1.5-3.5).
CONCLUSIONS:
HVA abnormalities are observed in various neurological diseases, but some are probably an unspecific finding. No clear limits for CSF Homovanillic acid values pointing towards primary diseases can be stated. We report several neurological diseases showing Homovanillic acid alterations. No neuroimaging traits were associated with low Homovanillic acid values, except for white matter abnormalities.
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Jan 24;118:1068-74.
Molecular structure and spectroscopic analysis of homovanillic acid and its sodium salt--NMR, FT-IR and DFT studies.[Pubmed:
24161870]
The estimation of the electronic charge distribution in metal complex or salt allows to predict what kind of deformation of the electronic system of ligand would undergo during complexation. It also permits to make more precise interpretation of mechanism by which metals affect the biochemical properties of ligands.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Theinfluence ofsodium cation on the electronic system of Homovanillic acid was studied in this paper. Optimized geometrical structures of studied compounds were calculated by B3LYP/6-311++G(**) method. Mulliken, MK and ChelpG atomic charges were analyzed. The theoretical NMR and IR spectra were obtained. (1)H and (13)C NMR as well as FT-IR and FT-Raman spectra of studied compounds were also recorded and analyzed. The calculated parameters are compared with experimental characteristics of these molecules.