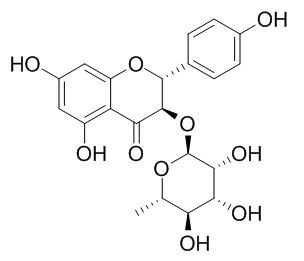
Engeletin
Engeletin, a bioactive flavonoid, has multiple biological activities such as anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. Engeletin possesses potent inhibition of PGE2 release with IC50 values of 19.6 μg/ml; it inhibits a recombinant human aldose reductase (IC50 value=1.16 microM).
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Structure2023, 36:100324.
J of Dentistry & Oral Health2019, 2641-1962
Front Immunol.2024, 15:1423776.
Molecules.2018, 23(7):E1817
Molecules.2023, 28(10):4121.
Int J Mol Med.2015, 35(5):1237-45
Molecules.2023, 28(5):2376.
Food Chem.2016, 191:81-90
Molecules.2020, 25(3):734
Nutrients.2021, 13(8):2901.
Related and Featured Products
J Agric Food Chem. 2011 May 11;59(9):4562-9.
Isolation and characterization of two flavonoids, engeletin and astilbin, from the leaves of Engelhardia roxburghiana and their potential anti-inflammatory properties.[Pubmed:
21476602]
Engeletin, a flavonoid compound, was isolated from the leaves of Engelhardia roxburghiana for the first time, along with astilbin, another flavonoid.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The chemical structures of Engeletin and astilbin were confirmed by (1)H and (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) spectra, and their anti-inflammatory activities were studied in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated mouse J774A.1 macrophage cells. LPS induced the inflammatory state in macrophage cells and increased mRNA expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Engeletin and astilbin exhibited remarkable inhibitory effects on interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 mRNA expression. Significant inhibition of LPS-mediated mRNA expressions were also seen in LPS binding toll-like receptor (TLR)-4, pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-10, chemoattractant monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1, and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 genes.
CONCLUSIONS:
The reduced expression of these cytokines may alleviate immune response and reduce inflammatory activation, indicating that Engeletin and astilbin may serve as potential anti-inflammatory agents.
Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2012 Dec;30(4):268-74.
An in vitro inhibitory effect on RAW 264.7 cells by anti-inflammatory compounds from Smilax corbularia Kunth.[Pubmed:
23393906]
Smilax corbularia is a Thai medicinal plant locally known as 'Hua-Khao-Yen Neua', which is used for treating inflammatory conditions.
To evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of S. corbularia extracts and its isolated compounds by determination of inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated PGE2 release, and TNF-alpha and NO production from RAW 264.7 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The inhibitory effect of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of this plant were determined on LPS-induced NO production, TNF-alpha and PGE2 release in RAW 264.7 cells, as an in vitro indication of possible anti-inflammatory activity. The compounds from active extract were isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation.
Only the ethanolic extract of this plant inhibited TNF-alpha and NO production, with IC50 values of 61.97, and 83.90 microg/ml respectively. Three flavonols, Engeletin, astilbin and quercetin were isolated from the ethanolic extract. quercetin possessed the highest inhibitory effect on NO production with IC50 11.2 microg/ml (37.1 microM), whereas Engeletin and astilbin had no activity (IC50 >100 microg/ml). All three flavonols possessed potent inhibition of PGE2 release with IC50 values of 14.4, 19.6 and 19.9 microg/ml (33.2, 43.5 and 65.8 microM) respectively. Quercetin also exhibited the highest inhibitory effect on TNF-alpha production (IC50 = 1.25 microg/ml or 4.14 microM), but Engeletin and astilbin had no activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report of isolated compounds from S. corbularia with potential anti-inflammatory effects, and the results support the use of this plant by Thai traditional doctors for treatment of inflammatory diseases.
J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Aug 10;64(31):6171-8.
Engeletin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endometritis in Mice by Inhibiting TLR4-mediated NF-κB Activation.[Pubmed:
27411287 ]
Engeletin (dihydrokaempferol 3-rhamnoside) is a flavanonol glycoside. It can be found in the skin of white grapes and white wine and is widely distributed in southeast Asia, and the leaves are used in a tea. Here, we explored the impact of Engeletin against the inflammatory reaction in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endometritis mouse model.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Engeletin treatment significantly attenuated uterus damage and decreased myeloperoxidase activity. ELISA and qPCR assays showed that Engeletin dose-dependently suppressed the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Molecular studies also demonstrated that the levels of iNOS, COX-2, and TLR4, along with their downstream molecules MyD88, IRAK1, TRAF6, and TAK1, were also suppressed by Engeletin. In addition, Engeletin treatment inhibited NF-κB signaling-pathway activation. Moreover, immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that Engeletin suppressed NF-κB-p65 nuclear translocation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data indicated the protective action of Engeletin against LPS-stimulated endometritis in mice via negative regulation of pro-inflammatory mediators via the TLR4-regulated NF-κB pathway.
J Fluoresc. 2012 Jan;22(1):511-9.
Binding of engeletin with bovine serum albumin: insights from spectroscopic investigations.[Pubmed:
21947612]
In this paper, several spectroscopic techniques were used to investigate the interaction of Engeletin (ELN) with bovine serum albumin (BSA).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The analysis of UV-Vis absorption and fluorescence spectra revealed that ELN and BSA formed a static complex ELN-BSA, and ELN quenched the fluorescence of BSA effectively. According to the thermodynamic parameters ΔS(0) = 47.27 J·mol(-1)·K(-1) and ΔΗ(0) = -10.34 kJ·mol(-1), the hydrophobic and hydrogen bond interactions were suggested to be the major interaction forces between ELN and BSA.
CONCLUSIONS:
Raman spectroscopy indicated that the binding of ELN slightly changed the conformations and microenviroment of BSA and decreased the α-helix content of BSA.