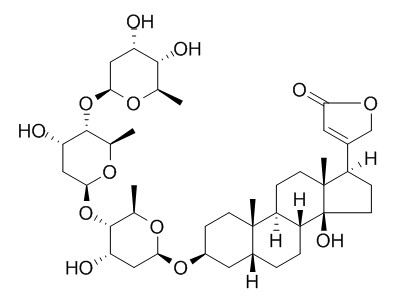
Digitoxin
The cardiac glycosides digitoxin and digoxin have been used in cardiac diseases for many years, digitoxin also has growth inhibition activity in three human cancer cell line, digitoxin activates pro-apoptotic, anti-proliferative signaling cascades and cell cycle arrest. Digitoxin could as a candidate drug for suppressing IL-8-dependent lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis (CF), it can suppress hypersecretion of IL-8 from cultured cystic fibrosis (CF) lung epithelial cells, the specific mechanism is to block phosphorylation of the inhibitor of NF-kappa.Digitoxin actively inhibits Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) replication with a 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) of 0.05 microM, the inhibitory effects of digitoxin are likely to be introduced at the early stage of HSV-1 replication and the virus release stage.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2016, 21(6)
Int Immunopharmacol.2023, 7:127:111322.
LWT2020, 110397
Phytochem Anal.2024, pca.3319.
Asian Pac J Tropical Bio.2020, 10(6):239-247
Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(23),11099.
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom.2021, 32(9):2451-2462.
Int J Biol Macromol.2025, 292:139225.
Heliyon.2024, 10(23):e40758.
Separations2021, 8(1), 1.
Related and Featured Products
Anticancer Drugs. 2014 Jan;25(1):44-52.
Digitoxin sensitizes glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by upregulation of death receptor 5 and downregulation of survivin.[Pubmed:
24045365]
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most lethal and aggressive astrocytoma among primary brain tumors in adults. However, most glioblastoma cells have been reported to be resistant to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we have shown that Digitoxin (DT), a clinically approved cardiac glycoside for heart failure, can induce TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of glioblastoma cells. DT in noncytotoxic doses (20 nmol/l) can increase TRAIL-induced apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant U87MG glioblastoma cells. Treatment with DT led to apoptosis and a robust reduction in the levels of the antiapoptotic protein survivin by inducing its proteasomal degradation; however, it did not affect the levels of many other apoptosis regulators. Moreover, silencing survivin with small interfering RNAs sensitized glioma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, underscoring the functional role of survivin depletion in the TRAIL-sensitizing actions of DT.
CONCLUSIONS:
We demonstrate that inactivation of survivin and death receptor 5 expression by DT is sufficient to restore TRAIL sensitivity in resistant glioma cells. Our results suggest that combining DT with TRAIL treatments may be useful in the treatment of TRAIL-resistant glioma cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Jan 1;258(1):51-60.
Digitoxin and a synthetic monosaccharide analog inhibit cell viability in lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:
22037315]
Mechanisms of Digitoxin-inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer (NCI-H460) cells remain unclear. Understanding how Digitoxin or derivate analogs induce their cytotoxic effect below therapeutically relevant concentrations will help in designing and developing novel, safer and more effective anti-cancer drugs.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, NCI-H460 cells were treated with Digitoxin and a synthetic analog D6-MA to determine their anti-cancer activity. Different concentrations of Digitoxin and D6-MA were used and the subsequent changes in cell morphology, viability, cell cycle, and protein expressions were determined. Digitoxin and D6-MA induced dose-dependent apoptotic morphologic changes in NCI-H460 cells via caspase-9 cleavage, with D6-MA possessing 5-fold greater potency than Digitoxin. In comparison, non-tumorigenic immortalized bronchial and small airway epithelial cells displayed significantly less apoptotic sensitivity compared to NCI-H460 cells suggesting that both Digitoxin and D6-MA were selective for NSCLC. Furthermore, NCI-H460 cells arrested in G(2)/M phase following Digitoxin and D6-MA treatment. Post-treatment evaluation of key G2/M checkpoint regulatory proteins identified down-regulation of cyclin B1/cdc2 complex and survivin. Additionally, Chk1/2 and p53 related proteins experienced down-regulation suggesting a p53-independent cell cycle arrest mechanism.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, Digitoxin and D6-MA exert anti-cancer effects on NCI-H460 cells through apoptosis or cell cycle arrest, with D6-MA showing at least 5-fold greater potency relative to Digitoxin.
Antiviral Res. 2008 Jul;79(1):62-70.
Anti-HSV activity of digitoxin and its possible mechanisms.[Pubmed:
18353452 ]
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) can establish latent infection in the nervous system and usually leads to life-threatening diseases in immunocompromised individuals upon reactivation. Treatment with conventional nucleoside analogue such as acyclovir is effective in most cases, but drug-resistance may arise due to prolonged treatment in immunocompromised individuals.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we identified an in-use medication, Digitoxin, which actively inhibited HSV-1 replication with a 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) of 0.05 microM. The 50% cytotoxicity concentration (CC(50)) of Digitoxin is 10.66 microM and the derived selective index is 213. Several structural analogues of Digitoxin such as digoxin, ouabain octahydrate and G-strophanthin also showed anti-HSV activity. The inhibitory effects of Digitoxin are likely to be introduced at the early stage of HSV-1 replication and the virus release stage.
CONCLUSIONS:
The observation that Digitoxin can inhibit acyclovir-resistant viruses further implicates that Digitoxin represents a novel drug class with distinct antiviral mechanisms from traditional drugs.
Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Sep 15;59:192-9.
Real-time analysis of the effects of toxic, therapeutic and sub-therapeutic concentrations of digitoxin on lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:
24727605]
Digitoxin belongs to a naturally occurring class of cardiac glycosides (CG); Digitoxin is clinically approved for heart failure and known for its anti-cancer effects against non-small lung cancer cells (NSCLC). However, concerns associated with its narrow therapeutic index and its concentration-dependent mechanism of action are rising. Thus, before Digitoxin implementation in designing and developing safer and more effective CG-based anti-cancer therapies, its pharmacological and safety profiles need to be fully elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this research we used a combinatorial approach to evaluate the anti-cancer mechanisms of Digitoxin in real-time. Our approach employed a non-invasive electric cell impedance sensing technique as a proxy to monitor NSCLC behavior post-exposure to toxic, therapeutic and sub-therapeutic concentrations of the drug.
CONCLUSIONS:
By developing structure-function combinatorial relations we showed that Digitoxin targets cancer cells in a time and dose-dependant manner by activating pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative signaling cascades that results in strengthening cellular adhesion and sequestration of key regulatory proliferation protein from the nucleus.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Mar 1;88(1):23-35.
Monosaccharide digitoxin derivative sensitize human non-small cell lung cancer cells to anoikis through Mcl-1 proteasomal degradation.[Pubmed:
24231508]
Advanced stage cancers acquire anoikis resistance which provides metastatic potential to invade and form tumors at distant sites. Suppression of anoikis resistance by novel molecular therapies would greatly benefit treatment strategies for metastatic cancers. Recently, Digitoxin and several of its novel synthetic derivatives, such as α-l-rhamnose monosaccharide derivative (D6-MA), have been synthesized and studied for their profound anticancer activity in various cancer cell lines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the anoikis sensitizing effect of D6-MA compared with Digitoxin to identify their anti-metastatic mechanism of action. D6-MA sensitized NSCLC H460 cells to detachment-induced apoptosis with significantly greater cytotoxicity (IC50=11.9 nM) than Digitoxin (IC50=90.7 nM) by activating caspase-9. Screening of the Bcl-2 protein family revealed that degradation of anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 protein is a favorable target. Mcl-1 over-expression and knockdown studies in D6-MA and Digitoxin exposed cells resulted in rescue and enhancement, respectively, indicating a facilitative role for decreased Mcl-1 expression in NSCLC anoikis. Transfection with mutant Mcl-1S159 attenuated detachment-induced cell death and correlated with a remaining of Mcl-1 level. Furthermore, D6-MA suppressed Mcl-1 expression via ubiquitin proteasomal degradation that is dependent on activation of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β signaling. In addition, D6-MA also targeted Mcl-1 degradation causing an increased anoikis in A549 lung cancer cells. Anoikis sensitizing effect on normal small airway epithelial cells was not observed indicating the specificity of D6-MA and Digitoxin for NSCLC.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results identify a novel cardiac glycoside (CG) sensitizing anoikis mechanism and provide a promising anti-metastatic target for lung cancer therapy.
J Nat Prod. 2005 Nov;68(11):1642-5.
Digitoxin inhibits the growth of cancer cell lines at concentrations commonly found in cardiac patients.[Pubmed:
16309315]
The cardiac glycosides Digitoxin (1) and digoxin (3) have been used in cardiac diseases for many years. During this time several reports have suggested the possible use of digitalis in medical oncology.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Several analogues of Digitoxin (1) were evaluated for growth inhibition activity in three human cancer cell lines; this study showed that Digitoxin (1) was the most active compound and revealed some structural features that may play a role in the growth inhibition activity of these drugs. The IC50 values for 1 (3-33 nM) were within or below the concentration range seen in the plasma of patients with cardiac disease receiving this glycoside (20-33 nM). A renal adenocarcinoma cancer cell line (TK-10) was hypersensitive to this drug, and Digitoxin toxicity on these cells was mediated by apoptosis. In vitro experiments showed that 1 at 30 nM induced levels of DNA-topoisomerase II cleavable complexes similar to etoposide, a topoisomerase II poison widely used in cancer chemotherapy.
CONCLUSIONS:
Using the individual cell assay TARDIS, cells exposed to 1 for 30 min showed low but statistically significant levels of DNA-topoisomerase II cleavable complexes; however these complexes disappeared after 24 h exposure.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 May 18;101(20):7693-8.
Digitoxin mimics gene therapy with CFTR and suppresses hypersecretion of IL-8 from cystic fibrosis lung epithelial cells.[Pubmed:
15136726 ]
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a fatal, autosomal, recessive genetic disease that is characterized by profound lung inflammation. The inflammatory process is believed to be caused by massive overproduction of the proinflammatory protein IL-8, and the high levels of IL-8 in the CF lung are therefore believed to be the central mechanism behind CF lung pathophysiology.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We show here that Digitoxin, at sub nM concentrations, can suppress hypersecretion of IL-8 from cultured CF lung epithelial cells. Certain other cardiac glycosides are also active but with much less potency. The specific mechanism of Digitoxin action is to block phosphorylation of the inhibitor of NF-kappa B (I kappa B alpha). I kappa B alpha phosphorylation is a required step in the activation of the NF-kappa B signaling pathway and the subsequent expression of IL-8. Digitoxin also has effects on global gene expression in CF cells. Of the informative genes expressed by the CF epithelial cell line IB-3, 58 are significantly (P < 0.05) affected by gene therapy with wild-type (CFTR CF transmembrane conductance regulator). Of these 58 genes, 36 (62%) are similarly affected by Digitoxin and related active analogues. We interpret this result to suggest that Digitoxin can also partially mimic the genomic consequences of gene therapy with CF transmembrane conductance regulator.
CONCLUSIONS:
We therefore suggest that Digitoxin, with its lengthy history of human use, deserves consideration as a candidate drug for suppressing IL-8-dependent lung inflammation in CF.