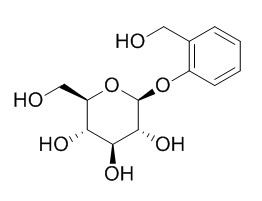
D-(-)-Salicin
D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities, it can inhibit the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Nutr Biochem.2022, 107:109064.
Foods.2023, 12(6):1130.
Hindawi J of Food Biochemistry2023, P17:8883860
Anal Biochem.2019, 569:10-15
Bull. Pharm. Sci., Assiut University2020, 43(2):149-155.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2018, 18(1):303
Acta Chromatographica2016, 29(3)
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy.2015, 46(4):352-364
Applied Biological Chemistry2023, 66(58):112.
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.2019, 1113:1-13
Related and Featured Products
Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Jun;26(2):286-94.
D(-)-Salicin inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models.[Pubmed:
25907238]
D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study aimed to investigate whether D(-)-Salicin inhibited the LPS-induced inflammation in vivo and in vitro. We evaluated the effect of D(-)-Salicin on cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10) in vivo and in vitro by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and signaling pathways (MAPKs and NF-κB) in vivo by Western blot. The results showed that D(-)-Salicin markedly decreased TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 concentrations and increased IL-10 concentration. In addition, western blot analysis indicated that D(-)-Salicin suppressed the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways stimulated by LPS. To examine whether D(-)-Salicin ameliorated LPS-induced lung inflammation, inhibitors of MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways were administrated intraperitoneally to mice. Interference with specific inhibitors revealed that D(-)-Salicin-mediated cytokine suppression was through MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. In the mouse model of acute lung injury, histopathologic examination indicted that D(-)-Salicin suppressed edema induced by LPS.
CONCLUSIONS:
So it is suggest that D(-)-Salicin might be a potential therapeutic agent against inflammatory diseases.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Jun;26(2):286-94.
D(-)-Salicin inhibits the LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells and mouse models.[Pubmed:
25907238]
D(-)-Salicin is a traditional medicine which has been known to exhibit anti-inflammation and other therapeutic activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study aimed to investigate whether D(-)-Salicin inhibited the LPS-induced inflammation in vivo and in vitro. We evaluated the effect of D(-)-Salicin on cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10) in vivo and in vitro by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and signaling pathways (MAPKs and NF-κB) in vivo by Western blot. The results showed that D(-)-Salicin markedly decreased TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 concentrations and increased IL-10 concentration. In addition, western blot analysis indicated that D(-)-Salicin suppressed the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways stimulated by LPS. To examine whether D(-)-Salicin ameliorated LPS-induced lung inflammation, inhibitors of MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways were administrated intraperitoneally to mice. Interference with specific inhibitors revealed that D(-)-Salicin-mediated cytokine suppression was through MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. In the mouse model of acute lung injury, histopathologic examination indicted that D(-)-Salicin suppressed edema induced by LPS.
CONCLUSIONS:
So it is suggest that D(-)-Salicin might be a potential therapeutic agent against inflammatory diseases.
Int J Pharm. 2008 Jun 24;358(1-2):192-7.
Relaxation behaviour of D(-)-salicin as studied by Thermally Stimulated Depolarisation Currents (TSDC) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC).[Pubmed:
18417303]
Thermally Stimulated Depolarisation Currents (TSDC) measurements on D-(-)-Salicin have been carried out in the temperature region from -165 degrees C up to 150 degrees C. The slow molecular mobility was characterised in the crystal and in the glassy state. The value of the steepness index or fragility (T(g)-normalized temperature dependence of the relaxation time) was obtained by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) from the analysis of the scanning rate dependency of T(g). The existence of an unknown polymorph of salicin is also reported.