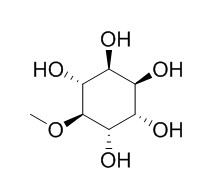
D-Pinitol
D-Pinitol is a safe nutrient to reduce calorie consumption when supplementing with creatine. It exerts anti-inflammatory, insulin-like activities; and inhibits osteoclastogenesis from bone marrow stromal cells and macrophage cells, which in turn protect bone loss from ovariectomy. It inhibits the activation of p38, JNK, and NF-κB, the expression of p53, Bcl-2, Bax and NF-kB proteins, and reduces focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation, c-Src kinase activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Cancer Sci.2022, 113(4):1406-1416.
J Ethnopharmacol.2016, 192:370-381
Protoplasma.2024, 261(6):1267-1280.
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(21):E5488
Sci Rep.2017, 7(1):3249
Free Radic Biol Med.2017, 112:191-199
Indian J Pharm Sci.2022, 84(4): 874-882.
Biomed Pharmacother.2021, 137:111362.
Am J Chin Med.2023, 51(4):1019-1039.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(8):7045.
Related and Featured Products
Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 8;14(5):9790-802.
D-pinitol Inhibits Prostate Cancer Metastasis through Inhibition of αVβ3 Integrin by Modulating FAK, c-Src and NF-κB Pathways.[Pubmed:
23698767]
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in men and shows a predilection for metastasis to the bone. D-Pinitol, a 3-methoxy analogue of d-chiro-inositol, was identified as an active principle in soy foods and legumes, and it has been proven to induce tumor apoptosis and metastasis of cancer cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the anti-metastasis effects of D-Pinitol in human prostate cancer cells. We found that D-Pinitol reduced the migration and the invasion of prostate cancer cells (PC3 and DU145) at noncytotoxic concentrations. Integrins are the major adhesive molecules in mammalian cells and have been associated with the metastasis of cancer cells. Treatment of prostate cancer cells with D-Pinitol reduced mRNA and cell surface expression of αvβ3 integrin. In addition, D-Pinitol exerted its inhibitory effects by reducing focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation, c-Src kinase activity and NF-kB activation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, D-Pinitol may be a novel anti-metastasis agent for the treatment of prostate cancer metastasis.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2012 Mar;12(3):494-500.
D-pinitol inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis.[Pubmed:
22269833]
Numerous studies have indicated that inflammatory cytokines play a major role in osteoclastogenesis, leading to the bone resorption that is frequently associated with osteoporosis. D-Pinitol, a 3-methoxy analogue of D-chiroinositol, was identified as an active principle in soy foods and legumes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we found that D-Pinitol markedly inhibited the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastic differentiation from bone marrow stromal cells and RAW264.7 macrophage cells. In addition, D-Pinitol also reduced RANKL-induced p38 and JNK phosphorylation. Furthermore, RANKL-mediated increase of IKK, IκBα, and p65 phosphorylation and NF-κB-luciferase activity was inhibited by D-Pinitol. However, D-Pinitol did not affect the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. In addition, D-Pinitol also prevented the bone loss induced by ovariectomy in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data suggest that D-Pinitol inhibits osteoclastogenesis from bone marrow stromal cells and macrophage cells via attenuated RANKL-induced p38, JNK, and NF-κB activation, which in turn protect bone loss from ovariectomy.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(4):1757-62.
D-pinitol promotes apoptosis in MCF-7 cells via induction of p53 and Bax and inhibition of Bcl-2 and NF-κB.[Pubmed:
24641404]
Development of drugs from natural products has been undergoing a gradual evoluation. Many plant derived compounds have excellent therapeutic potential against various human ailments. They are important sources especially for anticancer agents. A number of promising new agents are in clinical development based on their selective molecular targets in the field of oncology.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
D-Pinitol is a naturally occurring compound derived from soy which has significant pharmacological activitites. Therefore we selected D-Pinitol in order to evaluate apoptotic potential in the MCF-7 cell line. Human breast cancer cells were treated with different concentrations of D-Pinitol and cytotoxicity was measured by MTT and LDH assays. The mechanism of apoptosis was studied with reference to expression of p53, Bcl-2, Bax and NF-kB proteins. The results revealed that D-Pinitol significantly inhibited the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a concentration-dependent manner, while upregulating the expression of p53, Bax and down regulating Bcl-2 and NF-kB.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus the results obtained in this study clearly vindicated that D-Pinitol induces apotosis in MCF-7 cells through regulation of proteins of pro- and anti-apoptotic cascades.