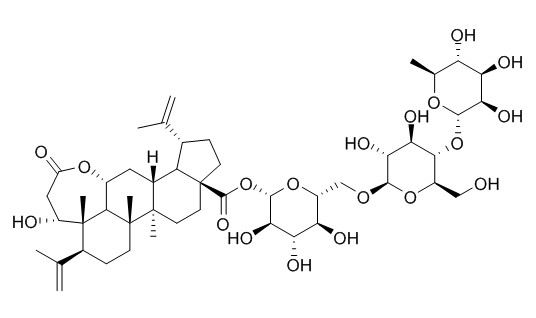
Chiisanoside
Chiisanoside has anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-rotaviral activities, it can inhibit xanthine oxidase activity and increase superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase and catalase, it also inhibits NO and PGE2 production. Chiisanoside has the potential to prevent obesity as a lipase inhibitor which suppresses fat absorption in vivo.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Asian J Beauty Cosmetol2022, 20(2):183-191
LWT-Food Sci Technol2020, 109163
Plants (Basel).2024, 13(23):3314.
Anticancer Res.2021, 41(3):1357-1364.
Food Chem. 2020, 320:126530
Int Immunopharmacol.2024, 143(Pt 2):113486.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2020, 177:114014.
Food Chem.2019, 274:345-350
Planta Med.2019, 85(9-10):766-773
National Natural Science Foundation of China2024, pages 33.
Related and Featured Products
Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Oct;28(10):1919-24.
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase-2 by chiisanoside via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.[Pubmed:
16204946]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the effects of several triterpenes isolated from the leaves of Acanthopanax chiisanensis (Araliaceae), namely, Chiisanoside, isoChiisanoside, 22-hydroxyChiisanoside and chiisanogenin (the aglycone of Chiisanoside) were evaluated on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production by the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line. Of the triterpenes tested, Chiisanoside was found to most potently inhibit NO and PGE2 production. In addition, Chiisanoside significantly reduced the release of inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Consistent with these observations, the protein and mRNA expression levels of iNOS and COX-2 enzyme were found to be inhibited by Chiisanoside in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, Chiisanoside inhibited the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activation induced by LPS and this was associated with a reduction in p65 protein in the nucleus and with the phosphorylations of ERK1/2 and JNK MAP kinases.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data indicate that the anti-inflammatory properties of Chiisanoside might be the result from the inhibition of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta expression through the down-regulation of NF-kappaB binding activity.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2001 May;24(5):582-5.
Metabolism of chiisanoside from Acanthopanax divaricatus var. albeofructus by human intestinal bacteria and its relation to some biological activities.[Pubmed:
11379786]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The metabolic pathway of Chiisanoside isolated from leaves of Acanthopanax divaricatus var. albeofructus (Araliaceae) by human intestinal bacteria and by the protein fraction of leaves of this plant were investigated, and the cytotoxic and anti-rotaviral activities of Chiisanoside and its metabolite, chiisanogenin, were assayed. Chiisanogenin was produced as a main metabolite, when Chiisanoside were incubated for 15 h with human intestinal bacteria. This metabolic pathway proceeded more potently with the protein fraction than with human intestinal bacteria.
CONCLUSIONS:
The in vitro cytotoxicity of chiisanogenin was superior to that of Chiisanoside. H+/K+ ATPase was more potently inhibited by chiisanogenin than by Chiisanoside. However, the anti-rotaviral activity of Chiisanoside was more potent than that of chiisanogenin.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008 Apr;72(4):1126-9.
Chiisanoside is not absorbed but inhibits oil absorption in the small intestine of rodents.[Pubmed:
18391464]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Chiisanoside is the main component of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus leaves. Simultaneous administration of Chiisanoside resulted in a decrease in the plasma TG level and increase of undigested TG in the intestinal lumen after oil gavage to mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
This suggests that Chiisanoside has the potential to prevent obesity as a lipase inhibitor which suppresses fat absorption in vivo.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Feb 28;97(2):359-67.
Antiinflammatory effects of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin obtained from the leaves of Acanthopanax chiisanensis in the carrageenan- and Freund's complete adjuvant-induced rats.[Pubmed:
15707776]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To find the antiinflammtory constituents of Acanthopanax chiisanensis (Araliaceae) leaves, Since BuOH extract among the fractionated extracts exhibited the most potent effect, it was subjected to column chromatography to yield a main triterpene glycoside, Chiisanoside (1). This compound was hydrolyzed in alkaline solution to find the biological activity of produced aglycone, chiisanogenin (1a). Oral treatment with Chiisanoside and 1a produced significant antiinflammtory effects at 10 and 30 mg/kg dose, and 1a was more potent than Chiisanoside. The antiiflammtory effects of the two compounds were supported by the reduction of carrageenan-induced lipid peroxidation and hydroxy radical in serum. Furthermore, treatment with Chiisanoside and 1a significantly reduced rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and C-reactive protein (CRP) factors in the rat induced by Freund's complete adjuvant reagent.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds, Chiisanoside and 1a, inhibited xanthine oxidase activity and increased superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase and catalase indicating that both compounds scavenged reactive oxygen species (ROS).