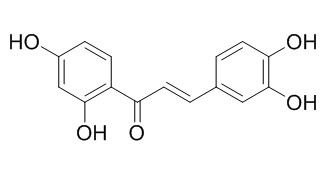
Butein
Butein is a chelator of ferrous and copper ions, is able to inhibit the activation of protein tyrosine kinase, NF-κB and STAT3, also inhibits EGFR. Butein can inactivate PMA-activated AP-1, due to the blocking of JNK-mediated c-Jun phosphorylation through the inhibition of ATP binding. Butein has potent anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant activities, it also has a hypotensive effect, at least in part, via the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules 2021, 26(4),1092.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2017, 17(1):393
Trop J Nat Prod Res2023, 7(12):5611-5615.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 326:117902.
Int J Mol Med.2016, 37(2):501-8
Phytomedicine.2020, 79, 153351
Food Science and Biotechnology2022, 10.1007.
University of Central Lancashire2017, 20472
Am J Chin Med.2015, 30:1-22
Molecules.2021, 26(6):1635.
Related and Featured Products
Am J Chin Med. 2015 Jun 28:1-14.
Butein Shows Cytotoxic Effects and Induces Apoptosis in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:
26119952]
Butein is a polyphenol, one of the compounds of chalcones, which are flavonoids that are widely biosynthesized in plants, and exhibits different pharmacological activities. Plants containing Butein have been used in Chinese traditional medicine.
Recently, it has been reported that Butein suppresses proliferation and triggers apoptosis in various human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. The aim of this study was to investigate its pro-apoptotic effect and mechanisms in two cultured human ovarian cancer cells (ES-2 and TOV-21G).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effects of Butein on cell viability were assessed by a MTT assay at 3, 10, 30, and 100 μ/M. The apoptotic pathway related factors, including the mitochondrial transmembrane potential (MTP), cytochrome c, caspase cascade, and Bcl-2 family proteins, were examined. MTT assay revealed that Butein was cytotoxic to both ovarian cancer cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. JC-1 flow cytometry, cytochrome c, and caspase activity assays revealed that Butein damaged the MTP, increased the level of cytosol cytochrome c and the activities of caspase-3, -8, and -9 in the two ovarian cancer cells. Western blot analysis revealed that Butein down-regulated the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL and increased the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bad. These findings suggest that Butein-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells via the activation of both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. In addition, Butein also down-regulated the expressions of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins, XIAP, survivin, CIAP-1, and CIAP-2. This indicates that the inhibition of IAP proteins was also involved in Butein-induced apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of our study suggest that Butein may be a promising anticancer agent in treating ovarian cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Jun 15;1392(2-3):291-9.
Antioxidant properties of butein isolated from Dalbergia odorifera.[Pubmed:
9630680]
The antioxidant properties of Butein, isolated from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen, were investigated in this study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Butein inhibited iron-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenate in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50, 3.3+/-0.4 microM. It was as potent as alpha-tocopherol in reducing the stable free radical diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) with an IC0.200, 9.2+/-1.8 microM. It also inhibited the activity of xanthine oxidase with an IC50, 5.9+/-0.3 microM. Besides, Butein scavenged the peroxyl radical derived from 2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) in aqueous phase, but not that from 2,2-azobis(2, 4-dimethylvaleronitrile) (AMVN) in hexane. Furthermore, Butein inhibited copper-catalyzed oxidation of human low-density lipoprotein (LDL), as measured by conjugated dienes and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substance (TBARS) formations, and electrophoretic mobility in a concentration-dependent manner. Spectral analysis revealed that Butein was a chelator of ferrous and copper ions.
CONCLUSIONS:
It is proposed that Butein serves as a powerful antioxidant against lipid and LDL peroxidation by its versatile free radical scavenging actions and metal ion chelation.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Sep;26(9):1345-7.
Hypotensive effect of butein via the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme.[Pubmed:
12951484]
Butein (3,4,2',4'-tetrahydroxychalcone), a plant polyphenol, has been known to elucidate endothelium-dependent vasodilation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the hypotensive effect of Butein and its possible mechanism, especially an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory effect, were investigated. Intravenous injection of Butein lowered the arterial blood pressure of anesthetized rats in a dose-dependent manner. The plasma ACE activities were significantly inhibited by the addition of Butein in a dose-dependent manner, the IC(50) value of which was 198 microg/ml (730 microM). Moreover, angiotensin I-induced contraction was markedly attenuated by prior exposure of endothelium-intact aortic rings to Butein, but angiotensin II-induced contraction was not altered.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Butein has a hypotensive effect, at least in part, via the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme.
Mol Carcinog. 2015 Apr;54(4):322-31.
Butein, a novel dual inhibitor of MET and EGFR, overcomes gefitinib-resistant lung cancer growth.[Pubmed:
24974831]
Lung cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide and MET amplification is a major therapeutic limitation in acquired-resistance lung cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We hypothesized that Butein, a phytochemical, can overcome gefitinib-induced resistance by targeting both EGFR and MET in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). To investigate the ability of Butein to target EGFR and MET, we used in silico docking, a library of natural compounds and kinase assays. The effects of Butein on growth, induction of apoptosis and expression of EGFR/MET signaling targets were examined in HCC827 (gefitinib-sensitive) and HCC827GR (gefitinib-resistant) NSCLC cells. Results were confirmed in vivo by a HCC827 or HCC827GR cell xenograft mouse model, each treated with vehicle, Butein or gefitinib. Butein inhibited phosphorylation and kinase activity of EGFR and MET as well as soft agar colony formation and decreased viability of HCC827 and HCC827GR cells. Butein increased apoptosis-related protein expression in these cells. Results were confirmed by co-treatment with inhibitors of EGFR/MET or double knock-down. Finally, xenograft study results showed that Butein strongly suppressed HCC827 and HCC827GR tumor growth.
CONCLUSIONS:
Immunohistochemical data suggest that Butein inhibited Ki-67 expression. These results indicate that Butein has potent anticancer activity and targets both EGFR and MET in acquired-resistance NSCLC.
J Med Food. 2015 May;18(5):557-64.
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Butein and Luteolin Through Suppression of NFκB Activation and Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1.[Pubmed:
25692285]
Butein and luteolin are members of the flavonoid family, which displays a variety of biological activities. In this study, we demonstrated that Butein and luteolin exert anti-inflammatory activities in RAW264.7 macrophages by inducing heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Butein and luteolin dose-dependently attenuated inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, leading to the suppression of iNOS-derived nitric oxide (NO) production. The inhibitory effect of Butein on NO production was greater than that of luteolin. Consistent with this finding, Butein also showed higher inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced translocation of nuclear factor κB (NFκB) and NFκB reporter gene activity in macrophages than luteolin. Furthermore, the expression of HO-1 was dose-dependently induced by Butein and luteolin treatments in macrophages. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory activities of Butein and luteolin involved the induction of HO-1 expression, as confirmed by the zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) treatment (HO-1 selective inhibitor) and HO-1 small interfering (si)RNA system. ZnPP-mediated downregulation and siRNA-mediated knockdown of HO-1 significantly abolished the inhibitory effects of Butein and luteolin on the production of NO in LPS-induced macrophages.
CONCLUSIONS:
Consequently, Butein and luteolin were shown to be effective HO-1 inducers capable of inhibiting macrophage-derived proinflammatory mechanisms. These findings indicate that Butein and luteolin are potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Feb;24(2):267-75.
Butein suppresses ICAM-1 expression through the inhibition of IκBα and c-Jun phosphorylation in TNF-α- and PMA-treated HUVECs.[Pubmed:
25533502]
Butein (3,4,2',4'-tetrahydroxychalcone), a flavonoid derivative, has been reported to show several biological actions, including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer. However, the possible molecular mechanisms involved are poorly understood.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Treatment of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) with Butein significantly inhibited cell surface intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression, ICAM-1 protein synthesis, and mRNA expression induced by tumor necrotic factor-α (TNF-α) and/or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Electrophoretic mobility shift assay revealed that Butein blocked activation of transcription factors, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1), induced by TNF-α and PMA. Moreover, Butein abolished TNF-α- and PMA-induced IκBα phosphorylation, which participates in NF-κB activation, and PMA-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun, a subunit composed of AP-1. In vitro, Butein inhibited the phosphorylation of c-Jun, binding to GST beads, mediated by JNK isolated from PMA-treated cells. The inhibitory action of Butein on the JNK-mediated in vitro c-Jun phosphorylation was abrogated in the presence of ATP.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that in HUVECs, Butein suppresses the expression of ICAM-1 mRNA and protein through the inhibition of the activation of NF-κB and AP-1 induced by TNF-α and PMA, that the inhibitory action of Butein on NF-κB activation results from the inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation by IκB kinase (IKK), and that the inactivation of PMA-activated AP-1 by Butein is due to the blocking of JNK-mediated c-Jun phosphorylation through the inhibition of ATP binding.
World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 14;21(2):465-74.
Butein effects in colitis and interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expression.[Pubmed:
25593461]
To evaluate the effects of Butein on inflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and colitis in interleukin (IL)-10(-/-) mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To synchronize colitis, 8- to 10-wk-old IL-10(-/-) mice were fed pellet-chow containing piroxicam for 2 wk. Subsequently, phosphate-buffered saline or Butein (1 mg/kg per day, ip) was injected for 4 wk. Histologic scores, inflammatory cytokines, MMP-9 and phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (pSTAT3) expressions were analyzed in IL-10(-/-) mice and in Colo 205 cells.
Butein reduced the colonic inflammatory score by > 50%. Expression levels of IL-6, IL-1β, interferon (IFN)-γ and MMP-9 were decreased in the colons of mice exposed to Butein, whereas other inflammatory cytokines (IL-17A, IL-21 and IL-22) were unchanged. Immunohistochemical staining for pSTAT3 and MMP-9 was significantly decreased in the Butein-treated groups compared with the controls. Butein inhibited IL-6-induced activation of STAT3 in Colo 205 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Butein ameliorated colitis in IL-10(-/-) mice by regulating IL-6/STAT3 and MMP-9 activation.