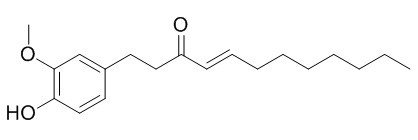
8-Shogaol
8-Shogaol can induce apoptosis in a time- and concentration-dependent manner by reactive oxygen species production and depletion of glutathione in HL-60 cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Curr Res Virol Sci.2022, 3:100019.
Environ Toxicol.2021, 36(9):1848-1856.
Preprints2021, doi:10.20944
J AOAC Int.2024, qsae028.
Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(8),3437.
Food Sci Biotechnol.2016, 25(5):1437-1442
J Pain Res.2022, 15:3469-3478.
Mol Biol Rep.2024, 51(1):56.
Nutrients.2022, 14(19):4170.
PLoS One.2018, 13(11):e0208055
Related and Featured Products
Drug Metab Dispos . 2015 Aug;43(8):1181-9.
Ginsenosides Regulate PXR/NF-κB Signaling and Attenuate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis[Pubmed:
25986850]
Abstract
Pregnane X receptor (PXR) activation exhibits anti-inflammatory effects via repressing nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB); however, its overactivation may disrupt homeostasis of various enzymes and transporters. Here we found that ginsenosides restore PXR/NF-κB signaling in inflamed conditions without disrupting PXR function in normal conditions. The effects and mechanisms of ginsenosides in regulating PXR/NF-κB signals were determined both in vitro and in vivo. Ginsenosides significantly inhibited NF-κB activation and restored the expression of PXR target genes in tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated LS174T cells. Despite not being PXR agonists, ginsenosides repressed NF-κB activation in a PXR-dependent manner. Ginsenosides significantly increased the physical association between PXR and the NF-κB p65 subunit and thereby decreased the nuclear translocation of p65. Ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K (CK) were major bioactive compounds in the regulating PXR/NF-κB signaling. Consistently, ginsenosides significantly attenuated dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis, which was associated with restored PXR/NF-κB signaling. This study indicates that ginsenosides may elicit anti-inflammatory effects via targeting PXR/NF-κB interaction without disrupting PXR function in healthy conditions. Ginsenoside Rb1 and CK may serve as leading compounds in the discovery of new drugs that target PXR/NF-κB interaction in therapy for inflammatory bowel disease.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Mar;57(3):447-58.
Characterization of thiol-conjugated metabolites of ginger components shogaols in mouse and human urine and modulation of the glutathione levels in cancer cells by [6]-shogaol.[Pubmed:
23322393]
Shogaols, a series of major constituents in dried ginger with the most abundant being [6]-, [8]-, and [10]-shogaols, show much higher anticancer potencies than gingerols. Previously, we reported the mercapturic acid pathway as a major metabolic route for [6]-shogaol in mice. However, it is still unclear how the side chain length affects the metabolism of shogaols and how shogaols are metabolized in humans.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We first investigate the metabolism of [10]-shogaol in mouse urine, and then investigate the biotransformation of shogaols in human urine. Our results show that eight major thiol-conjugated metabolites of [10]-shogaol were detected in mouse urine, while six major thiol-conjugated metabolites of [6]-shogaol, two thiol-conjugated metabolites of 8-Shogaol, and two thiol-conjugated metabolites of [10]-shogaol were detected in urine collected from human after drinking ginger tea, using LC/ESI-MS/MS. Our results clearly indicate the mercapturic acid pathway is a major metabolic route for [10]-shogaol in mice and for shogaols in human. Furthermore, we also investigated the regulation of glutathione (GSH) by [6]-shogaol in human colon cancer cells HCT-116.
Our results show [6]-shogaol, after initially depleting glutathione levels, can subsequently restore and increase GSH levels over time.
CONCLUSIONS:
Shogaols are metabolized extensively in mouse and human to form thiol-conjugated metabolites and GSH might play an important role in the cancer-preventive activity of ginger.
Oxid Med Cell Longev . 2015;2015:843721.
Ginsenoside Rb1 Treatment Attenuates Pulmonary Inflammatory Cytokine Release and Tissue Injury following Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Mice[Pubmed:
26161243]
Abstract
Objective. Intestinal ischemia reperfusion (II/R) injury plays a critical role in remote organ dysfunction, such as lung injury, which is associated with nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) signaling pathway. In the present study, we tested whether ginsenoside Rb1 attenuated II/R induced lung injury by Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Methods. II/R injury was induced in male C57BL/6J mice by 45 min of superior mesenteric artery (SMA) occlusion followed by 2 hours of reperfusion. Ginsenoside Rb1 was administrated prior to reperfusion with or without ATRA (all-transretinoic acid, the inhibitor of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway) administration before II/R. Results. II/R induced lung histological injury, which is accompanied with increased levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), interleukin- (IL-) 6, and tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-) α but decreased levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and IL-10 in the lung tissues. Ginsenoside Rb1 reduced lung histological injury and the levels of TNF-α and MDA, as well as wet/dry weight ratio. Interestingly, the increased Nrf2 and HO-1 expression induced by II/R in the lung tissues was promoted by ginsenoside Rb1 treatment. All these changes could be inhibited or prevented by ATRA. Conclusion. Ginsenoside Rb1 is capable of ameliorating II/R induced lung injuries by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Mar 24;58(6):3847-54.
Induction of apoptosis by 8-shogaol via reactive oxygen species generation, glutathione depletion, and caspase activation in human leukemia cells.[Pubmed:
20163181]
Ginger, the rhizome of Zingiber officinale , is a traditional medicine with a carminative effect and antinausea, anti-inflammatory, and anticarcinogenic properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study examined the growth inhibitory effects of 8-Shogaol , one of the pungent phenolic compounds in ginger, on human leukemia HL-60 cells. It demonstrated that 8-Shogaol was able to induce apoptosis in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Treatment with 8-Shogaol caused a rapid loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential, stimulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, release of mitochondrial cytochrome c into cytosol, and subsequent induction of procaspase-9 and procaspase-3 processing.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggest for the first time that ROS production and depletion of glutathione that contributed to 8-Shogaol -induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells.