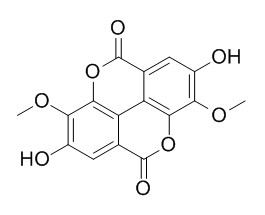
3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid
3,3'-Di-O-methylellagic acid reveals moderate antibacterial activity, it also shows strong DPPH radical scavenging activities with SC50 of 123.3 ug/mL. It has a lower capacity of stimulating murine peritoneal macrophages to release nitric oxide and tumoural-alpha necrose factor. 3,3'-Di-O-methylellagic acid may be a useful as pharmacological agent for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Nat Sc Biol Med2019, 10(2):149-156
Chemistry of Plant Materials.2019, 129-136
Industrial Crops and Products2023, 199:116746.
Cell Signal.2022, 99:110433.
Research J. Pharm. and Tech.2020, 13(7):3059-3064.
J Ethnopharmacol.2019, 235:406-414
Antioxidants (Basel).2022, 11(12):2411.
Antioxidants (Basel).2024, 13(3):340.
Molecules.2020, 25(18),4089.
Phytochem Anal.2021, 32(6):970-981.
Related and Featured Products
Z Naturforsch C. 2008 Nov-Dec;63(11-12):794-800.
Identification of ellagic acid derivatives in methanolic extracts from Qualea species.[Pubmed:
19227825]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanolic extract from the barks of the medicinal plant Qualea parviflora (Vochysiaceae) was fractionated by column chromatography over silica gel followed by gel permeation over Sephadex LH-20 to give 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid-4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), 3-O-methylellagic acid-4'-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (2), 3,3',4-tri-O-methylellagic acid-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), and 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid,4), together with triterpenes and saponins. We also performed comparative analyses among this species and Q. grandiflora and Q. multiflora using high-pressure liquid chromatography.
CONCLUSIONS:
The biological assays showed that, when compared to the standard ellagic acid, compounds 1-4 are less cytotoxic but have a lower capacity of stimulating murine peritoneal macrophages to release nitric oxide and tumoural-alpha necrose factor.
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Dec 24;56(24):11668-74.
Active compounds from Lagerstroemia speciosa, insulin-like glucose uptake-stimulatory/inhibitory and adipocyte differentiation-inhibitory activities in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed:
19053366 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Seven ellagitannins, lagerstroemin (1), flosin B (2), stachyurin (3), casuarinin (4), casuariin (5), epipunicacortein A (6), and 2, 3-(S)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-alpha/beta-D-glucose (7), together with one ellagic acid sulfate, 3-O-methyl-ellagic acid 4'-sulfate (8), ellagic acid (9), and four methyl ellagic acid derivatives, 3-O-methylellagic acid (10), 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid,11), 3,4,3'-tri-O-methylellagic acid (12), and 3,4,8,9,10-pentahydroxydibenzo[b,d]pyran-6-one (13), were identified by the bioassay-directed isolation from the leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers. The chemical structures of these components were established on the basis of one- and two-dimensional NMR and high-resolution mass spectroscopic analyses. Other known compounds, including corosolic acid, gallic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3-O-methylprotocatechuic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, kaempferol, quercetin, and isoquercitrin, were also isolated from the same plant. The obtained ellagitannins exhibited strong activities in both stimulating insulin-like glucose uptake (1-5 and 7) and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation (1 and 4) in 3T3-L1 cells. Meanwhile, ellagic acid derivatives (10-13) showed an inhibitory effect on glucose transport assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study is the first to report an inhibitory effect for methyl ellagic acid derivatives.
Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011,4, 272-272.
Chemical Constituents with DPPH Radical Scavenging, Elastase Inhnbition and Tyrosinase Inhibition Activities from Cleyera japonica Thunb[Reference:
WebLink]
Bioassay-guided investigation of the stem of Cleyera japonica Thunb. led to the isolation of five compounds such as 3,5,7-trihydroxylchromone 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (1), aviculin (2), 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid,3), 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid 4'-O-β-D-xylopyranoside (4) and betulinic acid (5). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral studies as well as by comparison of their data with literature values.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to study the skin related bioactivities for the isolated compounds, screenings on anti-oxidation, anti-tyrosinase and anti-elastase were conducted. For the anti-oxidation tests, compound 1, 2 and 3 showed strong DPPH radical scavenging activities with SC50 of 59.3, 58.1 and 123.3 μg/mL respectively, whose activities were comparable to a positive control BHT (SC50 89.0 μg/mL). On the tyrosinase inhibition studies, compound 4 (IC50 36.3 μg/mL) showed more potent activity than arbutin (IC50 67.2 μg/mL). On the elastase inhibition studies, compound 5 (IC50 17.9 μg/mL) showed higher activity than oleanolic acid (IC50 29.6 μg/mL), a positive control.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on these results, C. japonica stem extracts could be potentially applicable as an ingredient in skin care formulations.
Nat Prod Commun. 2009 Apr;4(4):517-20.
Induction of neuronal differentiation in neurosphere stem cells by ellagic acid derivatives.[Pubmed:
19475997]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A bioassay-guided fractionation of methanol extracts of stem barks, combined with screening based on Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-responsive neural stem cells (erNSCs) differentiation assay, has been used. This study resulted in the isolation of 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid(3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid )1, 3,3'-di-O-methyl ellagic acid-4-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside 2, ellagic acid 3, and arjunolic acid 4. Among them, compounds 1 and 2 exhibit potent induction of neuronal differentiation in neurosphere stem cells with no cytotoxic effect. These results indicate that compounds 1 and 2 may be useful as pharmacological agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds may account, for the use of T. superba in folk medicine for nervous system and mental disorders.
Nat Prod Res. 2008 Mar 10;22(4):353-9.
Chemical constituents with antibacterial activity from Euphorbia sororia.[Pubmed:
18322851 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A group of ceramide (1) was isolated from the aerial parts of Euphorbia sororia. On the basis of spectroscopic data, chemical methods and GC-MS analysis, the structure of 1 was characterised as (2S,3S,4R,8E)-2-(eicosanoyl approximately octacosanoyl amino)-1,3,4-octadecanetriol-8-ene. In addition, four known ellagic acid derivatives 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid,2), 3,3',4'-tri-O-methylellagic acid (3), 4-O-sulfooxy-3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (4) and 4-O-sulfooxy- 3,3',4'-tri-O-methylellagic acid (5) were isolated from the plant.
CONCLUSIONS:
Biological screening of all compounds revealed moderate antibacterial activity.