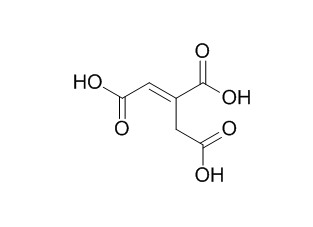
trans-Aconitic acid
Trans-aconitic acid inhibits the growth and photosynthesis of Glycine max.Trans-aconitic acid has antileishmanial activity ,the diesters of TAA as potential useful derivatives for the management of rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(16),5482.
Molecules.2021, 26(4):817.
Buildings2023, 13(5), 1112.
Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences2023, 27(4):840-848.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(2):770.
Sci Rep. 2017, 12953(7)
Chemical Engineering Journal2024, 500:157110
Saf Health Work.2019, 10(2):196-204
Journal of Ginseng Research2022, j.jgr.2022.09.005.
J Ethnopharmacol.2019, 228:132-141
Related and Featured Products
Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 2018, 132:490-496.
Trans-aconitic acid inhibits the growth and photosynthesis of Glycine max.[Reference:
WebLink]
Grasses producing trans-Aconitic acid, a geometric isomer of cis-aconitic acid, are often used in Glycine max rotation systems. However, the effects of trans-Aconitic acid on Glycine max are unknown.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We conducted a hydroponic experiment to evaluate the effects of 2.5–10 mM trans-Aconitic acid on Glycine max growth and photosynthesis. The results revealed that the enhanced H2O2 production in the roots increased the membrane permeability and reduced the water uptake. These effects culminated with a reduced stomatal conductance (gs), which seems to be the main cause for a decreased photosynthetic rate (A). Due to low gs, the limited CO2 assimilation may have overexcited the photosystems, as indicated by the high production of H2O2 in leaves. After 96 h of incubation, and due to H2O2-induced damage to photosystems, a probable non-stomatal limitation for photosynthesis contributed to reducing A. This is corroborated by the significant decrease in the quantum yield of electron flow through photosystem II in vivo (ΦPSII) and the chlorophyll content.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the damage to the root system and photosynthetic apparatus caused by trans-Aconitic acid significantly reduced the Glycine max plant growth.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2018, 99:87-95.
Esterification of trans-aconitic acid improves its anti-inflammatory activity in LPS-induced acute arthritis.[Reference:
WebLink]
trans-Aconitic acid (TAA) is an abundant constituent in the leaves of Echinodorus grandiflorus, a medicinal plant used to treat rheumatoid arthritis in Brazil. Esterification was explored as a strategy to increase lipophilicity and biopharmaceutical properties of TAA, a highly polar tricarboxylic acid. We herein report the synthesis of TAA esters via Fischer esterification with ethanol, n-butanol and n-octanol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The reaction kinetics was investigated to produce mono-, di- and tri- derivatives. Mono- and diesters of TAA were obtained as a mixture of positional isomers, whereas the triesters were recovered as pure compounds. The obtained esters were screened in a model of acute arthritis induced by the injection of LPS in the knee joint of Swiss mice. The diesters were the most active compounds, regardless of the alcohol employed in the reaction, whereas bioactivity of the derivatives improved by increasing the length of the aliphatic chain of the alcohol employed in esterification. In general, the esters showed higher potency than TAA. When administered orally to mice at doses of 0.017-172.3 μmol/Kg, the diethyl, di-n-butyl and di-n-octyl esters of TAA reduced the cellular infiltration into the knee joint, especially of neutrophils.
CONCLUSIONS:
The study identified diesters of TAA as potential useful derivatives for the management of rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
Biochemical medicine and metabolic biology, 1989, 42(3):171-178.
Evaluation of antileishmanial activity of trans-aconitic acid.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
TAA(trans-Aconitic acid), an inhibitor of the enzyme aconitase, inhibits the growth of L. donovani promastigotes. Morphogenic transformation of the amastigote to the promastigote form in vitro was also inhibited by 2 mm TAA. TAA also reduced multiplication of the parasite in macrophage culture.
CONCLUSIONS:
In the hamster model of leishmania, TAA significantly reduced the parasitic burden of liver. In acute toxicity tests with BALB/c mice no deaths were recorded even at a dose level of 2 g/kg body wt/day.